Abstract
Developmental events in the brain including neuronal morphogenesis and migration are highly orchestrated processes. In vitro and in vivo analyses allow for an in-depth characterization to identify pathways involved in these events. Cerebellar granule neurons (CGNs) that are derived from the developing cerebellum are an ideal model system that allows for morphological analyses. Here, we describe a method of how to genetically manipulate CGNs and how to study axono- and dendritogenesis of individual neurons. With this method the effects of RNA interference, overexpression or small molecules can be compared to control neurons. In addition, the rodent cerebellar cortex is an easily accessible in vivo system owing to its predominant postnatal development. We also present an in vivo electroporation technique to genetically manipulate the developing cerebella and describe subsequent cerebellar analyses to assess neuronal morphology and migration.
Keywords: Neuroscience, Issue 85, axons, dendrites, neuronal migration, cerebellum, cultured neurons, transfection, in vivo electroporation
Introduction
The cerebellum is an excellent system to study mechanisms of axon growth and migration. The cerebellum has been the subject of anatomical studies since the dawn of neuroscience1. Modern microscopy and immunohistochemical techniques have significantly expanded and refined the initial discoveries by Santiago, Ramon, and Cajal2-4. Mouse genetics and molecular studies uncovered essential growth and transcription factors in the control of cerebellar development, which led to greater understanding of crucial events required for proper wiring of different types of neurons including cerebellar granule neurons (CGNs)5-7.
The cerebellum is a derivative of rhombomere 1 of the developing hindbrain8. The rhombic lip, which is part of the roof of the 4th ventricle, gives rise to cerebellar granule neuron progenitors, which will constitute the most numerous neuronal population in the adult cerebellum9. Following rostral migration, they settle in the cerebellar anlage. Here, mitosis of granule neuron precursors leads to the dramatic expansion of the external granular layer (EGL), which takes place postnatally in rodents. From the EGL, neurons start migrating inward through the molecular layer (ML), past the Purkinje cell layer to ultimately take up residence in the internal granular layer (IGL2). During this migratory process, they acquire a bipolar shape with two axons extending into the ML. Upon further migration, the cell body migrates away from the axons and the two processes fuse to form one bifurcated, T-shaped axon10. Subsequently, these axons fasciculate and are referred to as parallel fibers. Having settled in the IGL, CGNs grow dendrites, which form dendritic claws to establish synapses with mossy fibers. To examine fundamental processes in the developing cerebellum, a combined in vitro and in vivo approach allows for reliable results and conclusions.
CGNs are not only the most numerous neurons of the cerebellum but of the entire brain and can be cultured to high purity11-13. In culture, this highly homogeneous neuronal population becomes rapidly postmitotic and acquires a polar morphology with easily identifiable axons and dendrites. Cultured CGNs have proven to be extremely useful to study various aspects of neuronal development including progenitor proliferation, differentiation, axonal and dendrite development, neuronal migration, apoptosis and electrophysiological properties (14-19 and many others). The use of genetic manipulation has expanded the versatility of cultured CGNs and allowed for further mechanistic insight into the aforementioned events. Transfection of cultured neurons using low-efficiency calcium phosphate or lipophilic methods followed by immunocytochemistry with polarity markers or software-supported analysis facilitates the assessment of e.g. the morphology of individual neurons in a dense neuronal culture. With this approach, the role of proteins of interest in axon or dendrite growth can be studied20-25,26-28. This culture system however is less useful to analyze neuronal migration as migration is very limited in high-density cultures and would require cocultures. The in vitro analysis of axon and dendrite growth also allows for the examination of interconnected proteins of a signaling pathway using combinations of RNA interference (i), over-expression or small molecules.
To establish the relevance of the protein of interest in axon and dendrite growth regulation or neuronal migration, the in vivo electroporation (IVE) technique allows for the analysis in the developing cerebellar cortex. Owing to the fact that cerebellar development in rodents extends way into the first two postnatal weeks, the cerebellum represents an accessible brain structure for genetic manipulations to examine developing axons and dendrites, neuronal migration, synaptogenesis and apoptosis20-24,29,30,26,27,31-34. In addition, this model system is also useful for other aspects of neuronal development that require the intact cerebellar cortex such as axon pathfinding, wiring and connectivity of neurons and neuron-glia interactions Taken together, this protocol provides in vitro and in vivo techniques to tackle a complementary approach regarding neuronal morphogenesis and migration.
Protocol
CGNs can be prepared either from postnatal day (P) 5 mouse pups or P6 rat pups. We follow a protocol, described by Bilimoria and colleagues, which uses a mitotic inhibitor to select for postmitotic CGNs13.
Ethics statement: All experiments involving live animals have been conducted according to the animal protocol approved by the "Verbraucherschutz und Lebensmittelsicherheit" of Lower Saxony, Germany.
In vitro assay:
1. Preparation of DNA Plasmid, Media, and Buffers for the Calcium Phosphate Transfection Method
Dissolve plasmid DNA in sterile, endotoxin-free water; DMEM (high glucose); make 2.5 M CaCl2; make 2x HBSS (dissolve 4 g NaCl, 0.1775 g KCl, 0.095 g Na2HPO4 •7H2O, 0.675 g glucose and 2.5 g HEPES in 250 ml ultrapure water and adjust pH to 7.05, 7.08, and 7.11). Note: When preparing the 2x HBSS solution, test which pH gives best results regarding transfection efficiency of given combination of plasmids.
