Abstract
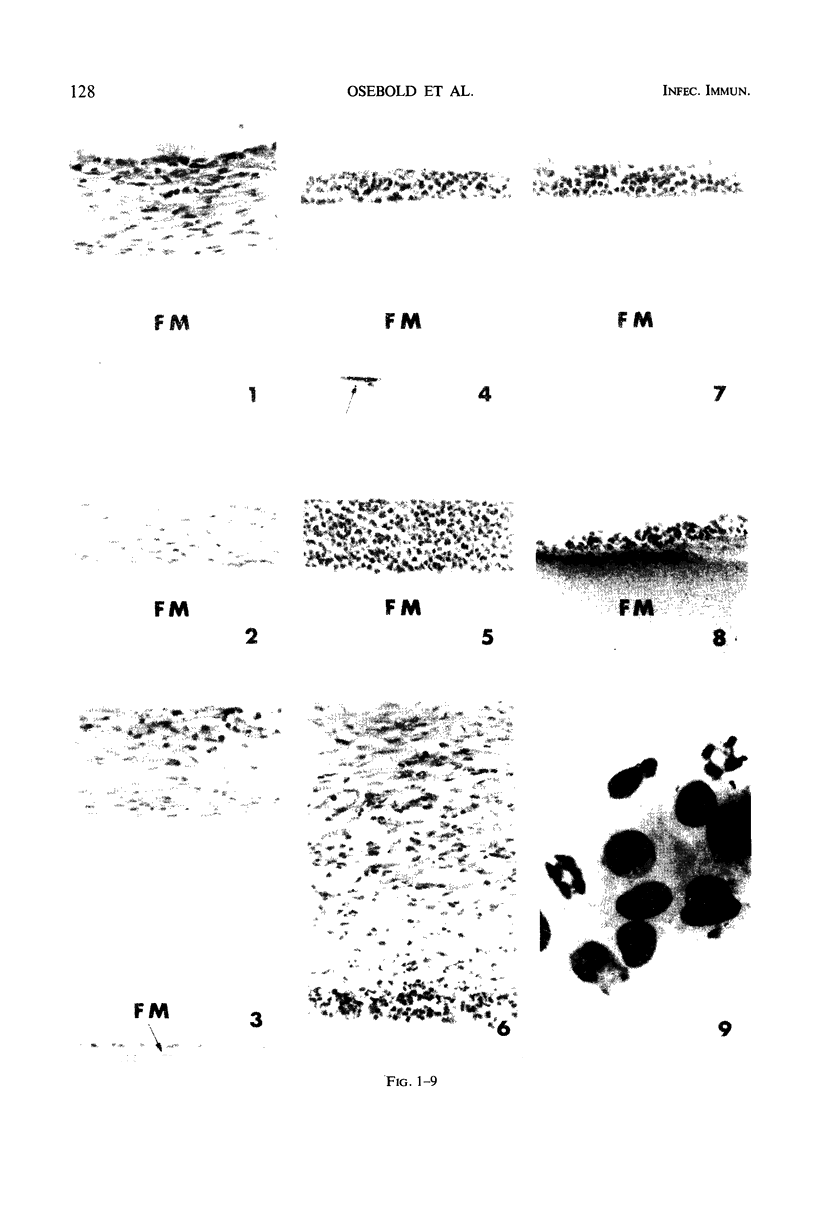
Diffusion chambers made with membranes having a pore size of 0.22 μm were implanted in the peritoneal cavities of mice. Chambers that contained no cells induced splenic lymphoreticular hyperplasia and a proliferation of fibroblasts around the chambers. When the chambers contained the bacterium, Listeria monocytogenes, there was strong and continuous chemotaxis of phagocytic cells to the membrane surface. The tendency to incite fibrosis around the chambers containing bacteria produced a tissue reaction resembling a chronic abscess or granuloma. The important difference from a natural lesion was the prevention of direct parasite-host cell interactions. In studies on the pathogenesis of long persisting host-parasite relationships, one might successfully use diffusion chambers to investigate the role of humoral antimicrobial substances as well as the effects of chronic inflammation, with its local concentration of metabolic products and constituents of phagocytic cells. On the other hand, the presence of diffusion chambers in the tissues is an abnormal situation and changes arising from their presence may complicate the interpretations of some experiments.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER F. L., FISHMAN M. Adjuvant effect of diffusion chambers on soluble antigens. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Dec;111:691–695. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN R. C., ROWSELL E. V. The application of the diffusion-chamber technique to the study of silicosis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1958 Oct;76(2):561–568. doi: 10.1002/path.1700760225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNN T. B. Normal and pathologic anatomy of the reticular tissue in laboratory mice, with a classification and discussion of neoplasms. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1954 Jun;14(6):1281–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Despommier D. D., Wostmann B. S. Diffusion chambers for inducing immunity to Trichinella spiralis in mice. Exp Parasitol. 1968 Oct;23(2):228–233. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(68)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eskeland G., Eskeland T. Development of mesothelium on the outer surface of intraperitoneal diffusion chambers. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(4):447–464. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.4.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUSER E. D., BERRY L. J. The pathogenesis of staphylococcus infections. I. The use of diffusion chambers in establishing the role of staphylococcus toxins. J Infect Dis. 1961 Jul-Aug;109:24–30. doi: 10.1093/infdis/109.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller G. J., Lynn R. J. Immune response of rabbits to Streptococci grown in intraperitoneal diffusion chambers. J Infect Dis. 1968 Apr;118(2):160–164. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAJARIAN J. S., FELDMAN J. D. Passive transfer of transplantation immunity. I. Tritiated lymphoid cells. II. Lymphoid cells in millipore chambers. J Exp Med. 1962 May 1;115:1083–1093. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.5.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nettesheim P., Nakinodan T., Chadwick C. J. Improved diffusion chamber cultures for cytokinetic analysis of antibody response. Immunology. 1966 Nov;11(5):427–439. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osebold J. W., DiCapua R. A. Cellular immunity of mice infected with Listeria monocytogenes in diffusion chambers. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2158–2164. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2158-2164.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osebold J. W., Outteridge P. M., Pearson L. D. Mutation of Listeria monocytogenes After Prolonged In Vivo Survival in Diffusion Chambers. Infect Immun. 1970 Feb;1(2):209–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.2.209-211.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHELTON E., RICE M. E. Growth of normal peritoneal cells in diffusion chambers: a study in cell modulation. Am J Anat. 1959 Nov;105:281–341. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001050302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulitzeanu D., Birnbaum M. Secondary response to bovine serum albumin in diffusion chambers. Stimulation with low doses of antigen. Immunology. 1969 Aug;17(2):181–187. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vann D. C., Makinodan T. In vitro antibody synthesis by diffusion chamber cultures of spleen cells. I. Methods and effect of 10,000 r on antibody synthesis. J Immunol. 1969 Feb;102(2):442–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]