Abstract
An electron microscopic study was conducted to explore the interaction between normal guinea pig peritoneal macrophages and phase I and II Coxeilla burnetii previously treated with either normal or immune serum. A comparison was made on the efficiency of phagocytosis and subsequent killing of rickettsiae by macrophages. Both phases of rickettsiae previously treated with normal serum multiplied within phagosomes after phagocytosis with resultant destruction of macrophages. In contrast, suspending rickettsiae in immune serum rendered them more susceptible to phagocytosis and potentiated their destruction within macrophages.
Full text
PDF


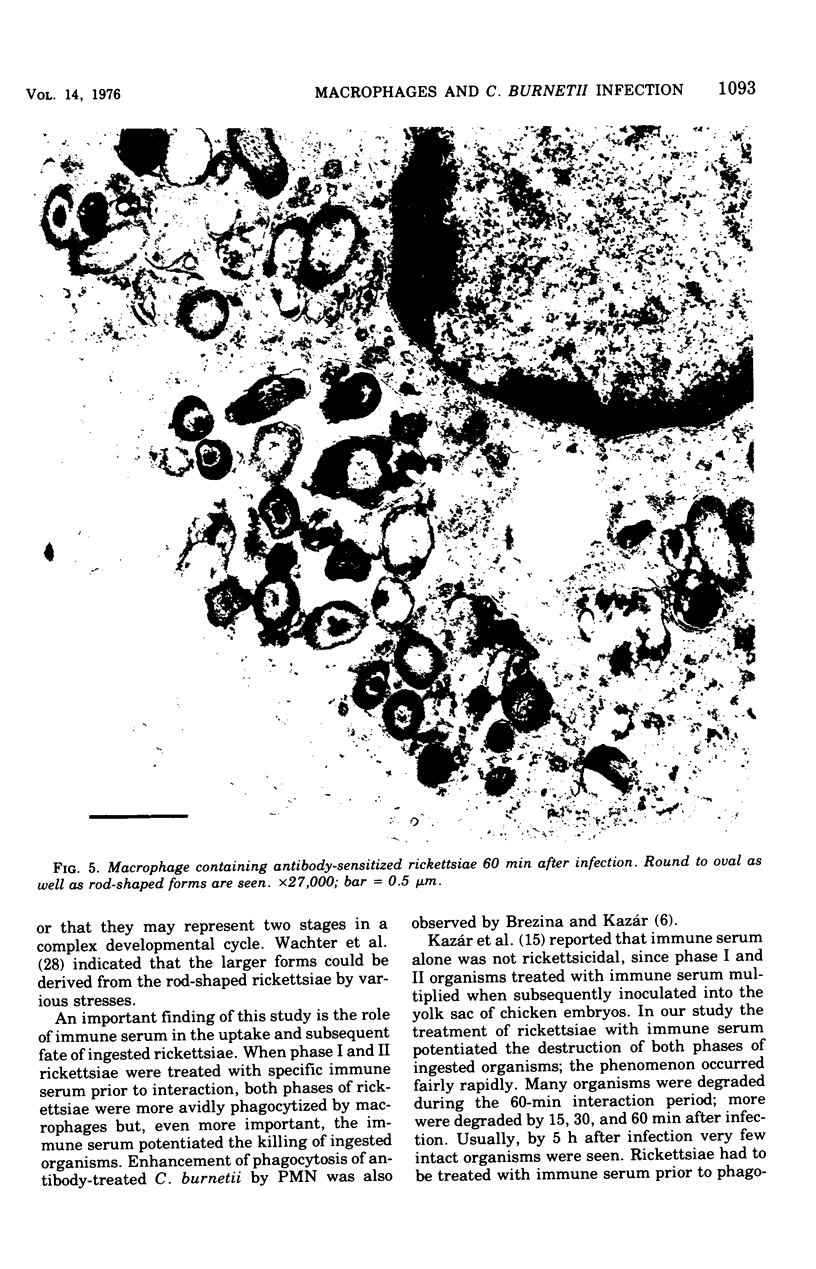


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABINANTI F. R., MARMION B. P. Protective or neutralizing antibody in Q fever. Am J Hyg. 1957 Sep;66(2):173–195. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANACKER R. L., FUKUSHI K., PICKENS E. G., LACKMAN D. B. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF COXIELLA BURNETII IN THE CHICK YOLK SAC. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1130–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1130-1138.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. E., Jr, Remington J. S. Effect of normal and activated human macrophages on Toxoplasma gondii. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1154–1174. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREZINA R., KAZAR J. STUDY OF THE ANTIGENIC STRUCTURE OF COXIELLA BURNETI. IV. PHAGOCYTOSIS AND OPSONIZATION IN RELATION TO THE PHASES OF C. BURNETI. Acta Virol. 1965 May;9:268–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C., Tappel A. L. Rat-liver lysosomal beta-glucosidase: a membrane enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 8;151(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P. R., Kordová N., Paretsky D. Electron microscopic studies of the rickettsia Coxiella burneti: entry, lysosomal response, and fate of rickettsial DNA in L-cells. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Feb;17(2):143–150. doi: 10.1139/m71-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. G., Bird J. W. Lysosomes in skeletal muscle tissue. Zonal centrifugation evidence for multiple cellular sources. J Cell Biol. 1970 May;45(2):321–333. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. G., Van Zwieten M. J., Christmas W. A. Purification of large quantities of coxiella burnetii rickettsia by density gradient zonal centrifugation. Appl Microbiol. 1972 May;23(5):1015–1022. doi: 10.1128/am.23.5.1015-1022.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVID J. R., AL-ASKARI S., LAWRENCE H. S., THOMAS L. DELAYED HYPERSENSITIVITY IN VITRO. I. THE SPECIFICITY OF INHIBITION OF CELL MIGRATION BY ANTIGENS. J Immunol. 1964 Aug;93:264–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downs C. M. Phagocytosis of coxiella burneti, phase I and phase II by peritoneal monocytes from normal and immune guinea pigs and mice. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1968 Apr;206(3):329–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambrill M. R., Wisseman C. L., Jr Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infections. 3. Influence of human immune serum and complement on the fate of Rickettsia mooseri within the human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):631–640. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.631-640.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley J., Paretsky D., Stueckemann J. Electron microscopic observations of Coxiella burnetii in the guinea pig. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):263–267. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.263-267.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazár J., Brezina R., Kovácová E., Urvölgyi J. Testing in various systems of the neutralizing capacity of Q fever immune sera. Acta Virol. 1973 Jan;17(1):79–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazár J., Skultétyová E., Brezina R. Phagocytosis of Coxiella burneti by macrophages. Acta Virol. 