2. Transfection of Cultured Neurons
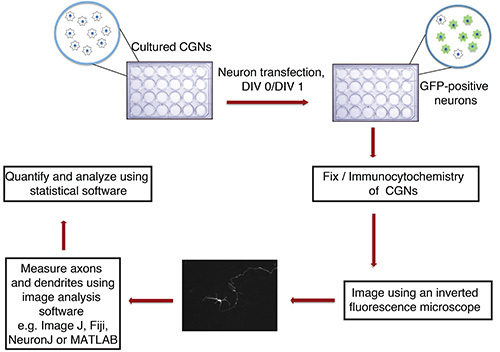 Figure 1. Flowchart of in vitro axon and dendrite growth assay. Cultured CGNs (24-well plate with glass coverslips), isolated from P6 rat pups, are transfected at DIV 0 or 1 with DNA precipitate containing a fluorescent transfection marker (e.g. GFP). After fixation and immunocytochemistry, neurons are imaged in a blinded manner. Images are imported into ImageJ and processes are measured. Measurements are then processed using a statistical program.
Figure 1. Flowchart of in vitro axon and dendrite growth assay. Cultured CGNs (24-well plate with glass coverslips), isolated from P6 rat pups, are transfected at DIV 0 or 1 with DNA precipitate containing a fluorescent transfection marker (e.g. GFP). After fixation and immunocytochemistry, neurons are imaged in a blinded manner. Images are imported into ImageJ and processes are measured. Measurements are then processed using a statistical program.
Seed CGNs (20 x 106 per 24-well plate; BME, 10% calf serum, 2 mM Penicillin-Streptomycin-Glutamine (PSG), 25 mM KCl) on nitric acid-washed, polyornithine-coated 12 mm glass coverslips in a 24-well plate with 500 μl of media per well.
On day in vitro (DIV) 0 (at least 8 hr after plating) or DIV 1, collect growth media and keep at 37 °C. Wash neurons twice with 500 μl of prewarmed DMEM and add 500 μl of DMEM.
Place neurons in incubator (37 °C, 5% CO2) for 45 min.
- Prepare 40 μl DNA precipitate for each well by mixing: DNA (2-2.5 μg/well, 10% of total DNA should be a transfection marker e.g. GFP to visualize transfected neurons), water (up to 18 μl), add 2 μl of 2.5 M CaCl2, mix well and add 20 μl of 2x HBSS.
- Incubate DNA precipitate for 5 min at RT.
Add DNA precipitate to each well and incubate neurons for 18 min in incubator.
Remove DMEM/DNA mix and wash neurons twice with 500 μl of prewarmed DMEM.
Add collected media from step 2.2 back to neurons. If neurons will be in culture for more than 3 days, supplement media with 25 mM glucose at DIV 3 to replenish carbon source.
After 1-5 days, subject neurons to immunocytochemistry using GFP antibodies.
Image at least 30 individual neurons per condition in a blinded manner using a fluorescent microscope.
3. Measure Axons and Dendrites with NeuronJ, an NIH ImageJ Plugin
Important: Ensure that Images are scaled correctluy by using appropriate pixel:μm ratio depending on magnification and resolution of image.
Convert images to 8-bit with ImageJ: Open image, choose 'Image' -> 'Type' -> '8-bit' -> 'Save' image.
Use the 'Add tracings' option to track the axon: click the left mouse button once at the beginning of the axon and move the mouse along the process. Double click on tip of axon if trace matches axonal shape.
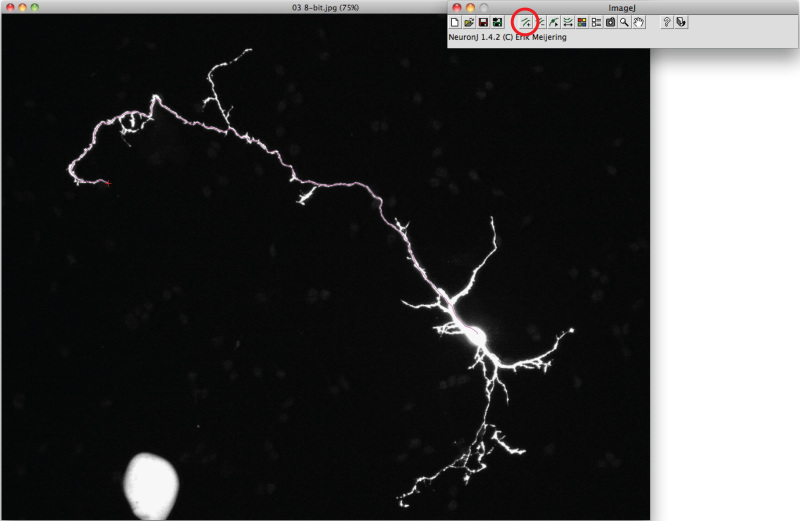 Note: Should the suggested trace differ from axonal shape, click once on the axonal process to anchor trace, then double click on tip of axon.
Note: Should the suggested trace differ from axonal shape, click once on the axonal process to anchor trace, then double click on tip of axon.Click on 'Measure tracings', choose the 'Display tracing measurements' option and press 'Run'. Axon measurements are all displayed in a new window. For dendrites, choose the 'Display group measurements option' and press 'Run'.
