Abstract
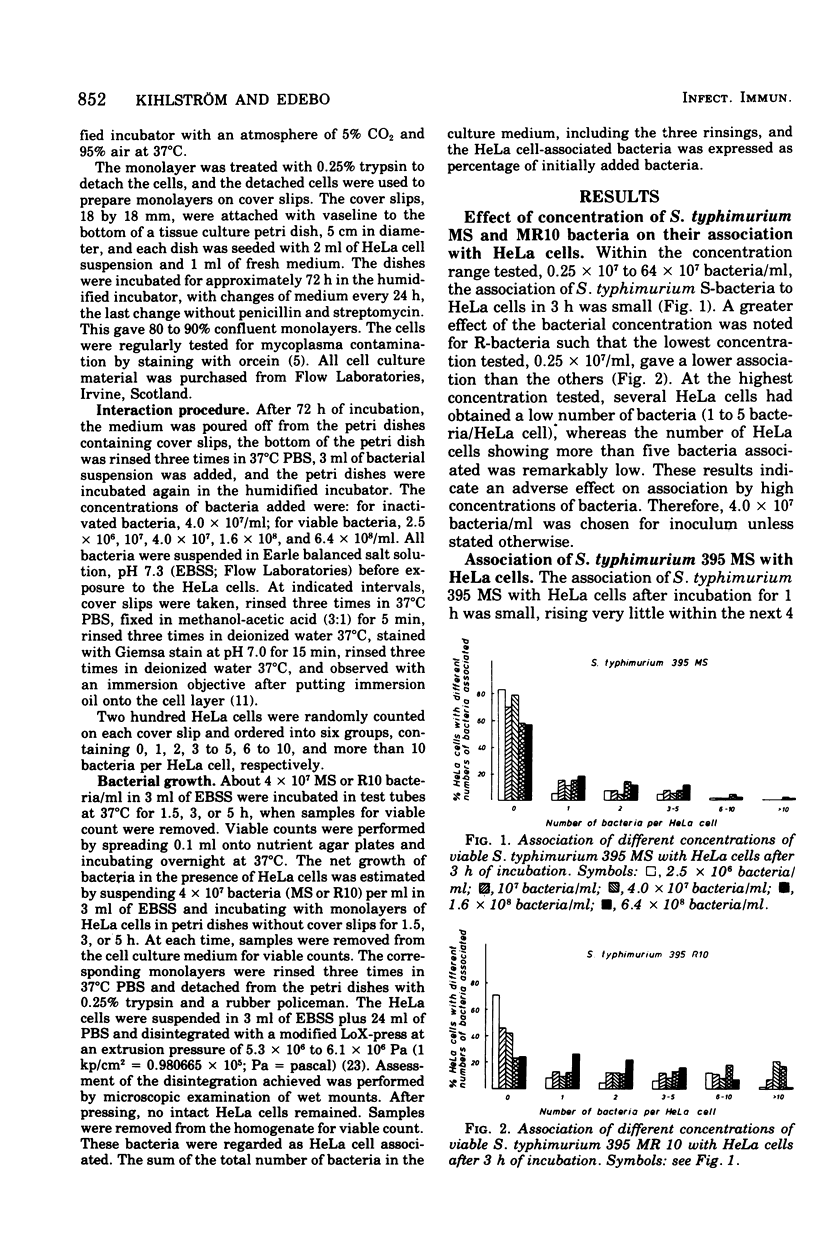
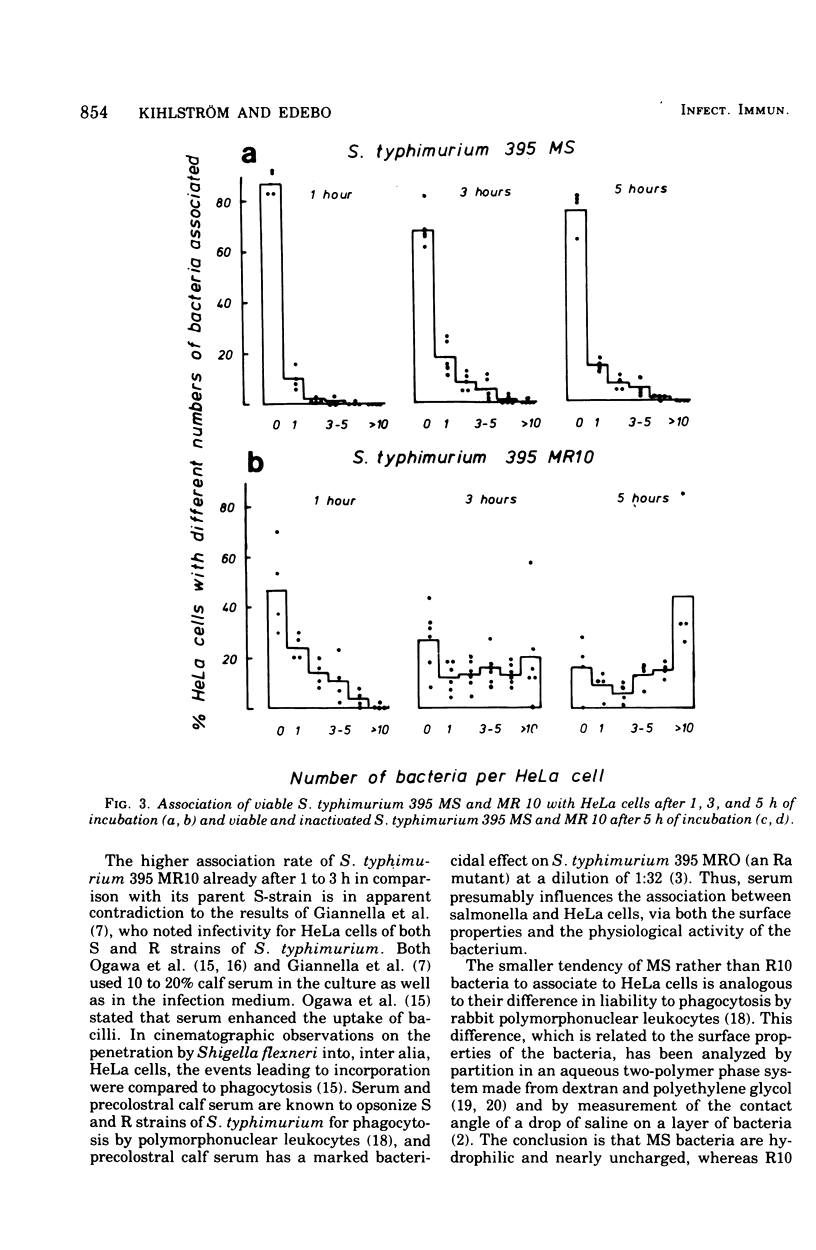
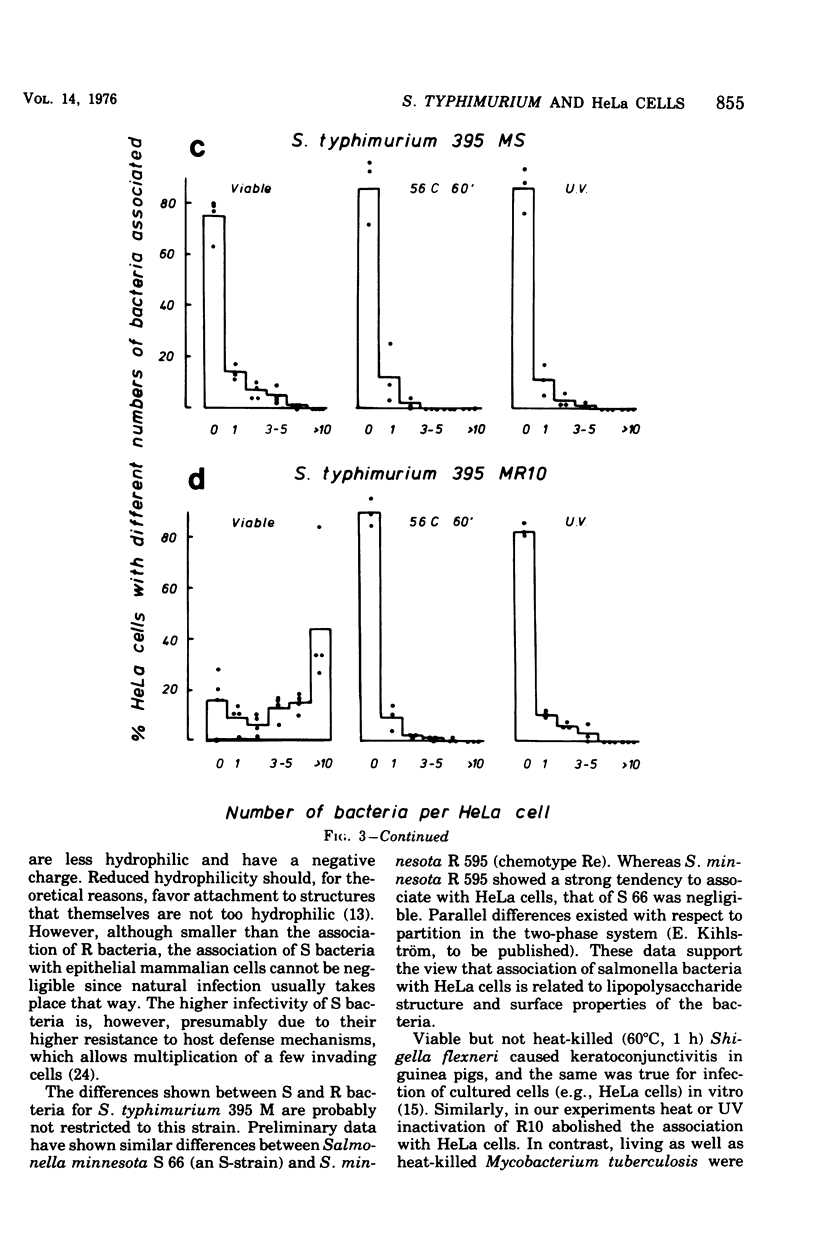
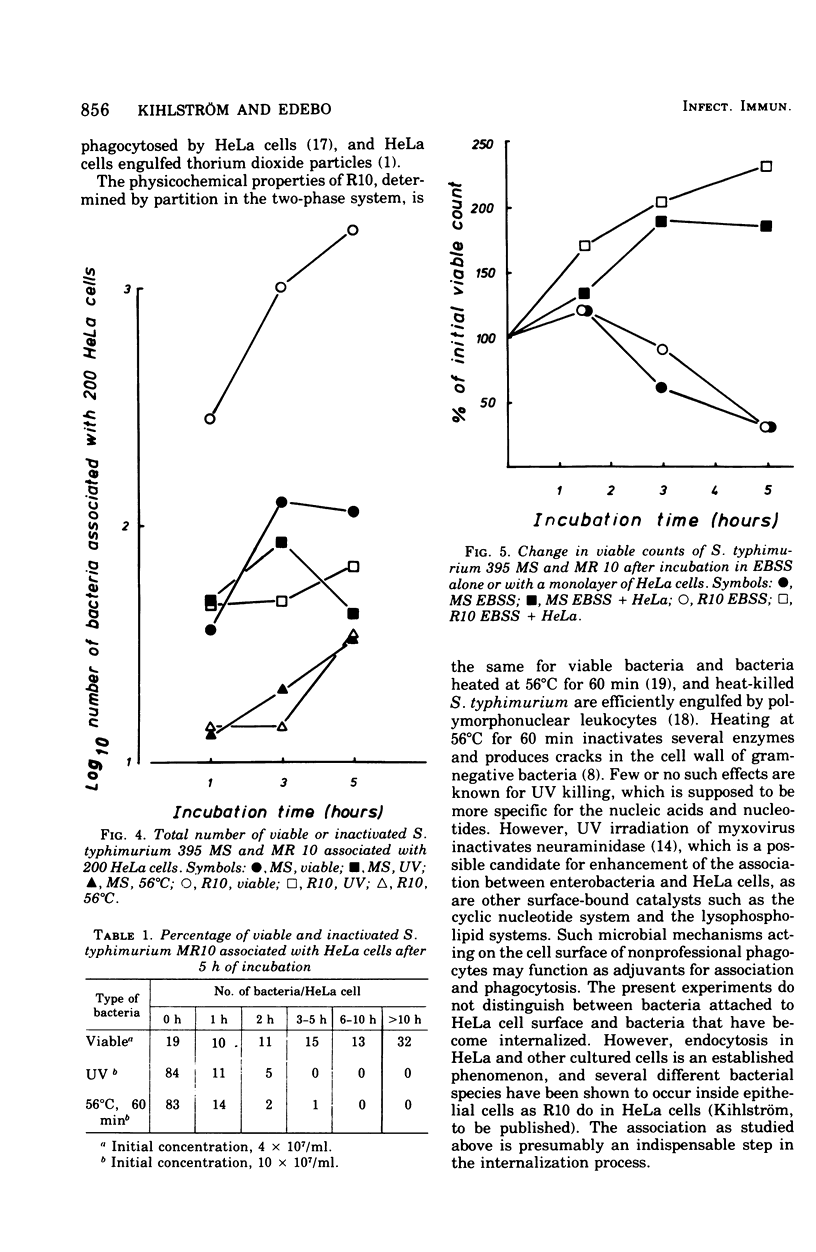
The mouse-virulent Salmonella typhimurium 395 MS, containing a complete lipopolysaccharide (LPS) structure with S-specific repeating units, and the nonvirulent, LPS-defective mutant 395 MR 10 (chemotype Rd), derived from it, were studied for their tendency to interact with HeLa cells. In the definition of interaction no distinction has been made between intracellular and cell membrane-attached bacteria. R10 bacteria were found to have a greater tendency to interact than MS bacteria. This difference was seen as early as 1 h after the start of incubation, but it became more pronounced beyond 3 h. Heat-killed and ultraviolet-killed R10 bacteria interacted with HeLa cells less than living ones. Killed MS bacteria interacted to an extent similar to that of living ones. These results are discussed in relation to the susceptibility of the bacteria to phagocytosis by professional phagocytic cells and to the physiochemical properties of the bacteria as measured by their distribution in a two-polymer, aqueous-phase system.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arstila A. U., Jauregui H. O., Chang J., Trump B. F. Studies on cellular autophagocytosis. Relationship between heterophagy and autophagy in HeLa cells. Lab Invest. 1971 Feb;24(2):162–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. K., Söderström T. O., Gillman C. F., van Oss C. J. