Abstract
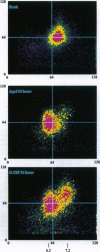
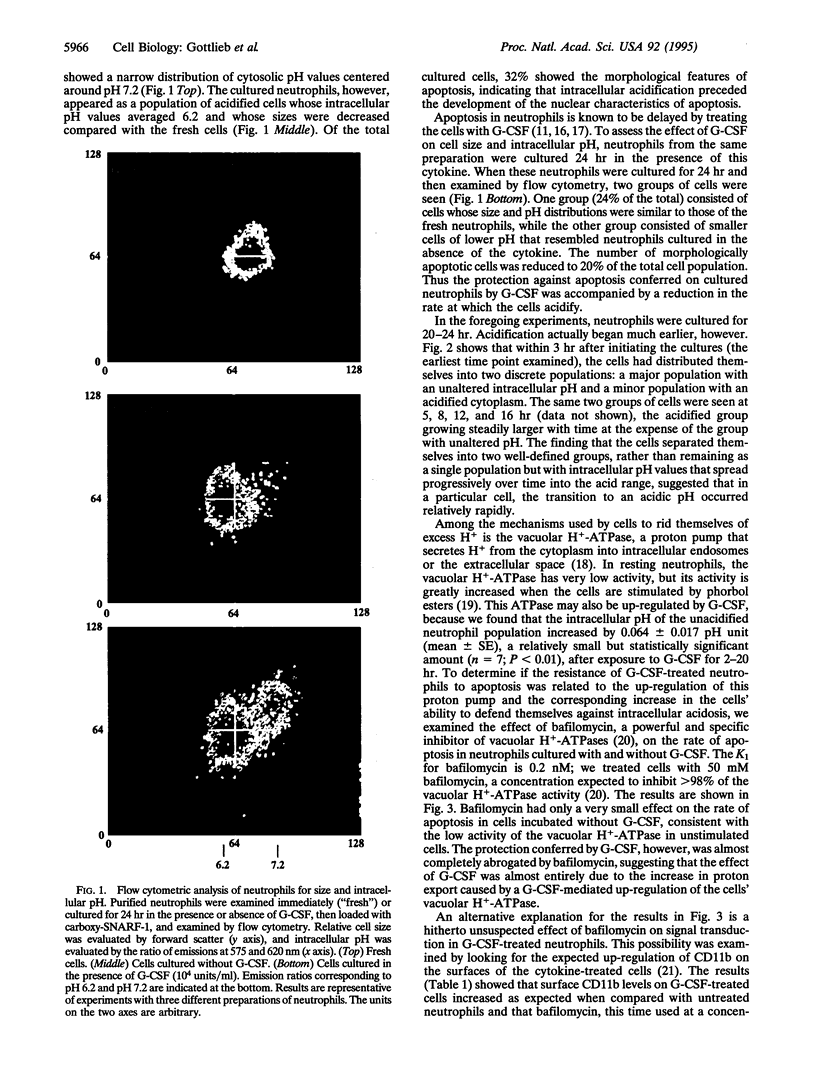
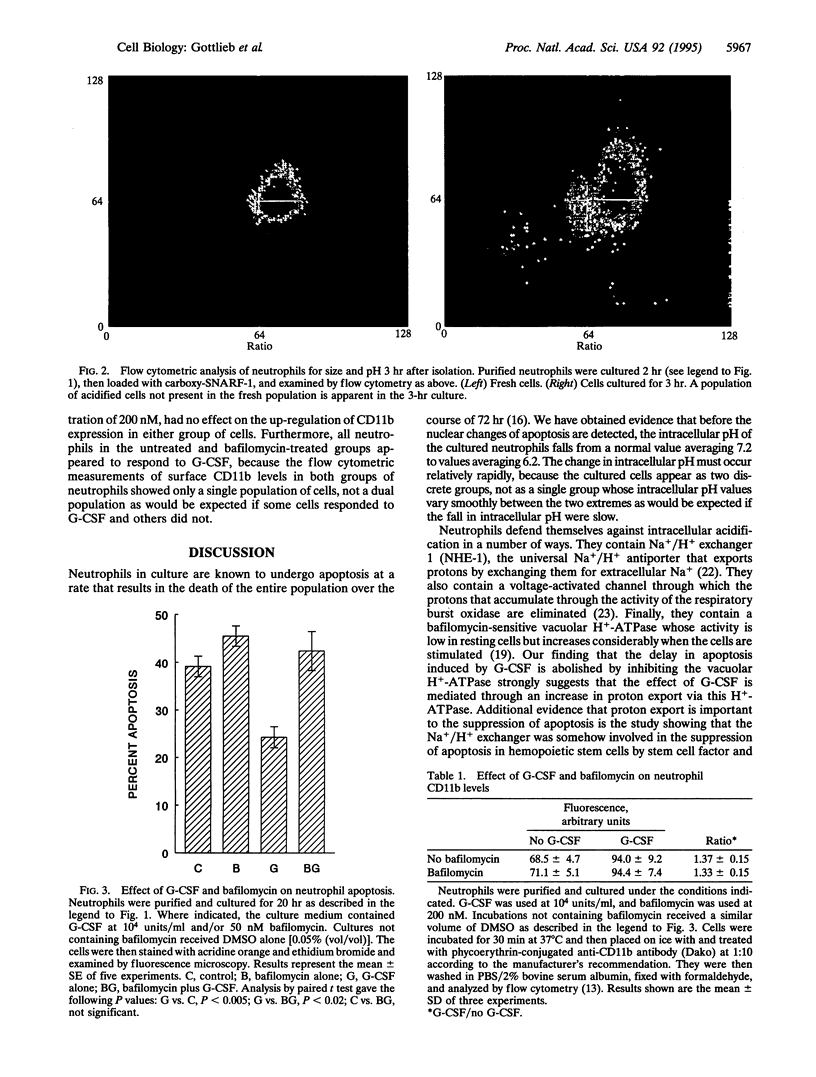
Neutrophils in tissue culture spontaneously undergo programmed cell death (apoptosis), a process characterized by well-defined morphological alterations affecting the cell nucleus. We found that these morphological changes were preceded by intracellular acidification and that acidification and the apoptotic changes in nuclear morphology were both delayed by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF). Among the agents that defend neutrophils against intracellular acidification is a vacuolar H(+)-ATPase that pumps protons out of the cytosol. When this proton pump was inhibited by bafilomycin A1, G-CSF no longer protected the neutrophils against apoptosis. We conclude that G-CSF delays apoptosis in neutrophils by up-regulating the cells' vacuolar H(+)-ATPase and that intracellular acidification is an early event in the apoptosis program.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNARDI G., GRIFFE M. STUDIES ON ACID DEOXYRIBONUCLEASE. II. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF SPLEEN-ACID DEOXYRIBONUCLEASE. Biochemistry. 1964 Oct;3:1419–1426. doi: 10.1021/bi00898a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry M. A., Eastman A. Identification of deoxyribonuclease II as an endonuclease involved in apoptosis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Jan;300(1):440–450. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry M. A., Reynolds J. E., Eastman A. Etoposide-induced apoptosis in human HL-60 cells is associated with intracellular acidification. Cancer Res. 1993 May 15;53(10 Suppl):2349–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassnett S., Reinisch L., Beebe D. C. Intracellular pH measurement using single excitation-dual emission fluorescence ratios. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):C171–C178. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.1.C171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates R. C., Buret A., van Helden D. F., Horton M. A., Burns G. F. Apoptosis induced by inhibition of intercellular contact. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(2):403–415. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colotta F., Re F., Polentarutti N., Sozzani S., Mantovani A. Modulation of granulocyte survival and programmed cell death by cytokines and bacterial products. Blood. 1992 Oct 15;80(8):2012–2020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crider B. P., Xie X. S., Stone D. K. Bafilomycin inhibits proton flow through the H+ channel of vacuolar proton pumps. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 1;269(26):17379–17381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cáceres-Cortés J., Rajotte D., Dumouchel J., Haddad P., Hoang T. Product of the steel locus suppresses apoptosis in hemopoietic cells. Comparison with pathways activated by granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 22;269(16):12084–12091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duronio V., Welham M. J., Abraham S., Dryden P., Schrader J. W. p21ras activation via hemopoietin receptors and c-kit requires tyrosine kinase activity but not tyrosine phosphorylation of p21ras GTPase-activating protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1587–1591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgac M. Structure and function of vacuolar class of ATP-driven proton pumps. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jul;69(3):765–796. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.3.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch S. M., Francis H. Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(4):619–626. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Furuya W. Cytoplasmic pH regulation in phorbol ester-activated human neutrophils. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 1):C55–C65. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.1.C55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Woodside M., Sardet C., Pouyssegur J., Rotin D. Activation of the Na+/H+ antiporter during cell volume regulation. Evidence for a phosphorylation-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23823–23828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagag N., Lacal J. C., Graber M., Aaronson S., Viola M. V. Microinjection of ras p21 induces a rapid rise in intracellular pH. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1984–1988. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslett C., Guthrie L. A., Kopaniak M. M., Johnston R. B., Jr, Henson P. M. Modulation of multiple neutrophil functions by preparative methods or trace concentrations of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Am J Pathol. 1985 Apr;119(1):101–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers M. C., De Groot E. R., Roos D. Phagocytosis and degradation of DNA-anti-DNA complexes by human phagocytes. I. Assay conditions, quantitative aspects and differences between human blood monocytes and neutrophils. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Oct;11(10):757–764. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A., Whyte M. K., Haslett C. Inhibition of apoptosis and prolongation of neutrophil functional longevity by inflammatory mediators. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Oct;54(4):283–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Eastman A. Apoptosis in an interleukin-2-dependent cytotoxic T lymphocyte cell line is associated with intracellular acidification. Role of the Na(+)/H(+)-antiport. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):3203–3211. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.3203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F. P., Gresham H. D., Schwarz E., Brown E. J. Molecular cloning of integrin-associated protein: an immunoglobulin family member with multiple membrane-spanning domains implicated in alpha v beta 3-dependent ligand binding. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(2):485–496. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maidorn R. P., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Tannock I. F. Therapeutic potential of analogues of amiloride: inhibition of the regulation of intracellular pH as a possible mechanism of tumour selective therapy. Br J Cancer. 1993 Feb;67(2):297–303. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert M., Andrews P. C., Babior B. M. Measurement of O2- production by human neutrophils. The preparation and assay of NADPH oxidase-containing particles from human neutrophils. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:358–365. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motyka B., Griebel P. J., Reynolds J. D. Agents that activate protein kinase C rescue sheep ileal Peyer's patch B cells from apoptosis. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jun;23(6):1314–1321. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musgrove E. A., Hedley D. W. Measurement of intracellular pH. Methods Cell Biol. 1990;33:59–69. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60511-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanda A., Grinstein S. Protein kinase C activates an H+ (equivalent) conductance in the plasma membrane of human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10816–10820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanda A., Gukovskaya A., Tseng J., Grinstein S. Activation of vacuolar-type proton pumps by protein kinase C. Role in neutrophil pH regulation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22740–22746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell K., Wood P., Stratford I., Tannock I. Effects of agents which inhibit the regulation of intracellular pH on murine solid tumours. Br J Cancer. 1992 Aug;66(2):311–317. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen N. E., Knapik J., Strebel F., Tarpley W. G., Gorman R. R. Regulation of Na+-H+ exchange in normal NIH-3T3 cells and in NIH-3T3 cells expressing the ras oncogene. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 1):C756–C763. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.4.C756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Sala D., Collado-Escobar D., Mollinedo F. Intracellular alkalinization suppresses lovastatin-induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells through the inactivation of a pH-dependent endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 17;270(11):6235–6242. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.11.6235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Nakafuku M., Kaziro Y. Function of Ras as a molecular switch in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24149–24152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savill J. S., Wyllie A. H., Henson J. E., Walport M. J., Henson P. M., Haslett C. Macrophage phagocytosis of aging neutrophils in inflammation. Programmed cell death in the neutrophil leads to its recognition by macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):865–875. doi: 10.1172/JCI113970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Lechene C. P. pH regulation in spread cells and round cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1327–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C. W., Lyons J. C., Griffin R. J., Makepeace C. M., Cragoe E. J., Jr Increase in thermosensitivity of tumor cells by lowering intracellular pH. Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 1;53(7):1599–1601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. R., Kwast-Welfeld J., Gourdeau H., Leblanc J., Neugebauer W., Sikorska M. Relationship between apoptosis and the cell cycle in lymphocytes: roles of protein kinase C, tyrosine phosphorylation, and AP1. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Jul;207(1):142–151. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijsman J. H., Jonker R. R., Keijzer R., van de Velde C. J., Cornelisse C. J., van Dierendonck J. H. A new method to detect apoptosis in paraffin sections: in situ end-labeling of fragmented DNA. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Jan;41(1):7–12. doi: 10.1177/41.1.7678025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yong K. L., Linch D. C. Differential effects of granulocyte- and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors (G- and GM-CSF) on neutrophil adhesion in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Haematol. 1992 Nov;49(5):251–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1992.tb00057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]