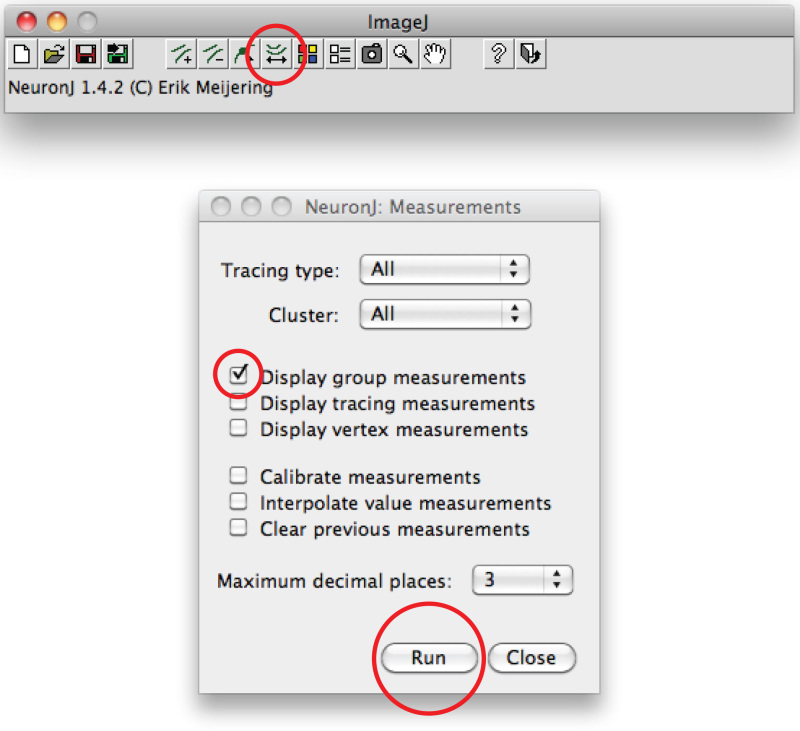 Total dendrite measurements are all displayed in a new window. Save them as a separate file that can be opened in any spreadsheet program.
Total dendrite measurements are all displayed in a new window. Save them as a separate file that can be opened in any spreadsheet program.Alternatively for manual tracing, use Fiji software: Right click on the 'Straight line' option, choose 'Freehand line',
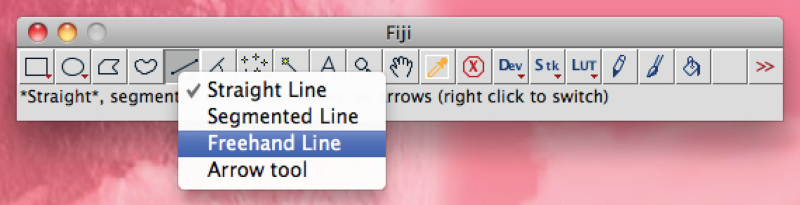 keep the left mouse button pressed and manually trace the process, press 'Ctrl+M' to measure.
keep the left mouse button pressed and manually trace the process, press 'Ctrl+M' to measure.Calculate average axonal/dendritic length per condition and use appropriate statistical test. In vivo electroporation:
1. Equipment and Preparation of Reagents
You need 30 G needles, spacer (1-2 mm), syringe, dead volume reducer (DVR), electroporator, and tweezertrodes, heating pad or infrared heat lamp, gooseneck lamp and isoflurane.
Put DVR into needle, then attach needle to syringe, and finally put spacer onto needle (Figure 2).
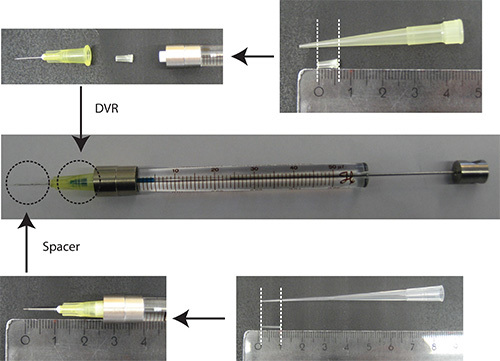 Figure 2. Preparation of needle. DVR is cut off a 200 μl pipette tip and placed into the needle to reduce the dead volume. Spacer is derived from a 200 μl loading tip and is placed on the end of the needle to regulate the depth of penetration into the cerebellum to approximately 2 mm. Ruler units: cm
Figure 2. Preparation of needle. DVR is cut off a 200 μl pipette tip and placed into the needle to reduce the dead volume. Spacer is derived from a 200 μl loading tip and is placed on the end of the needle to regulate the depth of penetration into the cerebellum to approximately 2 mm. Ruler units: cmDissolve DNA in PBS/0.03% Fast Green. Note: As a transfection marker, it is advantageous to use a fluorescent protein that is under a neuron-specific promoter (e.g. Synapsin) to visualize neurons only. 25% of the total plasmid amount should be the plasmid encoding the transfection marker.
Make 70% ethanol.
Mix equal volumes of OCT and 30% sucrose dissolved in PBS.
Fill syringe with 4 μl of DNA (4 μg/μl of plasmid DNA in PBS/0.03% Fast Green).