1975 Sep;19(5):426–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon R. H., McManus A. T. Rickettsial infectious antibody complexes: detection by antiglobulin plaque reduction technique. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):966–968. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.966-968.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon R. H., Pedersen C. E., Jr Preparation of Rocky Mountain spotted fever vaccine suitable for human immunization. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jun;1(6):500–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.6.500-503.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto R. A., Walker J. S. Interaction between Coxiella burnetii and guinea pig peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):416–421. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.416-421.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordová N., Burton P. R., Downs C. M., Paretsky D., Kovácová E. The interaction of Coxiella burnetti phase I and phase II in Earle's cells. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Feb;16(2):125–133. doi: 10.1139/m70-021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton F., Poole B., Beaufay H., Baudhuin P., Coffey J. W., Fowler S., De Duve C. The large-scale separation of peroxisomes, mitochondria, and lysosomes from the livers of rats injected with triton WR-1339. Improved isolation procedures, automated analysis, biochemical and morphological properties of fractions. J Cell Biol. 1968 May;37(2):482–513. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.2.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osserman E. F., Lawlor D. P. Serum and urinary lysozyme (muramidase) in monocytic and monomyelocytic leukemia. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):921–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG M., KORDOVA N. Multiplication of Coxiella burneti in Detroit-6 cell cultures. An electron microscope study. Acta Virol. 1962 Mar;6:176–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG M., KORDOVA N. Study of intracellular forms of Coxiella burneti in the electron microscope. Acta Virol. 1960 Jan;4:52–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOKER M. G., FISET P. Phase variation of the Nine Mile and other strains of Rickettsia burneti. Can J Microbiol. 1956 May;2(3):310–321. doi: 10.1139/m56-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberman R., Fiset P. Method for counting Rickettsiae and Chlamydiae in purified suspensions. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):259–261. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.259-261.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachter R. F., Briggs G. P., Gangemi J. D., Pedersen C. E., Jr Changes in buoyant density relationships of two cell types of Coxiella burneti phase I. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):433–436. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.433-436.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebe M. E., Burton P. R., Shankel D. M. Isolation and characterization of two cell types of Coxiella burneti phase I. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):368–377. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.368-377.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Fiset P., Ormsbee R. A. Interaction of rickettsiae and phagocytic host cells. V. Phagocytic and opsonic interactions of phase 1 and phase 2 Coxiella burneti with normal and immune human leukocytes and antibodies. J Immunol. 1967 Oct;99(4):669–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. D., Walsh W. T. Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infections. IV. Failure of chicken embryo cells in culture to restrict growth of antibody-sensitized Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):571–575. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.571-575.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]