Abstract
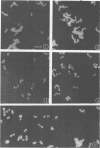
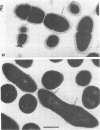
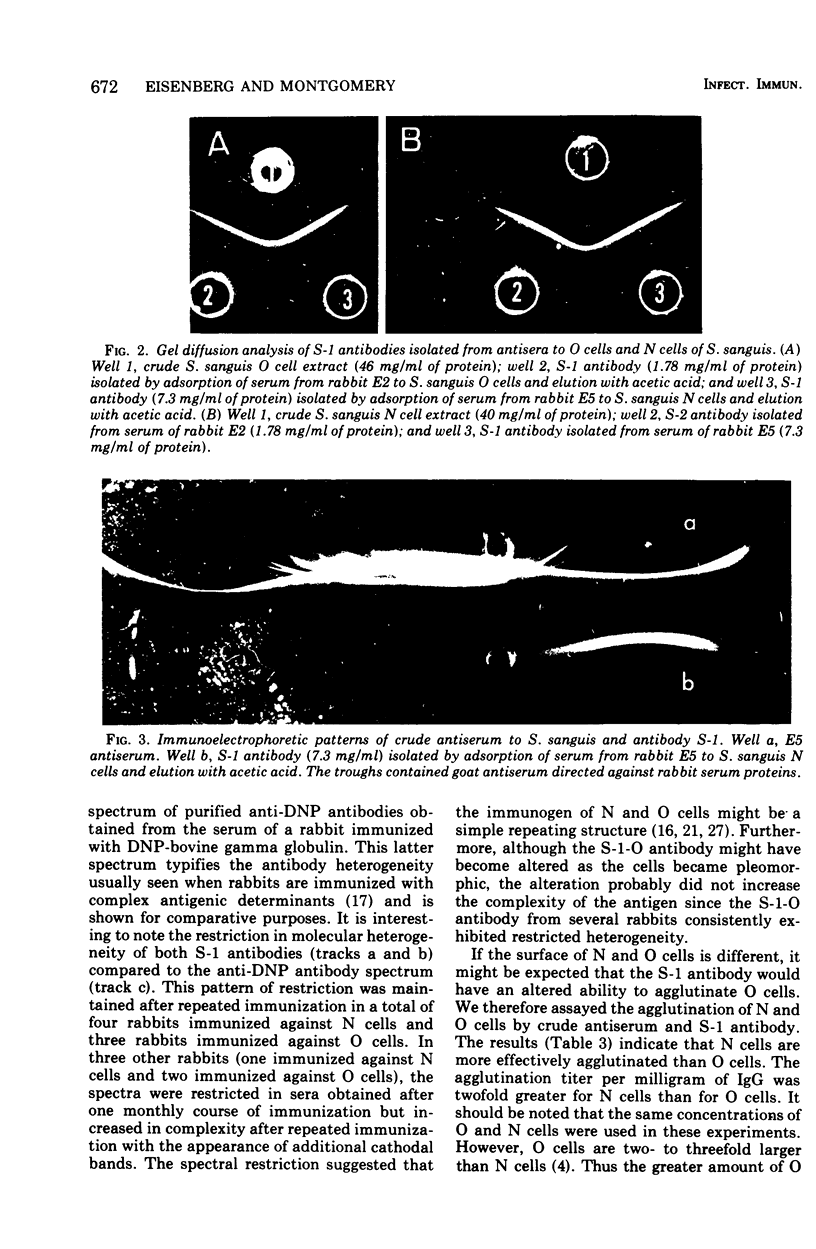
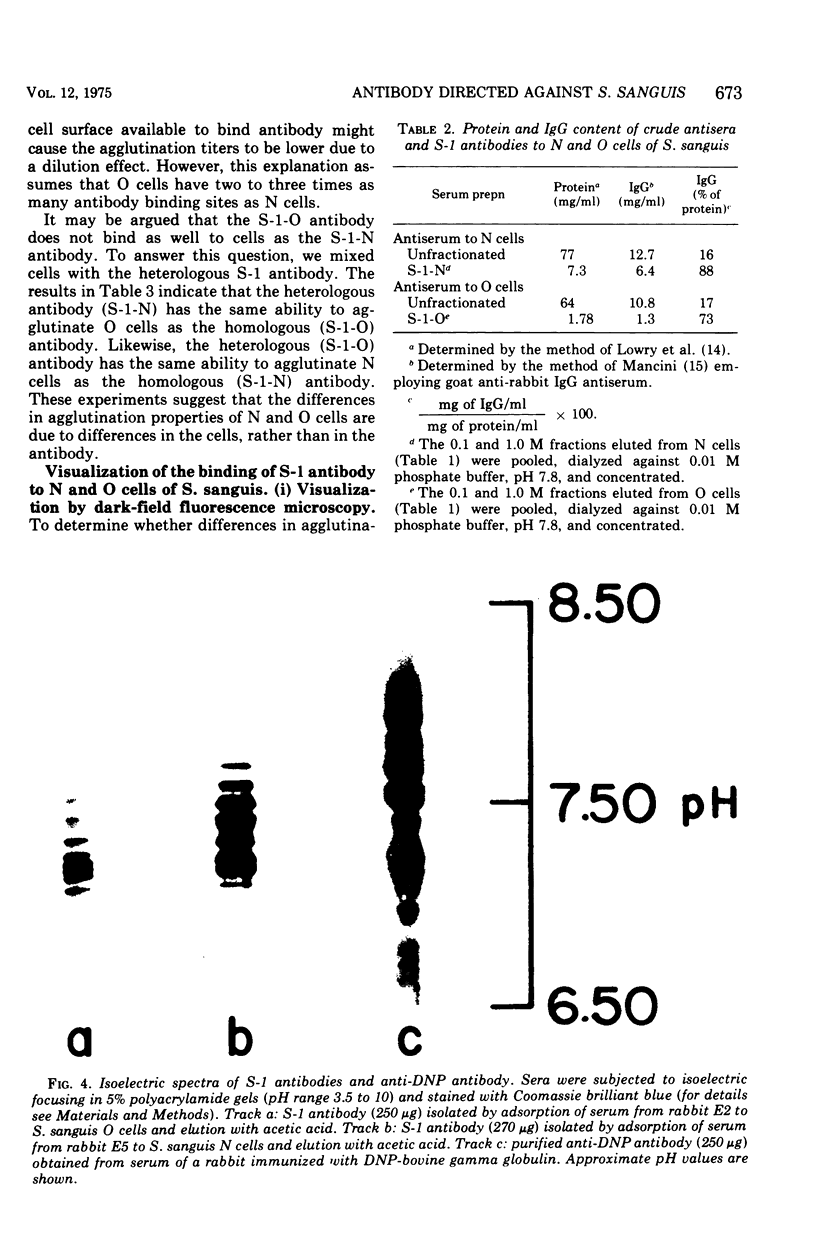
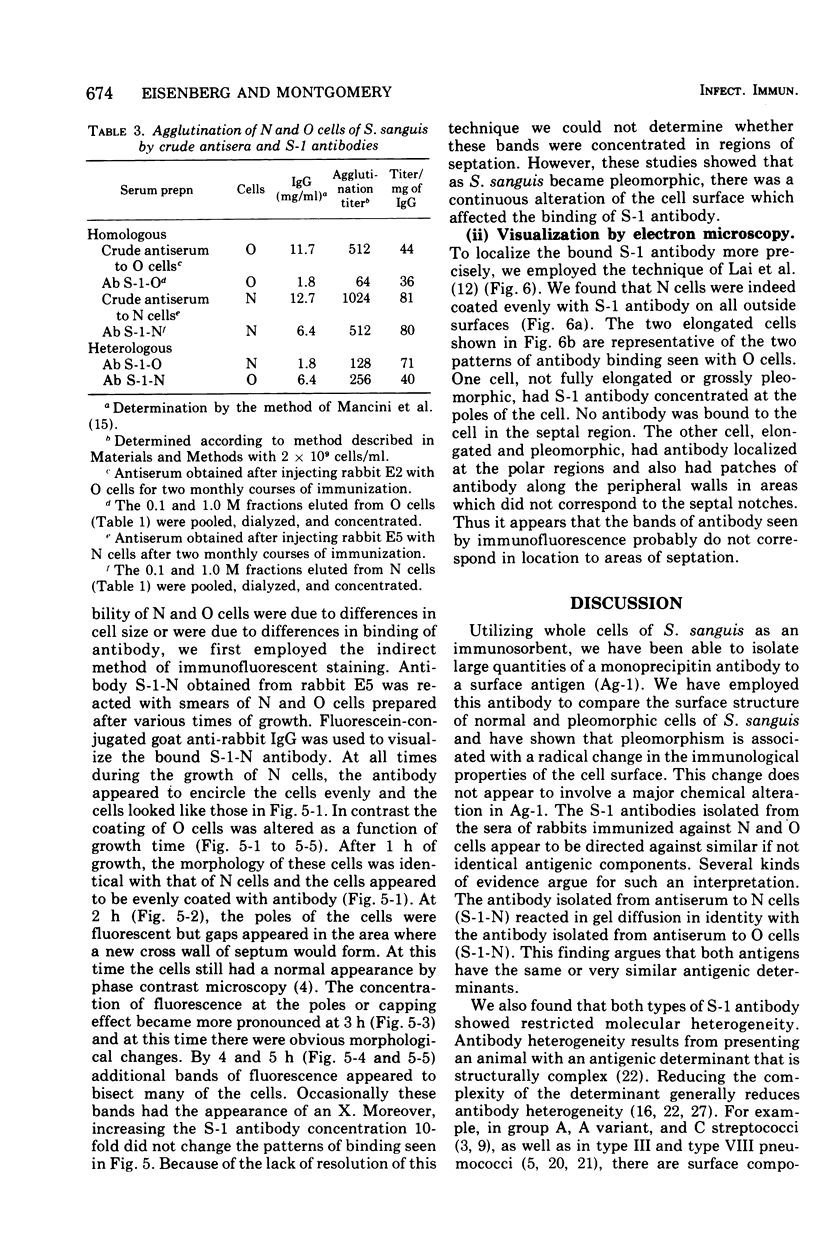
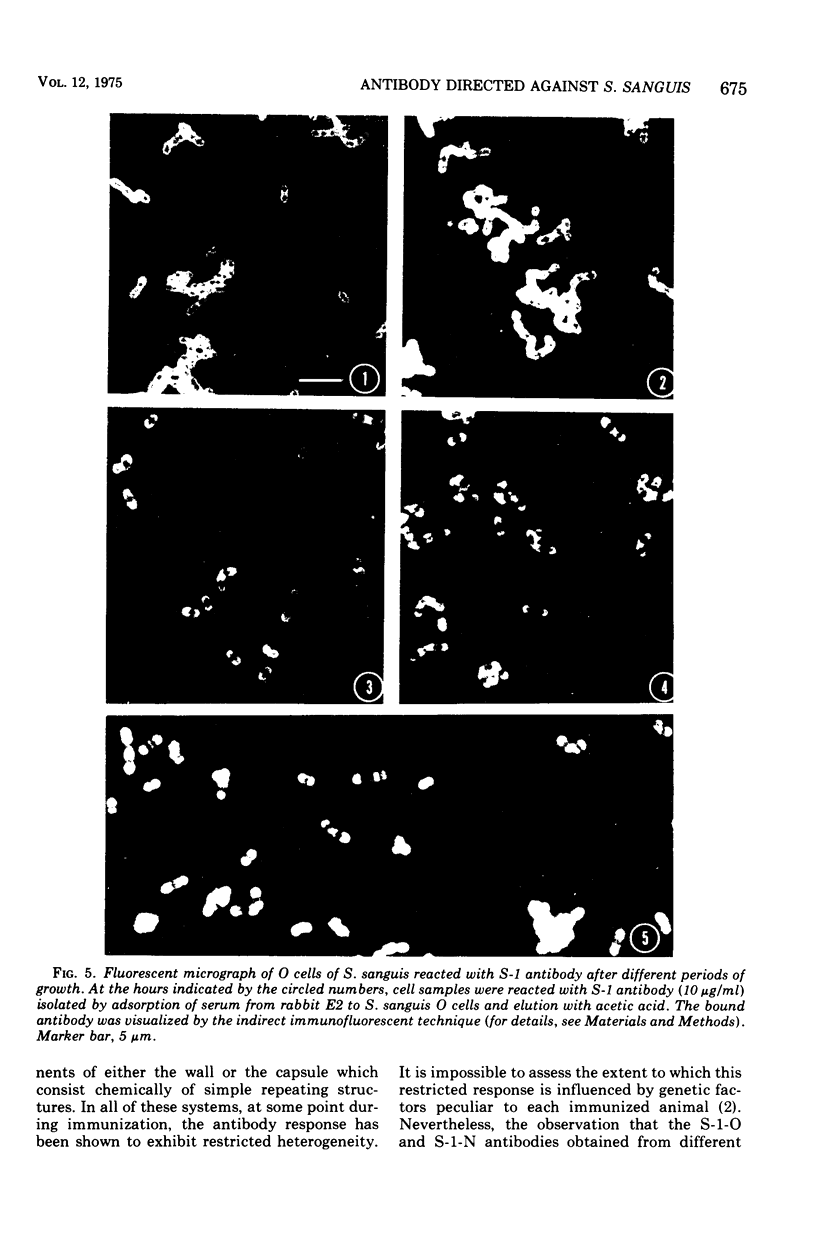
Whole cells of Streptococcus sanguis were utilized as an immunoadsorbent to purify large quantities of an antibody (S1) directed against a cell surface component. The S-1 antibody was isolated from antisera to normal (N) and pleomorphic (O) cells by a similar adsorption-elution procedure. The S-1 antibody isolated from antisera to N cells reacted in gel diffusion in identify with the S-1 antibody to O cells, indicating that the antigen which binds S-1 antibody (Ag-1) may not be radically altered when cells become pleomorphic. The S-1 antibodies directed against both N and O cells had restricted heterogeneity, indicating that for both types of cell Ag-1 may have a simple repeating structure. However, N cells were agglutinated to a greater extent by S-1 antibody than O cells. In addition the distribution of the bound S-1 antibody became altered as the cells became pleomorphic. Utilizing the technique of indirect immunofluorescence we observed that the S-1 antibody was distributed evenly on the surface of N cells. As the cells became pleomorphic, the antibody appeared to bind preferentially at the cell poles (capping). Later, as the cells became more grossly deformed, additional bands of immunofluorescence appeared to bisect the cells. Electron microscopic analysis indicated that the bound antibody was not associated with septal notches. The results suggest that the arrangement rather than the immunological properties of Ag-1 became altered as cells became pleomorphic.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boylan R. J., Mendelson N. H., Brooks D., Young F. E. Regulation of the bacterial cell wall: analysis of a mutant of Bacillus subtilis defective in biosynthesis of teichoic acid. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):281–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.281-290.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. G., Eichmann K., Krause R. M. Rabbit antibodies to streptococcal carbohydrates. Influence of primary and secondary immunization and of possible genetic factors on the antibody response. J Exp Med. 1969 Apr 1;129(4):809–830. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.4.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Lackland H., Hood L., Krause R. M. Induction of rabbit antibody with molecular uniformity after immunization with group C streptococci. J Exp Med. 1970 Jan 1;131(1):207–221. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J. Induction of unbalanced growth and death of Streptococcus sanguis by oxygen. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):183–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.183-191.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E. Antibodies of restricted heterogeneity for structural study. Fed Proc. 1970 Jan-Feb;29(1):66–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacono V. J., Taubman M. A., Smith D. J., Levine M. J. Isolation and immunochemical characterization of the group-specific antigen of Streptococcus mutants 6715. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):117–128. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.117-128.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause R. M. Experimental approaches to homogenous antibody populations. Factors controlling the occurrence of antibodies with uniform properties. Fed Proc. 1970 Jan-Feb;29(1):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Ensign J. C., Tipper D. J., Strominger J. L. Sphere-rod morphogenesis in Arthrobacter crystallopoietes. I. Cell wall composition and polysaccharides of the peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):734–740. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.734-740.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Ensign J. C., Tipper D. J., Strominger J. L. Sphere-rod morphogenesis in Arthrobacter crystallopoietes. II. Peptides of the cell wall peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):741–750. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.741-750.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C., Listgarten M., Rosan B. Serology of Streptococcus sanguis: localization of antigens with unlabeled antisera. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):475–481. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.475-481.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer R., Slade H. D. Purification and characterization of Streptococcus mutans group d cell wall polysaccharide antigen. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):361–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.361-368.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery P. C., Rockey J. H., Williamson A. R. Homogeneous antibody elicited with dinitrophenyl-gramicidin-S (rabbit-isoelectric focusing). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):228–232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery P. C., Williamson A. R. Molecular restriction of anti-hapten antibody elicited in neonatal rabbits: antibody production in littermates. J Immunol. 1972 Nov;109(5):1036–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Extraction, purification, and chemical and immunological properties of the Streptococcus mutans group "a" polysaccharide cell wall antigen. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):190–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.190-198.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus J. H., Jaton J. C., Bloch K. J., Haber E. Antibodies to type III and type VIII pneumococcal polysaccharides: evidence for restricted structural heterogeneity in hyperimmunized rabbits. J Immunol. 1970 May;104(5):1143–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus J. H., Jaton J. C., Bloch K. J., Haber E. Properties of structurally restricted antibody to type VIII pneumococcal polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1970 May;104(5):1149–1154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. F., Pincus J. H., Bloch K. J., Barnes W. T., Haber E. The relationship between antigenic complexity and heterogeneity in the antibody response. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1377–1384. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taubman M. A., Genco R. J. Induction and properties of rabbit secretory A antibody directed to group A streptococcal carbohydrate. Immunochemistry. 1971 Dec;8(12):1137–1155. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90392-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedros N. A., Hill P. R. Microagglutination technique for Neisseria meningitidis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):900–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.900-901.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
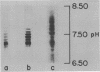
- Williamson A. R. Antibody isoelectric spectra. Analysis of the heterogeneity of antibody molecules in serum by isoelectric focusing in gel and specific detection with hapten. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Nov;1(5):390–394. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson A. R. Extent and control of antibody diversity. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(2):325–333. doi: 10.1042/bj1300325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]