2. IVE of Rat Pups
Flowchart of IVE: see Figure 3
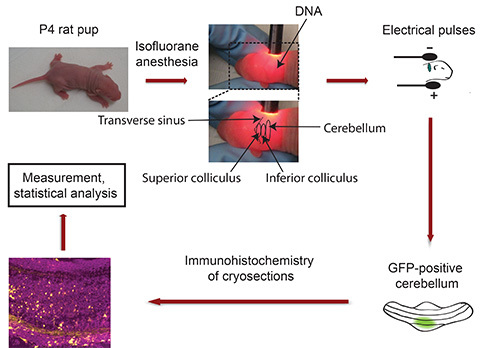 Figure 3. Flowchart of in vivo electroporation. P4 rat pups are anaesthetized with Isoflurane and plasmid DNA encoding a fluorescent transfection marker (e.g. GFP) is injected into the cerebellum, followed by exposure to 5 electrical pulses. Five days later, isolated GFP-positive cerebella are sectioned and subjected to immunohistochemistry. Images are captured using a confocal microscope and analyzed using Imaris software. Data are processed with a statistical program.
Figure 3. Flowchart of in vivo electroporation. P4 rat pups are anaesthetized with Isoflurane and plasmid DNA encoding a fluorescent transfection marker (e.g. GFP) is injected into the cerebellum, followed by exposure to 5 electrical pulses. Five days later, isolated GFP-positive cerebella are sectioned and subjected to immunohistochemistry. Images are captured using a confocal microscope and analyzed using Imaris software. Data are processed with a statistical program.
Use P4 rat pups from albino strain (Wistar or Long Evans).
Anesthetize pups (one after another) with isoflurane in small box (e.g. P1000 pipette tip box) with 200 μl of isoflurane (soaked in tissue) for 1-2 min until pup is no longer moving. Take care that pups do not get into contact with Iiquid isoflurane. Monitor time closely as individual pups respond differently to anesthesia.
Sterilize back of pup’s head with 70% ethanol.
Fix head of pup between thumb and index finger and use gooseneck lamp to locate cerebellum of albino pup. The transverse sinus sharply demarcates the midbrain (superior and inferior colliculus) from the cortical hemispheres (Figure 3). The cerebellum is located adjacent to midbrain and appears in a darker shade. Use a permanent marker to indicate the cerebellum with a dot. Important: Keep pup in fixed position! Note: Should anesthesia wear off during this procedure, expose pup to isoflurane prior to injecting the DNA.
Insert needle (Figure 3) and slowly inject 3 μl of DNA into the cerebellum.
- Let the DNA solution diffuse for 30-60 sec.
- Place head of pup between tweezertrodes so that the minus pole makes contact with the back of the head (cerebellar region) and that the plus pole contacts the opposite side of the head (Figure 3).
- Subject pup to 5 electrical pulses. Adjust voltage to weight of pups to ensure good electroporation efficiency without compromising their survival (Table 1).
Weight Voltage Pulse Interval 8-9 g 160 V 50 msec 950 msec 9-10 g 165 V 50 msec 950 msec > 10 g 170 V 50 msec 950 msec - Let pups recover on heated pad or underneath an infrared lamp. Return pups to dam. Important: Make sure that heating source does not inflict any burns.
- Sacrifice pups 5 days after electroporation by placing them in CO2 followed by decapitation.
- Isolate the cerebella and screen for GFP-positive ones cerebella using a fluorescent microscope.
Fix cerebella in 4% PFA O/N at 4 °C, then incubate in 30% sucrose at 4 °C until cerebella sink to bottom of tube.
Embed cerebella in OCT/30% sucrose and cut 40 μm coronal sections using a cryostat. Note: Section each cerebellum in a blinded manner.
Subject sections to immunohistochemistry using the GFP antibody. Counterstain with nuclear dye (DAPI or Hoechst 33258) and determine localization of at least 200 transfected neurons per animal.
For an in-depth analysis, subdivide the IGL into halves, resulting in an upper IGL facing the ML and a lower IGL facing the white matter and count GFP-positive neurons residing in each half. Note: Count GFP-positive neurons of each section in a blinded manner.
3. Measuring Dendrite Length, Acquire the Images of the Section in x, y, z Plane Using a Confocal Microscope
Note: for example, use 40 images for a 40 μm section with a z-stwp of 1 μm.
Open image series in the software, Imaris, to generate a 3D image of the dendrites.
Select 'Add new filament' and click 'Skip automatic creation' to start semiautomatic tracing.
