Abstract
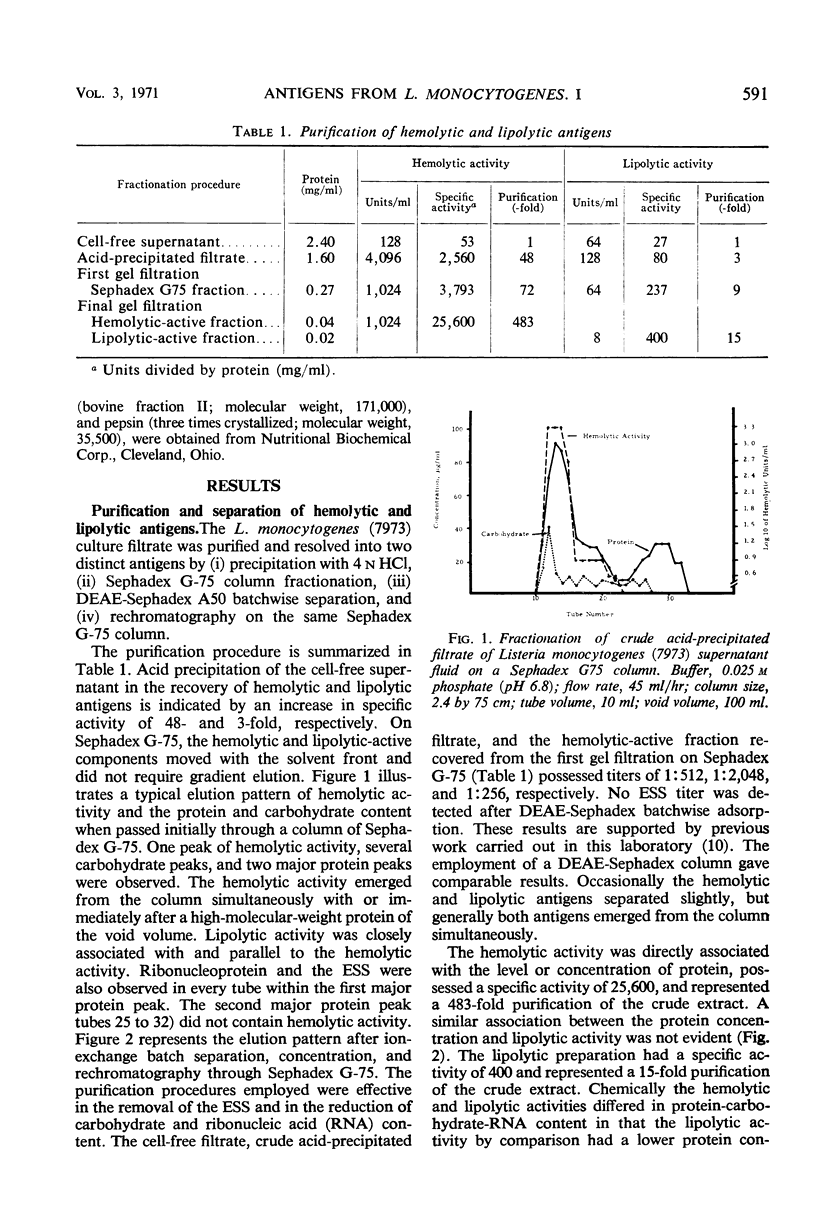
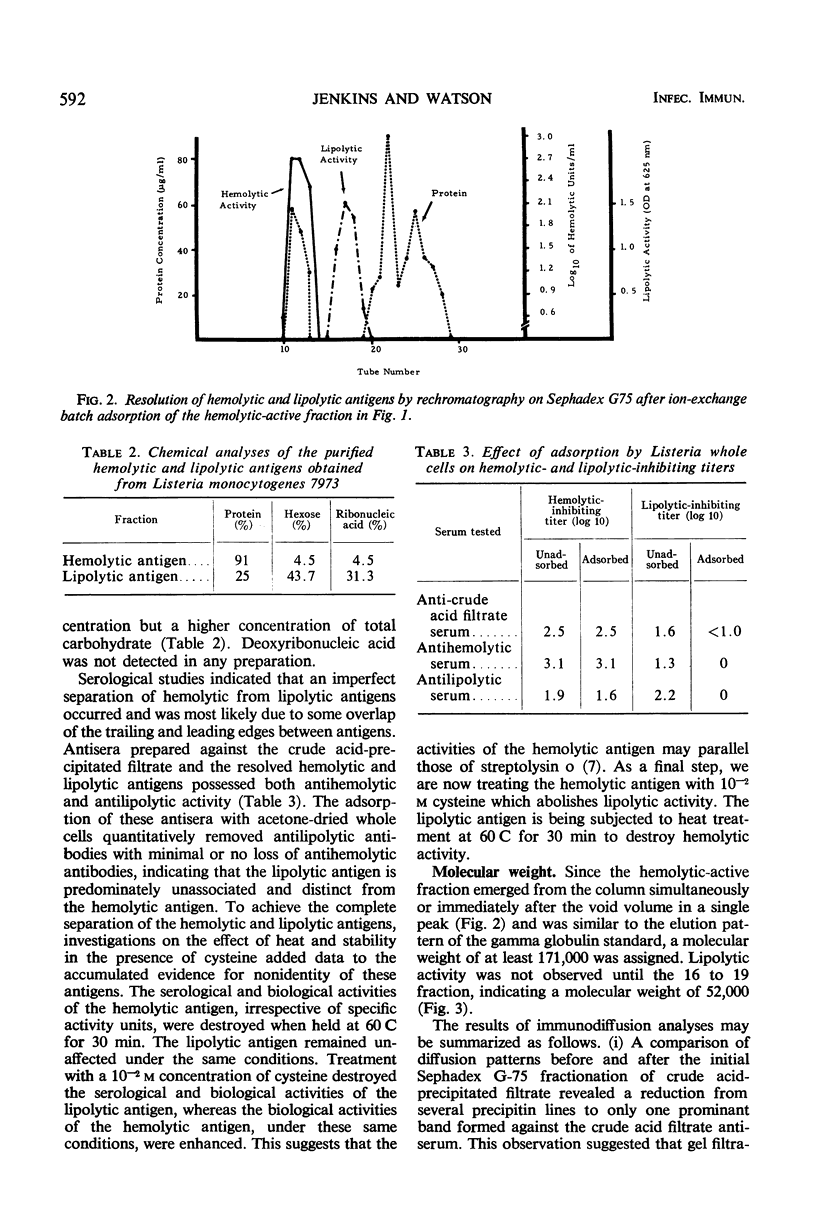
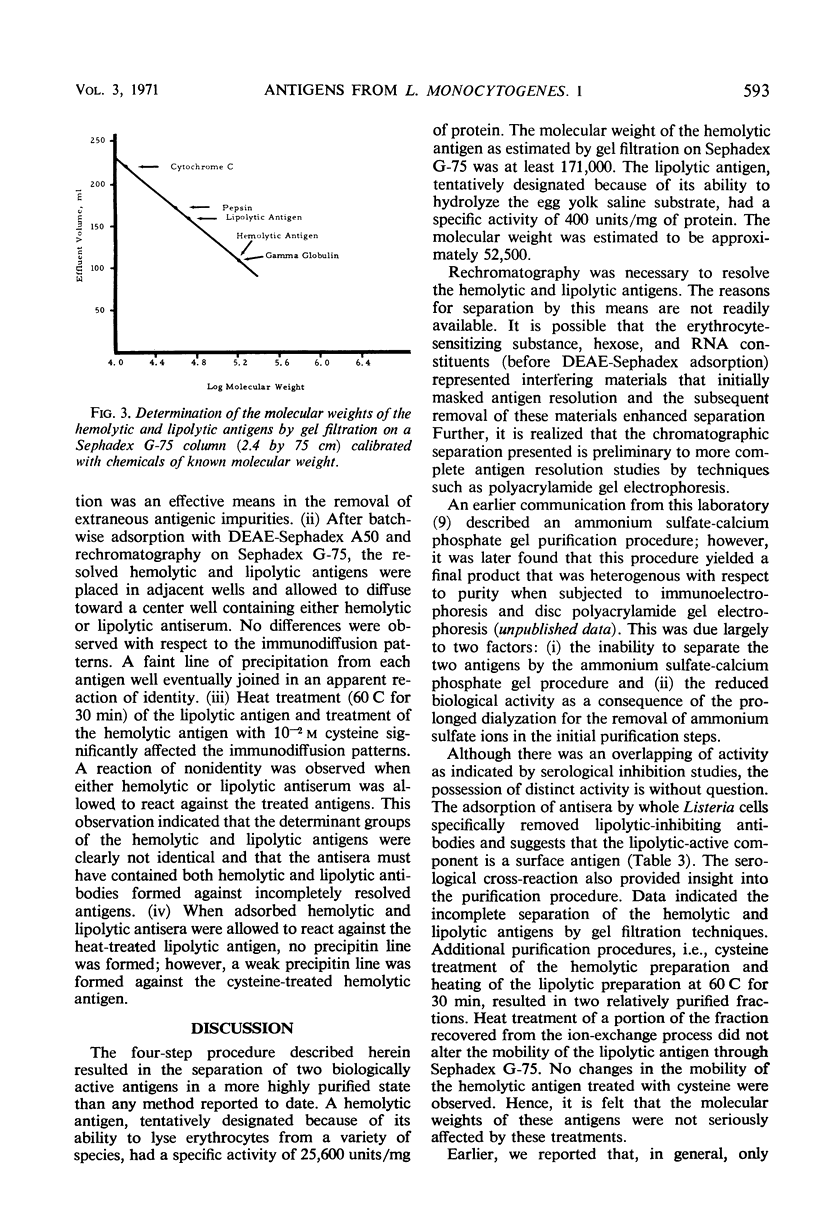
Two antigens were purified from culture filtrates of Listeria monocytogenes 7973 by the following procedure: (i) acid precipitation with 4 n HCl at pH 3.7, (ii) Sephadex G-75 column fractionation, (iii) diethylaminoethyl-Sephadex A50 batchwise adsorption, and (iv) rechromatography on Sephadex G-75. This procedure resulted in the resolution of two distinct antigens. One antigen, designated a hemolytic antigen because of its ability to lyse erythrocytes from a variety of species, had a specific activity of 25,000 units/mg of protein and an estimated molecular weight of at least 171,000. The other antigen, designated a lipolytic antigen because of its ability to hydrolyze egg yolk saline substrate, had a specific activity of 400 units/mg of protein and an estimated molecular weight of 52,500.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDREWS P. Estimation of molecular weights of proteins by gel filtration. Nature. 1962 Oct 6;196:36–39. doi: 10.1038/196036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREUND J. The effect of paraffin oil and mycobacteria on antibody formation and sensitization; a review. Am J Clin Pathol. 1951 Jul;21(7):645–656. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/21.7.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINS E. M., NJOKU-OBI A. N., ADAMS E. W. PURIFICATION OF THE SOLUBLE HEMOLYSINS OF LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:418–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.418-424.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins E. M., Watson B. B. Serum protein changes: an activity of the extracellular hemolytic-lipolytic protein from Listeria monocytogenes. Am J Vet Res. 1969 Apr;30(4):669–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUPPI A., CAVAZZINI G., BARETTA G. SU ALCUNE CARATTERISTICHE METABOLICHE DELLA LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. IV. INTORBIDAMENTO DEI TERRENI SOLIDI AL TUORLO D'UOVO (EY) ED AL SIERO UMANO PROVOCATO DALLA LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. Boll Ist Sieroter Milan. 1965 Jan-Feb;44:15–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane M. G., Knight B. C. The biochemistry of bacterial toxins: The lecithinase activity of Cl. welchii toxins. Biochem J. 1941 Sep;35(8-9):884–902. doi: 10.1042/bj0350884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheswaran S. K., Smith K. L., Lindorfer R. K. Saphylococcal beta-hemolysin. I. Purification of beta-hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):300–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.300-305.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. Separation and properties of a red cell sensitizing substance from streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2200–2204. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2200-2204.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NJOKU-OBI A. N., JENKINS E. M., NJOKU-OBI J. C., ADAMS J., COVINGTON V. PRODUCTION AND NATURE OF LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES HEMOLYSINS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:1–8. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.1-8.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'LEARY W. M., WELD J. T. LIPOLYTIC ACTIVITIES OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. I. NATURE OF THE ENZYME PRODUCING FREE FATTY ACIDS FROM PLASMA LIPIDS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1356–1363. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1356-1363.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUBENECK U. Susceptibility of Proteus mirabilis and its stable L-forms to erythromycin and other macrolides. Nature. 1962 Oct 13;196:195–196. doi: 10.1038/196195b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


