Abstract
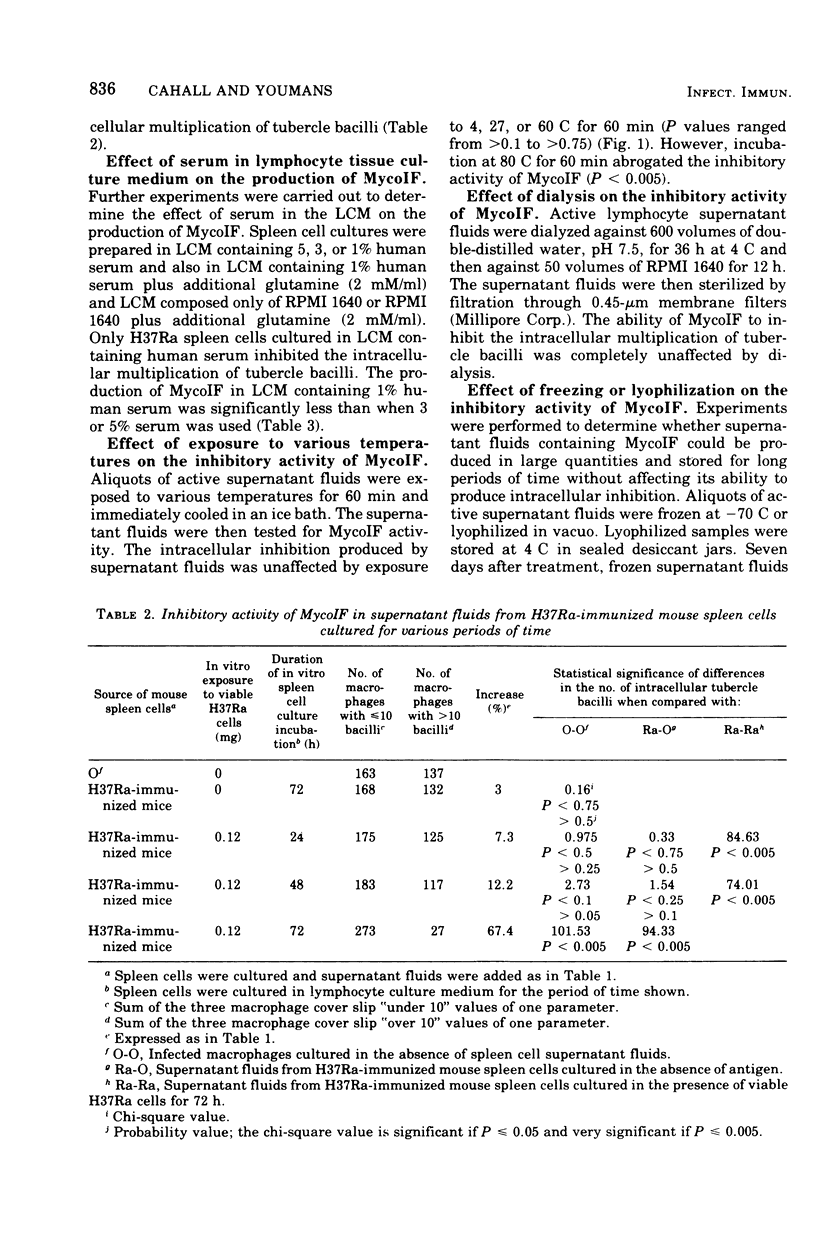
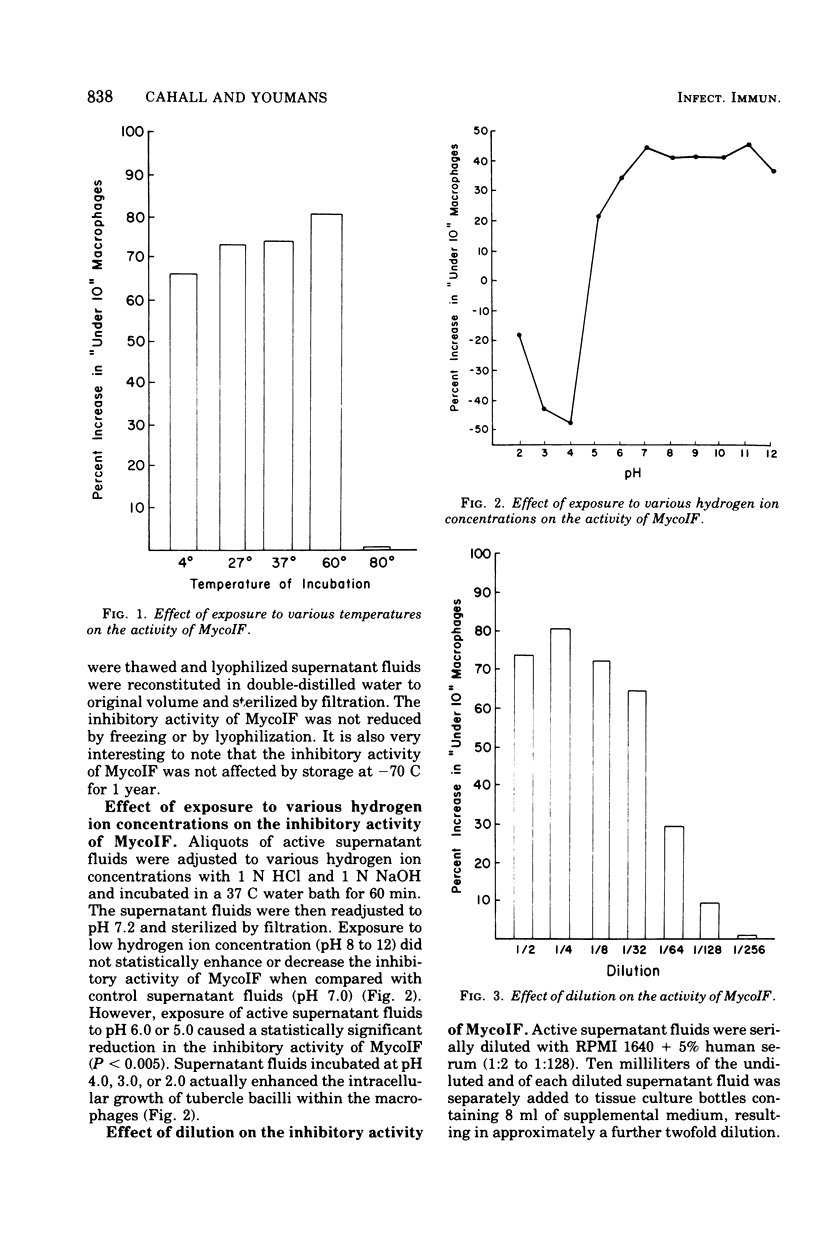
Mycobacterial growth inhibitory factor (MycoIF), found in supernatant fluids of mouse spleen cell cultures that have been stimulated in vitro with homologous antigen, inhibited the intracellular multiplication of virulent tubercle bacilli within normal mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro. Antigenically stimulated H37Ra-immunized mouse spleen cells required 72 h of incubation to produce supernatant fluids that would cause intracellular inhibition. Supernatant fluids from 48-h mouse spleen cell cultures were not able to produce intracellular inhibition. Investigation of the culture conditions showed that at lease 1.0% human serum was required in the tissue culture medium for the production of MycoIF by spleen cells from immunized mice. MycoIF activity was noted only in supernatant fluids from spleen cell cultures incubated with antigen for 72 h. MycoIF was nondialyzable and unaffected by freezing, lyophilization, or incubation at 60 C for 30 min. However, MycoIF was inactivated after incubation at 80 C for 30 min. MycoIF was unaffected by low hydrogen ion concentrations (pH 7 to 12), but exposure to higher hydrogen ion concentrations (pH 6, pH 5) significantly decrease MycoIF activity, and exposure to pH 4 to 2 abolished all activity. Supernatant fluids diluted 1:32 were still able to produce significant intracellular inhibition of growth of virulent tubercle bacilli.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler W. H., Takiguchi T., Marsh B., Smith R. T. Cellular recognition by mouse lymphocytes in vitro. I. Definition of a new technique and results of stimulation by phytohemagglutinin and specific antigens. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1049–1078. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG Y. T. LONG-TERM CULTIVATION OF MOUSE PERITONEAL MACROPHAGES. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 Jan;32:19–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazit E., Harris T. N. Mixed leukocyte culture with mouse spleen cells in a serum-free medium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jul;140(3):750–754. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H. S. The fate of Mycobacterium tuberculosis within macrophages of guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 May;103(5):607–611. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.5.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klun C. L., Youmans G. P. The effect of lymphocyte supernatant fluids on the intracellular growth of virulent tubercle bacilli. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1973 Mar;13(3):263–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan I. Mecahnism of tuberculostasis in mammalian serum. I. Role of transferrin in human serum tuberculostasis. J Infect Dis. 1969 Jan;119(1):11–18. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan I., Pellis N. R., Golden C. A. Mechanism of Tuberculostasis in Mammalian Serum III. Neutralization of Serum Tuberculostasis by Mycobactin. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):553–558. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.553-558.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K. Long-term survival of mouse thymic lymphoid cells in vitro: effect of human serum. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1459–1469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R. J., Youmans G. P. Demonstration in tissue culture of lymphocyte-mediated immunity to tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):600–603. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.600-603.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R. J., Youmans G. P. Multiplication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Within Normal and "Immune" Mouse Macrophages Cultivated With and Without Streptomycin. Infect Immun. 1970 Jan;1(1):30–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.1.30-40.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder M. S., Edberg J. C. Interaction of virulent and avirulent Listeria monocytogenes with cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):409–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.409-415.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