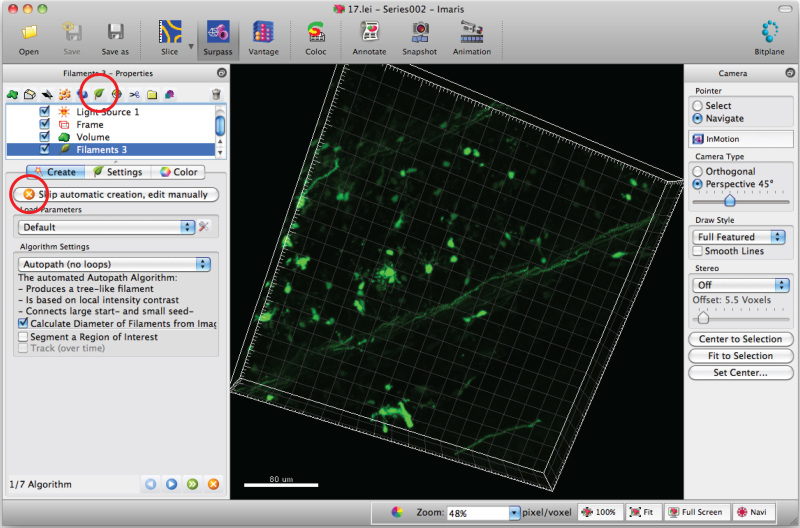 Note: Analyze each 3D image in a blinded manner
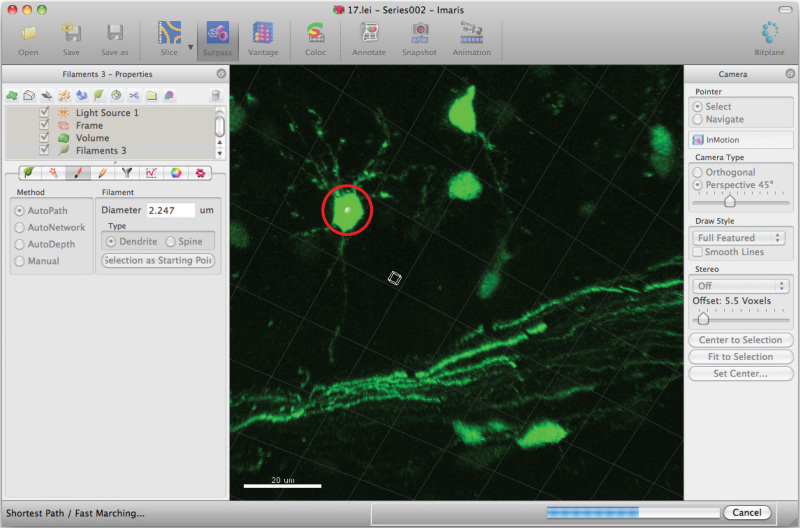
Note: Analyze each 3D image in a blinded mannerMove the mouse cursor on the cell body and Shift+mouse right click to select the cell body. Note: Autocalculation by software may require a few minutes.
Add paths to the filament (dendrite) using Shift+mouse left click. Note: Paths can be visualized in real time.
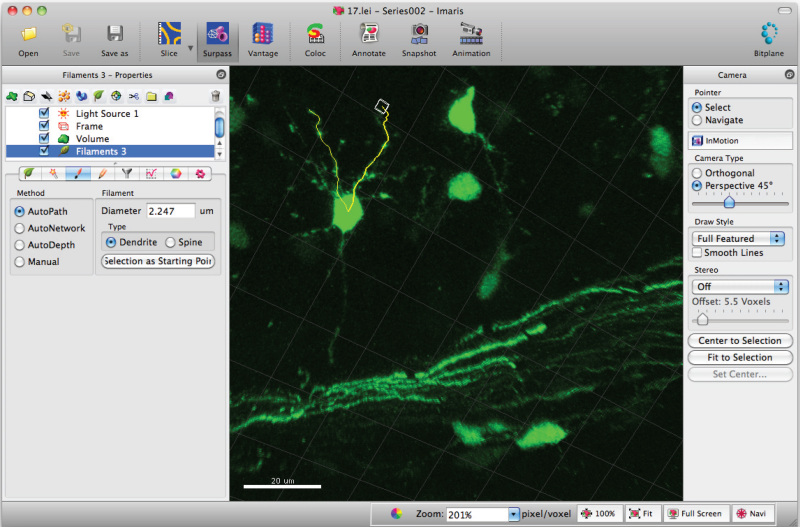
Go to filament statistics window and click on 'Detailed', 'Specific values' and 'Filament dendrite length (sum)' for sum of total dendrite length.
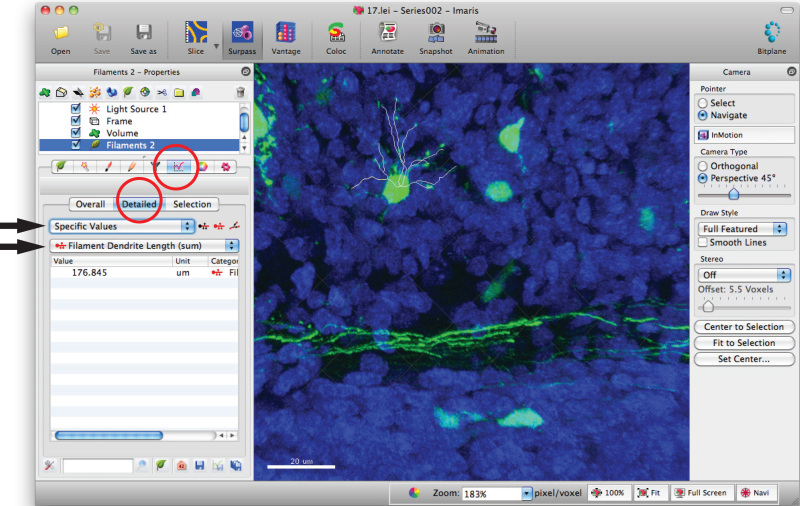
Use appropriate statistical tests to analyze data.