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. V. Contact angles and phagocytosis of rough and smooth strains of Salmonella typhimurium, and the influence of specific antiserum. Immunol Commun. 1975;4(5):429–442. doi: 10.3109/08820137509057331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edebo L., Normann B. Killing or protection of Salmonella typhimurium mutants by mammalian sera. Prog Immunobiol Stand. 1970;4:575–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edebo L., Normann B. Virulence and immunogenicity of mutant strains of Salmonella typhimurium. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1970;78(1):75–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1970.tb04271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOGH J., FOGH H. A METHOD FOR DIRECT DEMONSTRATION OF PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS IN CULTURED CELLS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Dec;117:899–901. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg D., Shilo M. Role of cell wall structure of salmonella in the interaction with phagocytes. Infect Immun. 1970 Sep;2(3):279–285. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.3.279-285.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Washington O., Gemski P., Formal S. B. Invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: a model for study of invasiveness of Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedén C. G., Wyckoff R. W. THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF HEATED BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1949 Aug;58(2):153–160. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. L. The metabolism of leukocytes. Semin Hematol. 1968 Apr;5(2):156–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nekliudova L. I., Orlova N. G., Makarova G. I. Vliianie fiziko-khimicheskikh faktorov na neiraminidazu virusa grippa. Vopr Virusol. 1973 May-Jun;18(3):338–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa H., Nakamura A., Sakazaki R. Pathogenic properties of "enteropathogenic" Escherichia coli from diarrheal children and adults. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1968 Oct;21(5):333–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPARD C. C. Phagocytosis by HeLa cells and their susceptibility to infection by human tubercle bacilli. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Nov;90(2):392–396. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-22043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Edebo L. Phagocytosis of mutants of Salmonella typhimurium by rabbit polymorphonuclear cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(4):481–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Magnusson K. E., Tagesson C., Cunningham R., Edebo L. Characterization of mutants of Salmonella typhimurium by counter-current distribution in an aqueous two-polymer phase system. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):573–577. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.573-577.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Tagesson C., Edebo L. Influence of hyperimmune immunoglobulin G on the physicochemical properties of the surface of Salmonella typhimurium 395 MS in relation to interaction with phagocytic cells. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):316–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.316-319.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Tagesson C., Edebo M. Partition of Salmonella typhimurium in a two-polymer acqueous phase system in relation to liability to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.36-41.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagesson C., Stendahl O. Influence of the cell surface lipopolysaccharide structure of Salmonella typhimurium on resistance to intracellular bactericidal systems. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Aug;81(4):473–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagesson C., Stendahl O., Magnusson K. E., Edebo L. Disintegration of single cells in suspension. Isolation of rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocyte granules. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Aug;81(4):464–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W., Blumershine R. V., Savage D. C. Association of Salmonella typhimurium with, and its invasion of, the ileal mucosa in mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):365–370. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.365-370.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


