Abstract
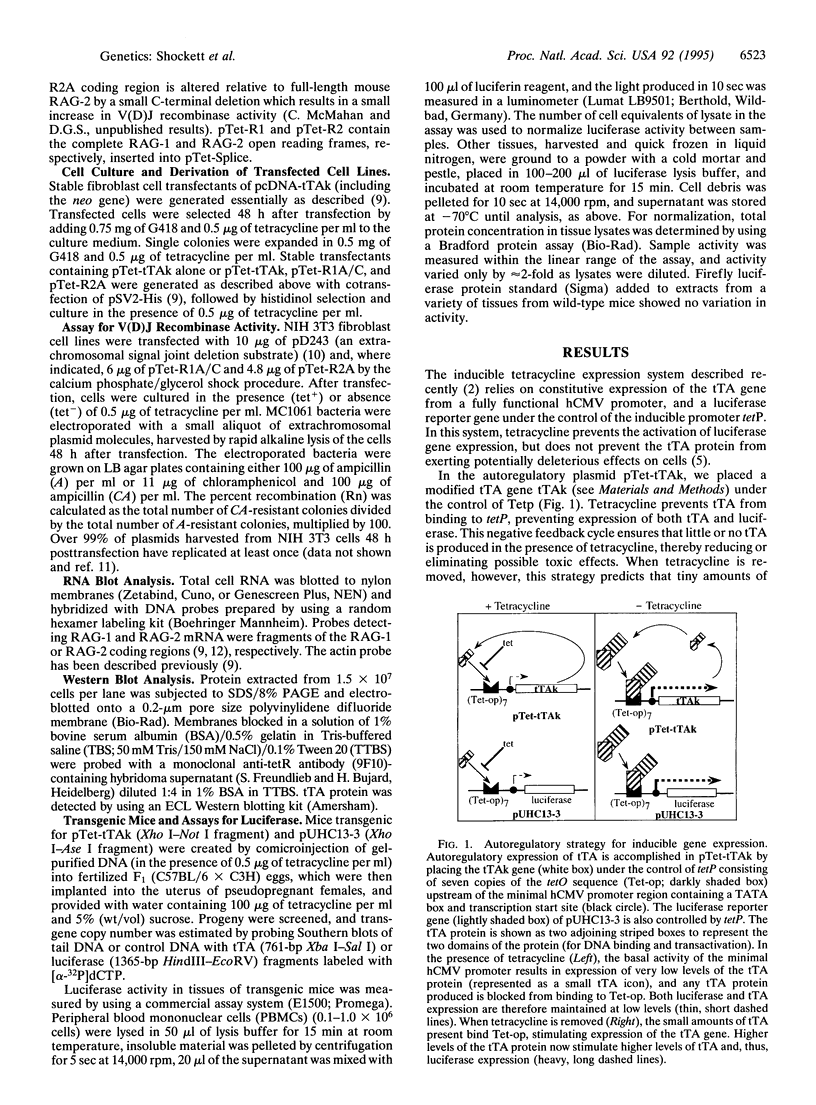
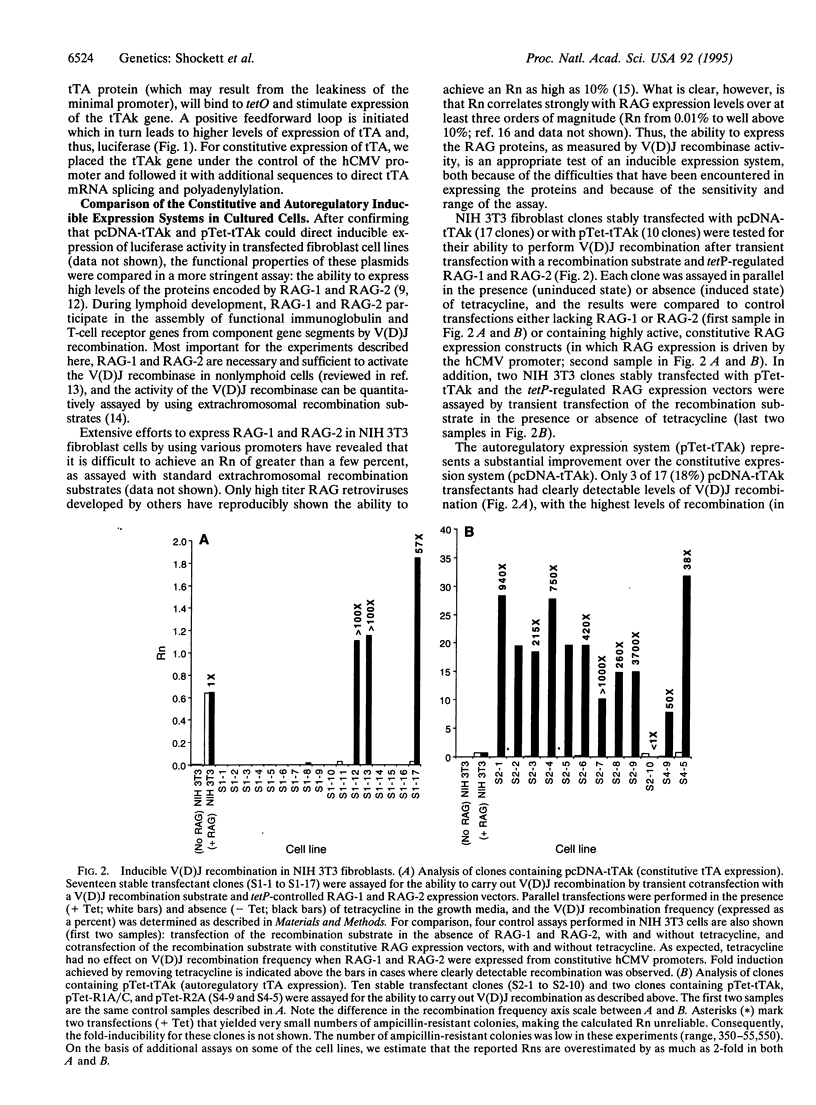
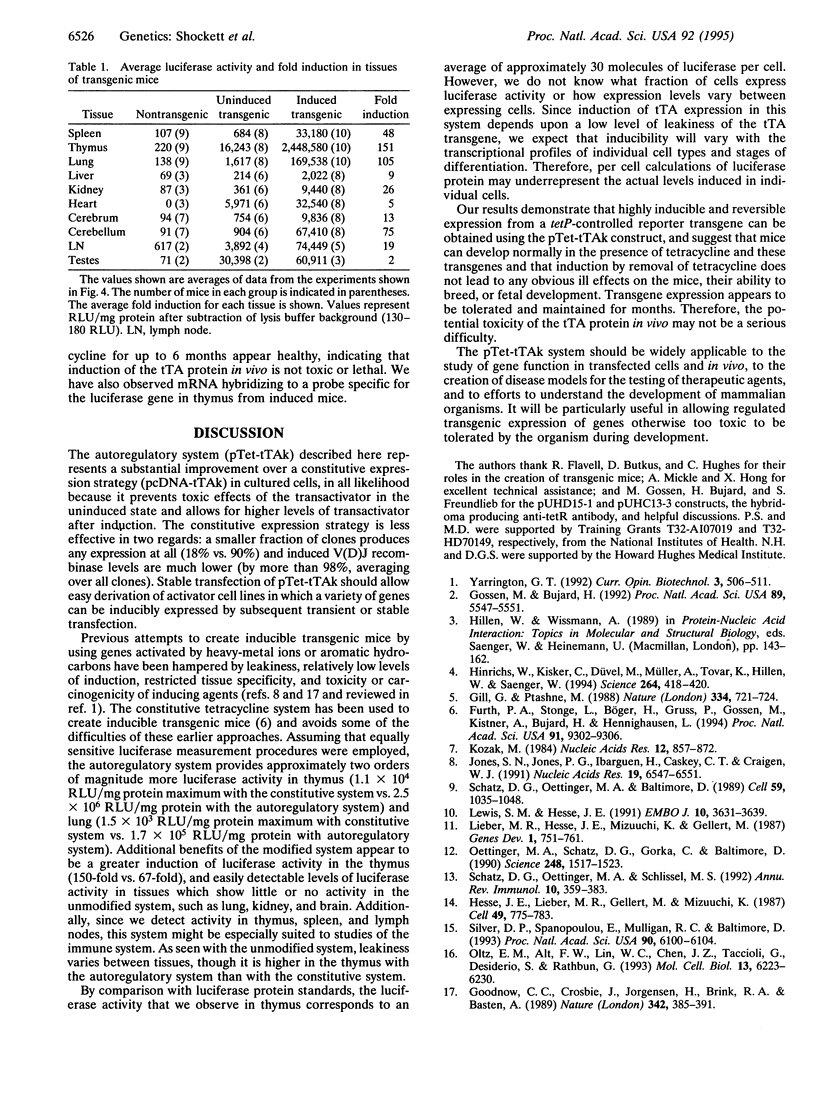
A system for tetracycline-regulated inducible gene expression was described recently which relies on constitutive expression of a tetracycline-controlled transactivator (tTA) fusion protein combining the tetracycline repressor and the transcriptional activation domain of VP16 [Gossen, M. & Bujard, H. (1992) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5547-5551]. This system yielded only low levels of transactivator protein, probably because tTA is toxic. To avoid this difficulty, we placed the tTA gene under the control of the inducible promoter to which tTA binds, making expression of tTA itself inducible and autoregulatory. When used to drive expression of the recombination activating genes 1 and 2 (RAG-1 and RAG-2), the autoregulatory system yielded both substantially higher levels of variable (diversity) joining [V(D)J] recombination activity (70-fold on average) and inducible expression in a much larger fraction of transfected cells (autoregulatory, 90%, vs. constitutive, 18%). In addition, this system allowed the creation of transgenic mice in which expression of a luciferase transgene was inducible tens to hundreds of times the basal levels in most tissues examined. Induced levels of expression were highest in thymus and lung and appear to be substantially higher than in previously reported inducible luciferase transgenic mice created with the constitutive system. With the modified system, inducible transactivator mRNA and protein were easily detected in cell lines by RNA and Western blotting, and transactivator mRNA was detected by RNA blotting in some tissues of transgenic mice. This autoregulatory system represents an improved strategy for tetracycline-regulated gene expression both in cultured cells and in transgenic animals.