Representative Results
To analyze the morphology of CGNs in response to different culturing conditions, we transfected the neurons on DIV 0 as described above. After transfection, we placed one set of neurons into full medium (BME, 10% calf serum, 2 mM PSG, 25 mM KCl) and another set into minimal medium containing insulin (BME, 25 mM glucose, 2 mM PSG, 10 μg/ml insulin). We subjected the neurons to immunocytochemistry using the GFP antibody at DIV 1, 2, and 3, followed by measuring axons and dendrites for set 1 and axons only for set 2. Owing to serum and KCl, which provide growth factors and mimic neuronal activity, respectively, axons and dendrites developed and grew rapidly over the time window indicated (Figure 4A). Axonal growth of set 2 was mainly a consequence of intrinsic stimulation and thus much reduced. Dendrites however failed to develop properly owing to the lack serum and KCl, which stimulate dendrite growth (Figure 4B).
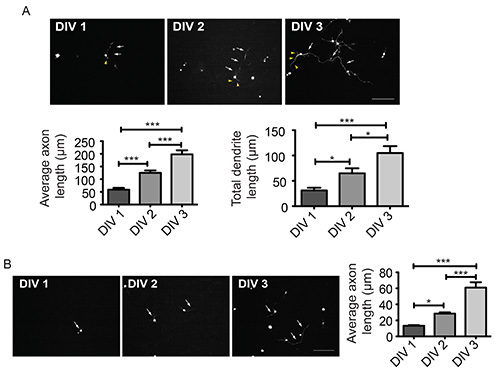 Figure 4. Analysis of axon and dendrite growth in CGNs (A, B) CGNs, transfected with a plasmid encoding GFP at DIV 0, were cultured for 1, 2, or 3 days in either full medium (A) or BME supplemented with insulin (B). After fixation, neurons were subjected to immunocytochemistry using the GFP antibody and axon and dendrite lengths were measured. A total of 82 (A) and 65 (B) neurons were measured (ANOVA, *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, mean + s.e.m.). White arrows and yellow arrowheads indicate axons and dendrites, respectively. Scale bar equals 100 μm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Figure 4. Analysis of axon and dendrite growth in CGNs (A, B) CGNs, transfected with a plasmid encoding GFP at DIV 0, were cultured for 1, 2, or 3 days in either full medium (A) or BME supplemented with insulin (B). After fixation, neurons were subjected to immunocytochemistry using the GFP antibody and axon and dendrite lengths were measured. A total of 82 (A) and 65 (B) neurons were measured (ANOVA, *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, mean + s.e.m.). White arrows and yellow arrowheads indicate axons and dendrites, respectively. Scale bar equals 100 μm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
To perform morphological analysis of the rat cerebella, we subjected P4 pups to IVE as described above and isolated cerebella 5 days later. Immunohistochemistry of 40 μm coronal cryosections revealed that 86% GFP-positive neurons descended from the EGL into the IGL (Figure 5A). Among those, 50% were observed in the upper part of the EGL and 36% migrated farther into the lower part of the IGL. We also determined dendrite growth of three independent electroporated cerebella and compared average lengths (Figure 5B).
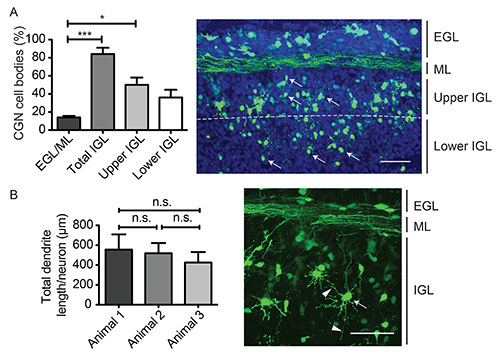 Figure 5. Analysis of neuronal migration and dendrite length in in vivo electroporated cerebella. Cerebella of P4 rat pups were electroporated with the pSyn-GFP plasmid and isolated 5 days later. 40 μm coronal sections were subjected to immunohistochemistry using the GFP antibody. (A) Localization of CGNs in cerebellum was assessed. (Kruskal Wallis, Mann Whitney correction, *p<0.05, ***p<0.001) (B) Total dendrite length was measured using Imaris software (ANOVA, Bonferroni correction, n.s. = nonsignificant, mean + s.e.m.). Arrows indicate CGN cell bodies. Arrowheads indicate dendrites. Scale bar equals 50 μm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Figure 5. Analysis of neuronal migration and dendrite length in in vivo electroporated cerebella. Cerebella of P4 rat pups were electroporated with the pSyn-GFP plasmid and isolated 5 days later. 40 μm coronal sections were subjected to immunohistochemistry using the GFP antibody. (A) Localization of CGNs in cerebellum was assessed. (Kruskal Wallis, Mann Whitney correction, *p<0.05, ***p<0.001) (B) Total dendrite length was measured using Imaris software (ANOVA, Bonferroni correction, n.s. = nonsignificant, mean + s.e.m.). Arrows indicate CGN cell bodies. Arrowheads indicate dendrites. Scale bar equals 50 μm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
Advantages and limitations of the described in vitro and in vivo methods:
Cultured CGNs from mouse and rats are equally well suited for morphological analyses. Owing to the bigger size of a rat cerebellum, the yield of CNGs from rat pups exceeds that of mouse pups 3-4x. Aside from CGNs, cortical and hippocampal neurons can be used as culture system as well. The calcium phosphate method results in a low (0.01-5%) transfection efficiency, which is desired to analyze the morphology of individual neurons. Alternative lipophilic transfection methods can be used as well, but are excessively expensive without further gain. Viral transfection methods of high-density cultures such as CGNs should be avoided as high efficiencies will make it very difficult to distinguish individual processes. In CGNs, we typically find a correlation of transfection efficiency and days in vitro. The longer the neurons have been cultured, the less affected they will be by transfection-induced stress. As a consequence the transfection efficiency will go up. Also, to focus on intrinsic mechanisms of axon growth and exclude the influence of growth factors derived from serum present in the media, CGNs can be cultured in survival media supplemented with insulin, a cheap surrogate for insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which promotes neuronal survival35. A media change from full media to insulin-containing media must occur either at DIV 0 or DIV 1 to prevent serum/KCl-withdrawal-induced apoptosis. The analysis of dendrite growth can be performed analogous to the axon growth assay. It is however important to keep CGNs in media supplemented with KCl to simulate neuronal activity, which promotes dendritic development. Analysis of neuronal migration should be carried out using the in vivo electroporation technique.
