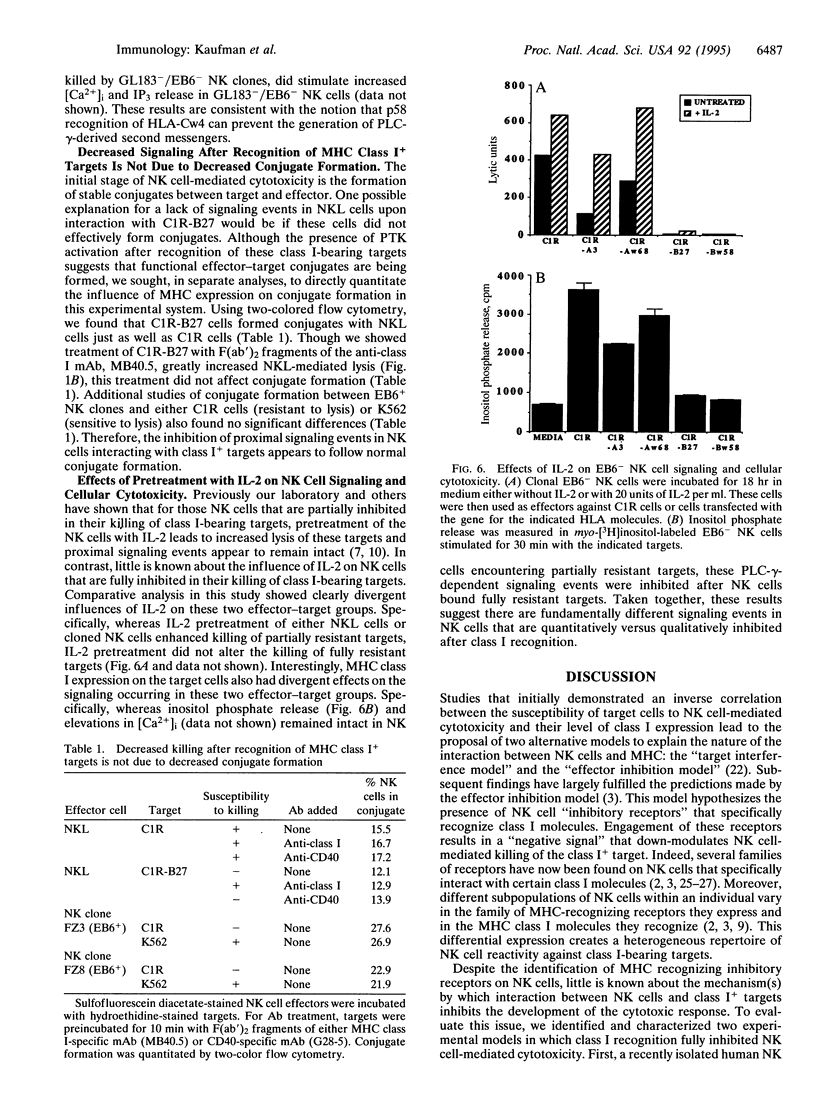
Abstract
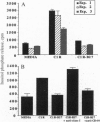
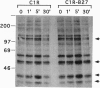
Many studies have characterized the transmembrane signaling events initiated after T-cell antigen receptor recognition of major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-bound peptides. Yet, little is known about signal transduction from a set of MHC class I recognizing receptors on natural killer (NK) cells whose ligation dramatically inhibits NK cell-mediated killing. In this study we evaluated the influence of MHC recognition on the proximal signaling events in NK cells binding tumor targets. We utilized two experimental models where NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity was fully inhibited by the recognition of specific MHC class I molecules. NK cell binding to either class I-deficient or class I-transfected target cells initiated rapid protein tyrosine kinase activation. In contrast, whereas NK cell binding to class I-deficient targets led to inositol phosphate release and increased intracellular free calcium ([Ca2+]i), NK recognition of class I-bearing targets did not induce the activation of these phospholipase C-dependent signaling events. The recognition of class I by NK cells clearly had a negative regulatory effect since blocking this interaction using anti-class I F(ab')2 fragments increased inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate release and [Ca2+]i and increased the lysis of the targets. These results suggest that one of the mechanisms by which NK cell recognition of specific MHC class I molecules can block the development of cell-mediated cytotoxicity is by inhibiting specific critical signaling events.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bix M., Liao N. S., Zijlstra M., Loring J., Jaenisch R., Raulet D. Rejection of class I MHC-deficient haemopoietic cells by irradiated MHC-matched mice. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):329–331. doi: 10.1038/349329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottino C., Vitale M., Olcese L., Sivori S., Morelli L., Augugliaro R., Ciccone E., Moretta L., Moretta A. The human natural killer cell receptor for major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Surface modulation of p58 molecules and their linkage to CD3 zeta chain, Fc epsilon RI gamma chain and the p56lck kinase. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Oct;24(10):2527–2534. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccone E., Pende D., Viale O., Than A., Di Donato C., Orengo A. M., Biassoni R., Verdiani S., Amoroso A., Moretta A. Involvement of HLA class I alleles in natural killer (NK) cell-specific functions: expression of HLA-Cw3 confers selective protection from lysis by alloreactive NK clones displaying a defined specificity (specificity 2). J Exp Med. 1992 Oct 1;176(4):963–971. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.4.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccone E., Pende D., Vitale M., Nanni L., Di Donato C., Bottino C., Morelli L., Viale O., Amoroso A., Moretta A. Self class I molecules protect normal cells from lysis mediated by autologous natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Apr;24(4):1003–1006. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone J. C., Lu Y., Trevillyan J. M., Bjorndahl J. M., Phillips C. A. Association of the p56lck protein tyrosine kinase with the Fc gamma RIIIA/CD16 complex in human natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Oct;23(10):2488–2497. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einspahr K. J., Abraham R. T., Binstadt B. A., Uehara Y., Leibson P. J. Tyrosine phosphorylation provides an early and requisite signal for the activation of natural killer cell cytotoxic function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6279–6283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlhofer F. M., Ribaudo R. K., Yokoyama W. M. MHC class I alloantigen specificity of Ly-49+ IL-2-activated natural killer cells. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):66–70. doi: 10.1038/358066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. S., Schoon R. A., Leibson P. J. MHC class I expression on tumor targets inhibits natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity without interfering with target recognition. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1429–1436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kärre K., Ljunggren H. G., Piontek G., Kiessling R. Selective rejection of H-2-deficient lymphoma variants suggests alternative immune defence strategy. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):675–678. doi: 10.1038/319675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin V., Gumperz J., Parham P., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. NKB1: a natural killer cell receptor involved in the recognition of polymorphic HLA-B molecules. J Exp Med. 1994 Aug 1;180(2):537–543. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.2.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin V., Gumperz J., Parham P., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Specificity of HLA class I antigen recognition by human NK clones: evidence for clonal heterogeneity, protection by self and non-self alleles, and influence of the target cell type. J Exp Med. 1993 Oct 1;178(4):1321–1336. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.4.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren H. G., Kärre K. In search of the 'missing self': MHC molecules and NK cell recognition. Immunol Today. 