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Furth P. A., St Onge L., Böger H., Gruss P., Gossen M., Kistner A., Bujard H., Hennighausen L. Temporal control of gene expression in transgenic mice by a tetracycline-responsive promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 27;91(20):9302–9306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Ptashne M. Negative effect of the transcriptional activator GAL4. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):721–724. doi: 10.1038/334721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow C. C., Crosbie J., Jorgensen H., Brink R. A., Basten A. Induction of self-tolerance in mature peripheral B lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):385–391. doi: 10.1038/342385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossen M., Bujard H. Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Lieber M. R., Gellert M., Mizuuchi K. Extrachromosomal DNA substrates in pre-B cells undergo inversion or deletion at immunoglobulin V-(D)-J joining signals. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90615-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinrichs W., Kisker C., Düvel M., Müller A., Tovar K., Hillen W., Saenger W. Structure of the Tet repressor-tetracycline complex and regulation of antibiotic resistance. Science. 1994 Apr 15;264(5157):418–420. doi: 10.1126/science.8153629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. N., Jones P. G., Ibarguen H., Caskey C. T., Craigen W. J. Induction of the Cyp1a-1 dioxin-responsive enhancer in transgenic mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6547–6551. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. M., Hesse J. E. Cutting and closing without recombination in V(D)J joining. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3631–3639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M. R., Hesse J. E., Mizuuchi K., Gellert M. Developmental stage specificity of the lymphoid V(D)J recombination activity. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):751–761. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettinger M. A., Schatz D. G., Gorka C., Baltimore D. RAG-1 and RAG-2, adjacent genes that synergistically activate V(D)J recombination. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1517–1523. doi: 10.1126/science.2360047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oltz E. M., Alt F. W., Lin W. C., Chen J., Taccioli G., Desiderio S., Rathbun G. A V(D)J recombinase-inducible B-cell line: role of transcriptional enhancer elements in directing V(D)J recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6223–6230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz D. G., Oettinger M. A., Baltimore D. The V(D)J recombination activating gene, RAG-1. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1035–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90760-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz D. G., Oettinger M. A., Schlissel M. S. V(D)J recombination: molecular biology and regulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:359–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver D. P., Spanopoulou E., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Dispensable sequence motifs in the RAG-1 and RAG-2 genes for plasmid V(D)J recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6100–6104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]