The transfection of cultured neurons will typically entail the cotransfection of at least two plasmids: a plasmid encoding the transfection marker, which can be a plasmid coding for a fluorescent protein (e.g. GFP) or b-Galactosidase, and either RNAi or overexpression plasmids. To ensure the successful coexpression of plasmids, the recommended amount of transfection marker should be 10% of the total amount of DNA (2-2.5 μg/well of a 24-well plate). We have previously established that the transfection of equal amounts of DNA (GFP together with DsRed) results in more than 85% of neurons coexpressing the two plasmids22,24 . Should knockdown, overexpression or exposure to small molecules induce neuronal cell death, a plasmid encoding Bcl-XL can be cotransfected to ensure neuronal survival without effects on morphology20. Cotransfection of up to three or four plasmids is also unproblematic, which is useful to carry out epistasis analyses to establish a linear pathway or synergy of two proteins in axon or dendrite growth. Here, two independent RNAi or overexpression plasmids or a combination of both can be cotransfected together with a transfection marker.
The in vivo electroporation technique is an ideal method for the analysis of neuronal migration in developing cerebellar cortex. It is of advantage to use pups from an albino strain as compared to a strain with dark complexion. Also, it is easier to work with rat pups owing to their larger sized cerebella. In our hands, almost all cerebella are GFP-positive but to different degrees. A well-electroporated cerebellum has many hundred GFP-positive neurons, a badly-transfected cerebellum less than 100. With a little practice, it is also possible to use mice if transgenic mice are required for the study. This method is significantly faster than the generation of transgenic mice and it allows for the analysis of different conditions (loss-of-function, gain-of-function and structure-function-analyses). IVE does not require stereotaxis, a gooseneck lamp is sufficient to detect the cerebellum of a fairly translucent albino pup. This will also shorten the procedure time per pup and a brief anesthesia with isoflurane suffices. It does however require a little practice to target the correct region and thus to master the technique.
Developmental problems caused by knockdown or overexpression are insignificant owing to the regionalized genetic manipulation of the cerebellum. This allows for the analysis of intrinsic mechanism as the electroporation results in a mosaic pattern of genetically-modified neurons embedded in a wild type environment. The downside is that the electroporated rats or mice cannot be subjected to behavioral test due to the low amount of transfected neurons. To ensure the coexpression of plasmids in neurons, we recommend the cotransfection with a plasmid encoding GFP (or any other fluorescent protein) under a neuron-specific promoter to avoid the visualization of transfected glial cells. Effects that result in a reduction of axonal length can be easily detected and measured24. In contrast, it is technically impossible to quantify stimulating effects on axons as their entire lengths cannot be traced. Defasciculation of parallel fibers however is measureable20. The same holds true for the assessment of dendrite length and neuronal migration23,24,30. We typically carry out our analyses 5 days after the electroporation. It is of course possible to perform the analysis sooner and later. A later time point is recommended to examine the formation of dendritic claws29, which represent the synaptic connection between CGNs and mossy fibers.
To finalize the analyses, it is important to choose the appropriate statistical test. For this, one has to take into account if the values of the groups follow a normal distribution (e.g. axonal or dendrites lengths) and if 2 or more than 2 groups are included in the analysis. For 2 groups, we use Student’s test, for more than 2 groups ANOVA. Should the values follow a non-normal distribution (e.g. migration distance), Mann Whitney U test and Kruskal Wallis test have to be used for 2 or more than 2 groups, respectively.
Disclosures
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Acknowledgments
We thank N. Schwedhelm-Domeyer for excellent technical assistance, C. Hammer and S. Papiol for help with statistical analyses. Our work is funded by the Max Planck Society, the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the Center for Nanoscale Microscopy, and Molecular Physiology of the Brain (CNMPB), Göttingen, Germany and by the GGNB Junior Group Stipend of the University of Göttingen.
