Abstract
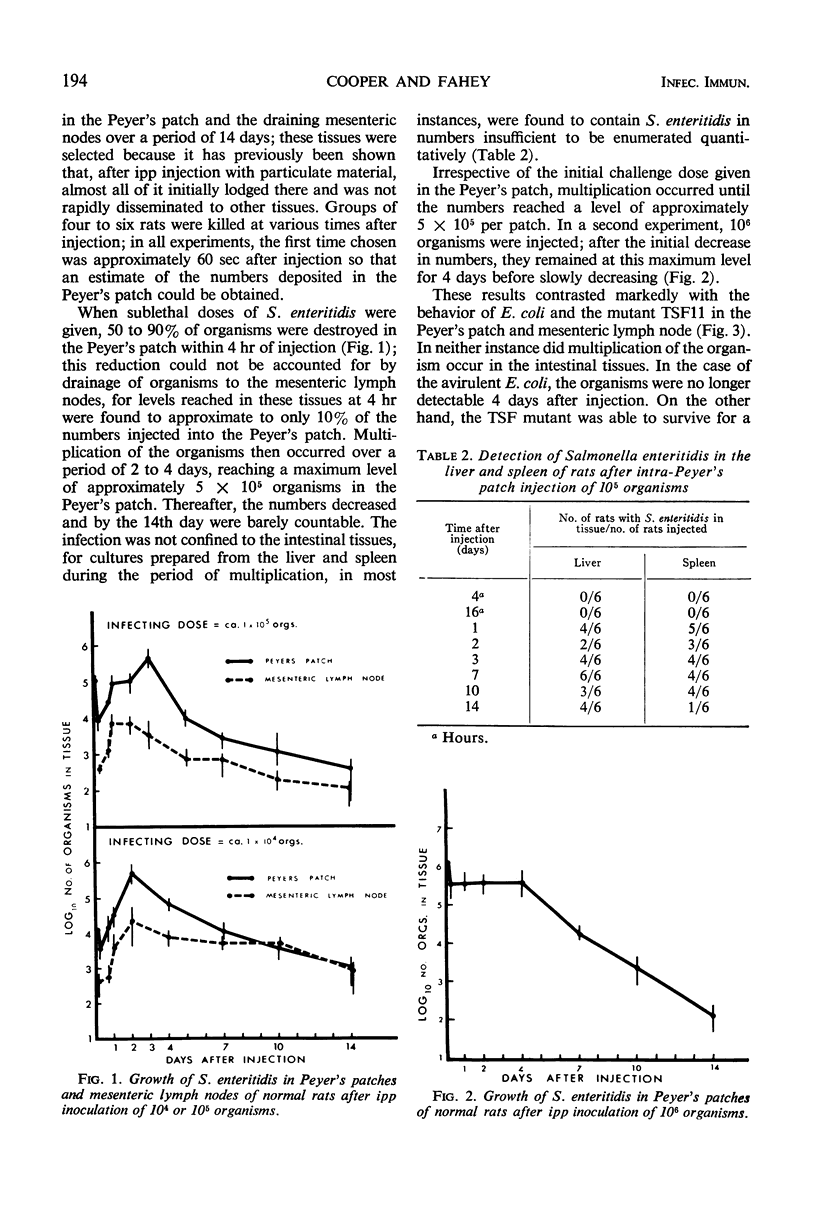
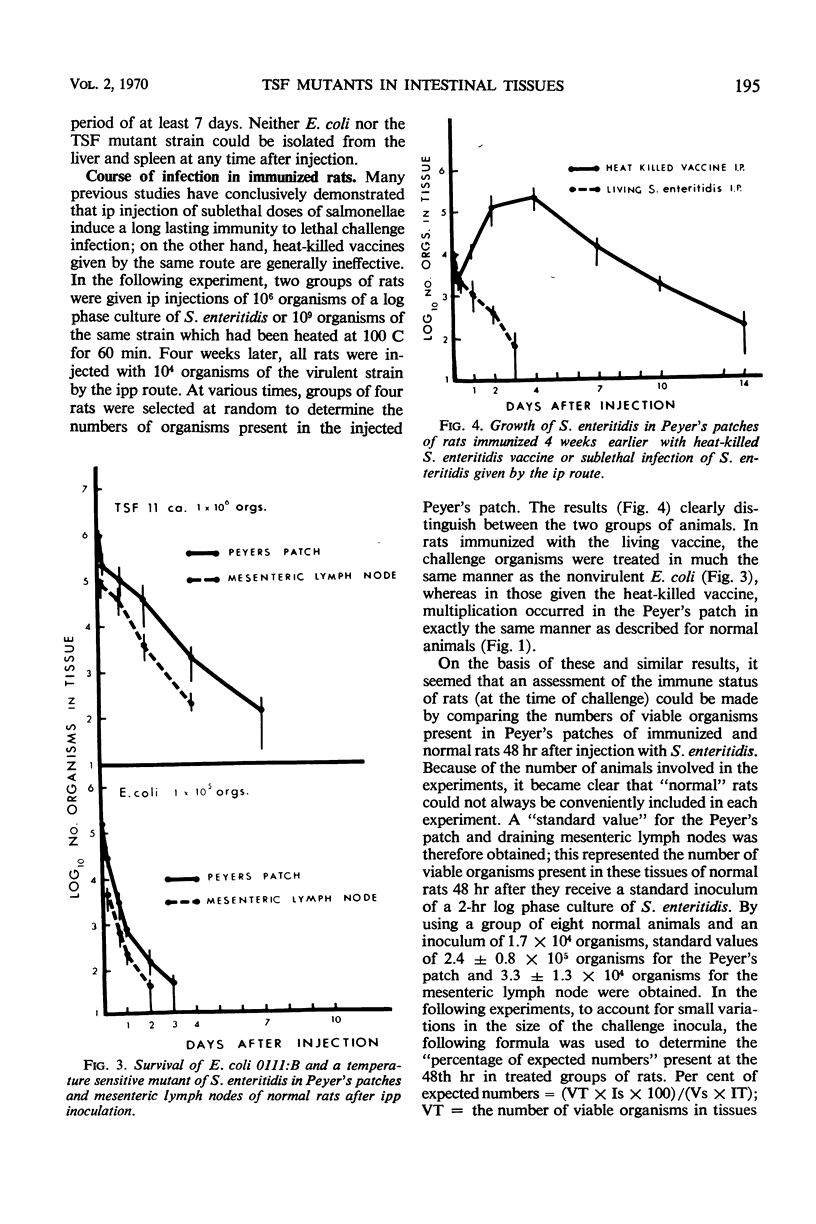
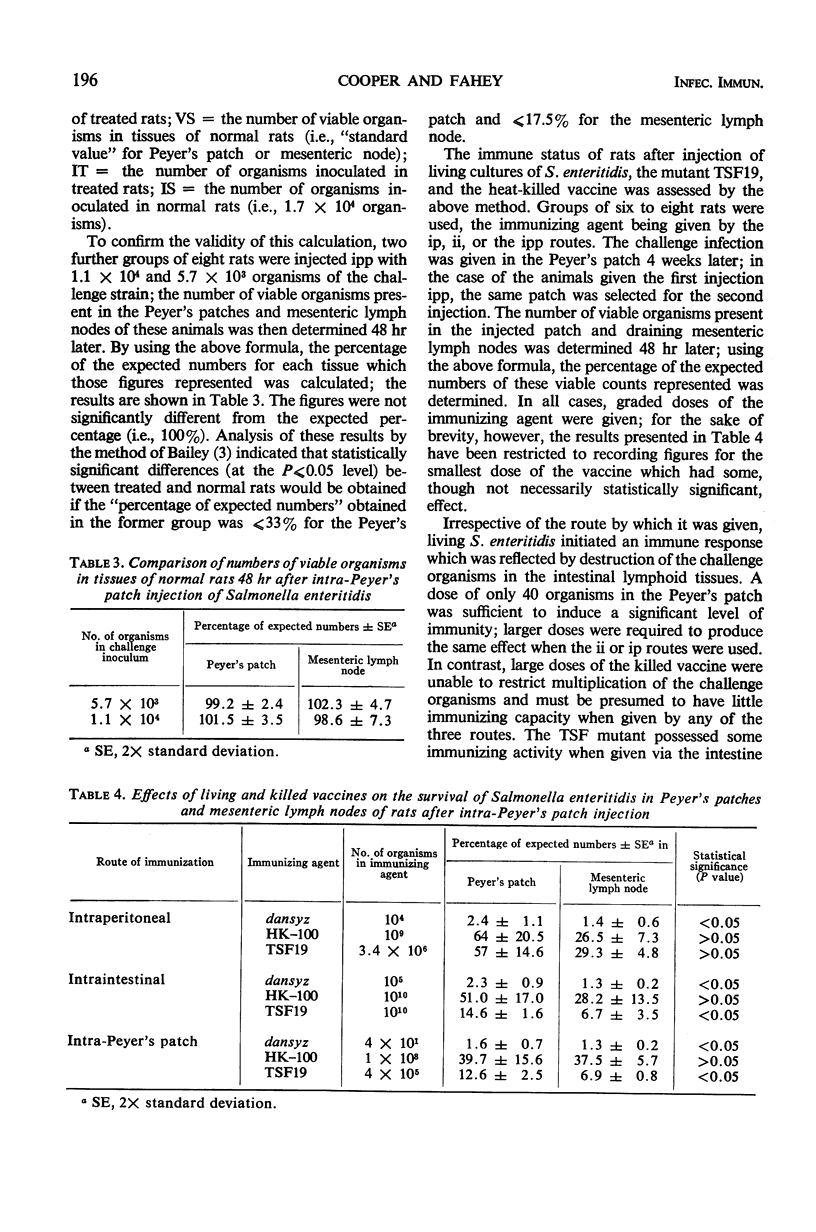
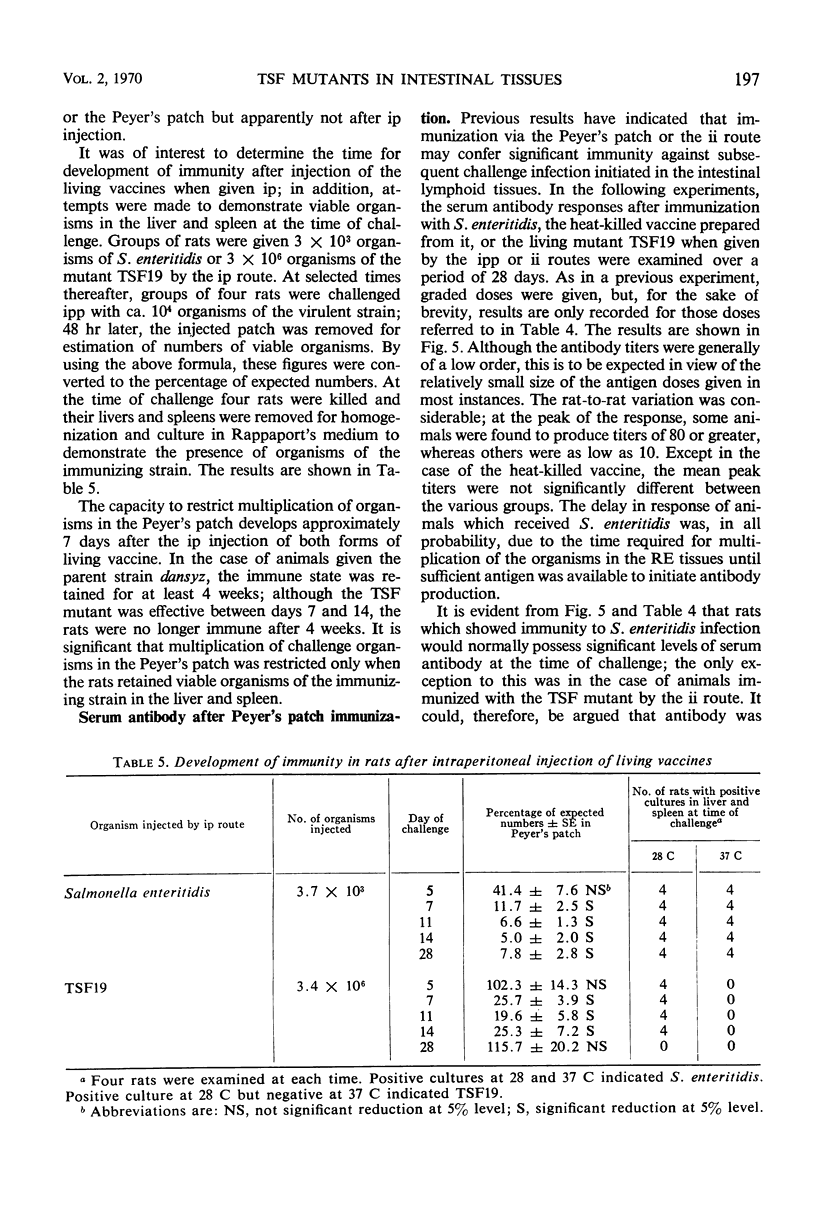
Infection of rats via a Peyer's patch has been used as a means of studying the behavior of Salmonella enteritidis in intestinal tissues. The course of infection in the Peyer's patch and draining mesenteric lymph node is characterized by multiplication of the organism over a period of 4 days followed by a gradual decline in numbers; the organism also passes to the liver and spleen and may be isolated from these organs as well as the intestinal tissues for at least 4 weeks. Temperature-sensitive mutants derived from the virulent strain are unable to multiply and do not pass to the liver and spleen; they remain viable for periods of less than 2 weeks. A quantitative technique based on the number of viable organisms remaining in the injected Peyer's patch 48 hr after infection has been used to assess the immune state of rats. The results have clearly demonstrated that Salmonella immunity can only be induced by living vaccines