1990 Jul;11(7):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90097-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren H. G., Van Kaer L., Ploegh H. L., Tonegawa S. Altered natural killer cell repertoire in Tap-1 mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6520–6524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Bottino C., Pende D., Tripodi G., Tambussi G., Viale O., Orengo A., Barbaresi M., Merli A., Ciccone E. Identification of four subsets of human CD3-CD16+ natural killer (NK) cells by the expression of clonally distributed functional surface molecules: correlation between subset assignment of NK clones and ability to mediate specific alloantigen recognition. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1589–1598. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Vitale M., Bottino C., Orengo A. M., Morelli L., Augugliaro R., Barbaresi M., Ciccone E., Moretta L. P58 molecules as putative receptors for major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules in human natural killer (NK) cells. Anti-p58 antibodies reconstitute lysis of MHC class I-protected cells in NK clones displaying different specificities. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):597–604. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Vitale M., Sivori S., Bottino C., Morelli L., Augugliaro R., Barbaresi M., Pende D., Ciccone E., Lopez-Botet M. Human natural killer cell receptors for HLA-class I molecules. Evidence that the Kp43 (CD94) molecule functions as receptor for HLA-B alleles. J Exp Med. 1994 Aug 1;180(2):545–555. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Ciccone E., Mingari M. C., Biassoni R., Moretta A. Human natural killer cells: origin, clonality, specificity, and receptors. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:341–380. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60513-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea J. J., McVicar D. W., Kuhns D. B., Ortaldo J. R. A role for protein tyrosine kinase activity in natural cytotoxicity as well as antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Effects of herbimycin A. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 15;148(8):2497–2502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea J. J., Weissman A. M., Kennedy I. C., Ortaldo J. R. Engagement of the natural killer cell IgG Fc receptor results in tyrosine phosphorylation of the zeta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):350–354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignata C., Prasad K. V., Robertson M. J., Levine H., Rudd C. E., Ritz J. Fc gamma RIIIA-mediated signaling involves src-family lck in human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):6794–6800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salcedo T. W., Kurosaki T., Kanakaraj P., Ravetch J. V., Perussia B. Physical and functional association of p56lck with Fc gamma RIIIA (CD16) in natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1475–1480. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storkus W. J., Alexander J., Payne J. A., Dawson J. R., Cresswell P. Reversal of natural killing susceptibility in target cells expressing transfected class I HLA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2361–2364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting A. T., Karnitz L. M., Schoon R. A., Abraham R. T., Leibson P. J. Fc gamma receptor activation induces the tyrosine phosphorylation of both phospholipase C (PLC)-gamma 1 and PLC-gamma 2 in natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1751–1755. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:187–376. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60664-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Recognition of major histocompatibility complex class I antigens by natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1994 Aug 1;180(2):417–421. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivier E., Morin P., O'Brien C., Druker B., Schlossman S. F., Anderson P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the Fc gamma RIII(CD16): zeta complex in human natural killer cells. Induction by antibody-dependent cytotoxicity but not by natural killing. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):206–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivier E., Sorrell J. M., Ackerly M., Robertson M. J., Rasmussen R. A., Levine H., Anderson P. Developmental regulation of a mucinlike glycoprotein selectively expressed on natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1993 Dec 1;178(6):2023–2033. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.6.2023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivier E., da Silva A. J., Ackerly M., Levine H., Rudd C. E., Anderson P. Association of a 70-kDa tyrosine phosphoprotein with the CD16: zeta: gamma complex expressed in human natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Aug;23(8):1872–1876. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windebank K. P., Abraham R. T., Powis G., Olsen R. A., Barna T. J., Leibson P. J. Signal transduction during human natural killer cell activation: inositol phosphate generation and regulation by cyclic AMP. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3951–3957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama W. M. Natural killer cell receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995 Feb;7(1):110–120. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(95)80036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemmour J., Little A. M., Schendel D. J., Parham P. The HLA-A,B "negative" mutant cell line C1R expresses a novel HLA-B35 allele, which also has a point mutation in the translation initiation codon. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1941–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]