References
- Cajal SR. Histology of the nervous system of man and vertebrates. Oxford University Press; 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Altman J, Bayer SA. Development of the cerebellar system : in relation to its evolution, structure, and functions. CRC Press; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- White JJ, Reeber SL, Hawkes R, Sillitoe RV. Wholemount immunohistochemistry for revealing complex brain topography. J. Vis. Exp. 2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Palay SL, Chan-Palay V. Cerebellar cortex: cytology and organization. Springer; 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Hatten ME, Alder J, Zimmerman K, Heintz N. Genes involved in cerebellar cell specification and differentiation. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1997;7:40–47. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(97)80118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatten ME, Heintz N. Mechanisms of neural patterning and specification in the developing cerebellum. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1995;18:385–408. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.18.030195.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillitoe RV, Joyner AL. Morphology molecular codes, and circuitry produce the three-dimensional complexity of the cerebellum. Ann. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2007;23:549–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervas M, Millet S, Ahn S, Joyner AL. Cell behaviors and genetic lineages of the mesencephalon and rhombomere 1. Neuron. 2004;43:345–357. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate RJ. The rhombic lip and early cerebellar development. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2001;11:82–88. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(00)00177-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaji K, Umeshima H, Eiraku M, Hirano T, Kengaku M. Dual phases of migration of cerebellar granule cells guided by axonal and dendritic leading processes. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2004;25:228–240. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2003.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatten ME, Gao W-Q, Morrison ME, Mason CA. MIT Press; Cellular and molecular neuroscience; pp. 419–41. [Google Scholar]
- Lee HY, Greene LA, Mason CA, Manzini MC. Isolation and culture of post-natal mouse cerebellar granule neuron progenitor cells and neurons. J. Vis. Exp. 2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bilimoria PM, Bonni A. Cultures of cerebellar granule neurons. CSH Protoc. 2008;2008 doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot5107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivas RJ, Hatten ME. Motility and cytoskeletal organization of migrating cerebellar granule neurons. J. Neurosci. 1995;15:981–989. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-02-00981.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar SG, et al. Changing patterns of gene expression define four stages of cerebellar granule neuron differentiation. Development. 1993;117:97–104. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird DH, Hatten ME, Mason CA. Cerebellar target neurons provide a stop signal for afferent neurite extension in vitro. J. Neurosci. 1992;12:619–634. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-02-00619.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal RA, Pomeroy SL, Stiles CD. Axonal growth and fasciculation linked to differential expression of BDNF and NT3 receptors in developing cerebellar granule cells. J. Neurosci. 1995;15:4970–4981. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-07-04970.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo V, Ciotti MT, Coletti A, Aloisi F, Levi G. Selective release of glutamate from cerebellar granule cells differentiating in culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1982;79:7919–7923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith TC, Wang LY, Howe JR. Distinct kainate receptor phenotypes in immature and mature mouse cerebellar granule cells. Physiol. 1999;517(1):51–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0051z.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi Y, Stegmuller J, Matsuda T, Bonni S, Bonni A. Cdh1-APC controls axonal growth and patterning in the mammalian brain) Science. 2004;303:1026–1030. doi: 10.1126/science.1093712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmuller J, Huynh MA, Yuan Z, Konishi Y, Bonni A. TGFbeta-Smad2 signaling regulates the Cdh1-APC/SnoN pathway of axonal morphogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2008;28:1961–1969. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3061-07.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmuller J, et al. Cell-intrinsic regulation of axonal morphogenesis by the Cdh1-APC target SnoN. Neuron. 2006;50:389–400. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.03.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannan M, Lee SJ, Schwedhelm-Domeyer N, Nakazawa T, Stegmuller J. p250GAP is a novel player in the Cdh1-APC/Smurf1 pathway of axon growth regulation. PLoS One. 2012;7 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannan M, Lee SJ, Schwedhelm-Domeyer N, Stegmuller J. The E3 ligase Cdh1-anaphase promoting complex operates upstream of the E3 ligase Smurf1 in the control of axon growth. Development. 2012;139:3600–3612. doi: 10.1242/dev.081786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudilliere B, Konishi Y, de la Iglesia N, Yao G, Bonni AA. CaMKII-NeuroD Signaling Pathway Specifies Dendritic Morphogenesis. Neuron. 2004;41:229–241. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00841-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y, et al. A Cdc20-APC ubiquitin signaling pathway regulates presynaptic differentiation. Science. 2009;326:575–578. doi: 10.1126/science.1177087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litterman N, et al. An OBSL1-Cul7Fbxw8 ubiquitin ligase signaling mechanism regulates Golgi morphology and dendrite patterning. PLoS Biol. 2011;9 doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim AH, et al. A centrosomal Cdc20-APC pathway controls dendrite morphogenesis in postmitotic neurons. Cell. 2009;136:322–336. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalizi A, et al. A calcium-regulated MEF2 sumoylation switch controls postsynaptic differentiation. Science. 2006;311:1012–1017. doi: 10.1126/science.1122513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadhvani M, Schwedhelm-Domeyer N, Mukherjee C, Stegmuller J. The Centrosomal E3 Ubiquitin Ligase FBXO31-SCF Regulates Neuronal Morphogenesis and Migration. PLoS One. 2013;8 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puram SV, et al. A CaMKIIbeta signaling pathway at the centrosome regulates dendrite patterning in the brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Jia Y, Zhou J, Tai Y, Wang Y. TRPC channels promote cerebellar granule neuron survival. Nat. Neurosci. 2007;10:559–567. doi: 10.1038/nn1870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh MA, et al. An isoform-specific SnoN1-FOXO1 repressor complex controls neuronal morphogenesis and positioning in the mammalian brain. Neuron. 2011;69:930–944. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.02.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Torre-Ubieta L, Bonni A. Transcriptional regulation of neuronal polarity and morphogenesis in the mammalian brain. Neuron. 2011;72:22–40. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.09.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calissano P, et al. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I exerts a trophic action and confers glutamate sensitivity on glutamate-resistant cerebellar granule cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1993;90:8752–8756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]