and that although viable organisms remain in the reticuloendothelial tissues, organisms given in a challenge infection are immediately subject to enhanced bactericidal activity within the intestinal tissues. Under the conditions used here, humoral antibody does not seem to offer any protective effect against Salmonella infection in the intestinal lymphoid tissues.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AKIYAMA T., MAEDA K., USHIBA D. [Studies on immunity in experimental typhoid. Challenge of mice passively immunized with antiserum through various routes (mechanism of immunization with killed vaccines)]. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 1962 Oct;17:829–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Mackaness G. B., Collins F. M. Mechanisms of acquired resistance in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):585–600. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Cross-protection against Salmonella enteritidis infection in mice. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1343–1349. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1343-1349.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Infection-immunity in experimental salmonellosis. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):601–619. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. N., Turner K. Immunological responses in rats following antigenic stimulation of Peyer's patches. I. Characteristics of the primary response. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1967 Aug;45(4):363–378. doi: 10.1038/icb.1967.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey K. J., Cooper G. N. Oral Immunization in Experimental Salmonellosis II. Characteristics of the Immune Response to Temperature-Sensitive Mutants Given by Oral and Parenteral Routes. Infect Immun. 1970 Aug;2(2):183–191. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.2.183-191.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey K. J., Cooper G. N. Oral immunization against experimental salmonellosis I. Development of temperature-sensitive mutant vaccines. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):263–270. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.263-270.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON D. The chemotherapy of experimental mouse typhoid with furazolidone. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Feb;37(1):20–31. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaroslow B. N., Nossal G. J. Effect of x-irradiation on antigen localization in lymphoid follicles. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1966 Dec;44(6):609–627. doi: 10.1038/icb.1966.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONFORTI N., NAVON B., RAPPAPORT F. A new enrichment medium for certain Salmonellae. J Clin Pathol. 1956 Aug;9(3):261–266. doi: 10.1136/jcp.9.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- USHIBA D., SAITO K., AKIYAMA T., NAKANO M., SUGIYAMA T., SHIRONO S. Studies on experimental typhoid: bacterial multiplication and host cell response after infection with Salmonella enteritidis in mice immunized with live and killed vaccines. Jpn J Microbiol. 1959 Apr;3:231–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1959.tb00119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


