Abstract
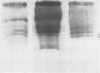
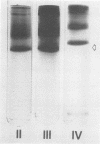
Separation of homogenates of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) into different fractions by sedimentation in centrifugal fields that ranged from 126 × g to 50,000 × g resulted in a differential distribution of the lysosomal enzymes. Peroxidase, lysozyme, beta-glucuronidase, and acid phosphatase activity were separated from each other. This demonstrates that the lysosomes of human PMN comprise at least three and possibly four physically and chemically different cytoplasmic particles. Proteins which are more cationic than lysozyme and which may be analogous to cationic lysosomal protein of rabbit PMN were associated with lysozyme and beta-glucuronidase rich granules. Antibacterial activity was present in four of the five cell fractions which this work produced. These results are significant because they differ from those obtained with rabbits and because they directly influence future experimental design and interpretation, in attempts to analyze antibacterial, scavenging, and inflammatory capacities of human PMN. Since lysosomes differ physically, biochemically, and morphologically, they may well differ with respect to their function in the PMN.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehner R. L., Karnovsky M. J., Karnovsky M. L. Degranulation of leukocytes in chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):187–192. doi: 10.1172/JCI105967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Hirsch J. G., De Duve C. Resolution of granules from rabbit heterophil leukocytes into distinct populations by zonal sedimentation. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):529–541. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Differences in enzyme content of azurophil and specific granules of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. I. Histochemical staining of bone marrow smears. J Cell Biol. 1968 Nov;39(2):286–298. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.2.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., HIRSCH J. G. The isolation and properties of the specific cytoplasmic granules of rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:983–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daems W. T. On the fine structure of human neutrophilic leukocyte granules. J Ultrastruct Res. 1968 Aug;24(3):343–348. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(68)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALLON H. J., FREI E., 3rd, DAVIDSON J. D., TRIER J. S., BURK D. Leukocyte preparations from human blood: evaluation of their morphologic and metabolic state. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 May;59:779–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOREY H. W., GRANT L. H. Leucocyte migration from small blood vessels stimulated with ultraviolet light: an electron-microscope study. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82:13–17. doi: 10.1002/path.1700820103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCHHORN R., WEISSMANN G. ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES OF HUMAN LEUKOCYTE LYSOSOMES IN VITRO. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 May;119:36–39. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Iodination of bacteria: a bactericidal mechanism. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):1063–1078. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOCKWOOD W. R., ALLISON F. ELECTRON MICROGRAPHIC STUDIES OF PHAGOCYTIC CELLS. I. MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGES OF THE CYTOPLASM AND GRANULES OF RABBIT GRANULOCYTES ASSOCIATED WITH INGESTION OF ROUGH PNEUMOCOCCUS. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Dec;44:593–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May C. D., Levine B. B., Weissmann G. Effects of compounds which inhibit antigenic release of histamine and phagocytic release of lysosomal enzyme on glucose utilization by leukocytes in humans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Mar;133(3):758–763. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Karnovsky M. J., Karnovsky M. L. The distributions of some granule-associated enzymes in guinea-pig polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(2):207–216. doi: 10.1042/bj1160207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. E. Killing and lysis of gram-negative bacteria through the synergistic effect of hydrogen peroxide, ascorbic acid, and lysozyme. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):949–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.949-955.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzansky J. J., Patterson R. Subcellular distribution of histamine in human leucocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jan;124(1):56–59. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUGAR D. The measurement of lysozyme activity and the ultra-violet inactivation of lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1952 Mar;8(3):302–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(52)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPITZNAGEL J. K., ZEYA H. I. BASIC PROTEINS AND LEUKOCYTE LYSOSOMES AS BIOCHEMICAL DETERMINANTS OF RESISTANCE TO INFECTION. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1964;77:126–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe I., Donahue S., Hoggatt N. Method for electron microscopic studies of circulating human leukocytes and observations on their fine structure. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Oct 31;20(5):366–382. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZEYA H. I., SPITZNAGEL J. K. ANTIBACTERIAL AND ENZYMIC BASIC PROTEINS FROM LEUKOCYTE LYSOSOMES: SEPARATION AND IDENTIFICATION. Science. 1963 Nov 22;142(3595):1085–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3595.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K. Antimicrobial specificity of leukocyte lysosomal cationic proteins. Science. 1966 Nov 25;154(3752):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3752.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic protein-bearing granules of polymorphonuclear leukocytes: separation from enzyme-rich granules. Science. 1969 Mar 7;163(3871):1069–1071. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3871.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]