Abstract
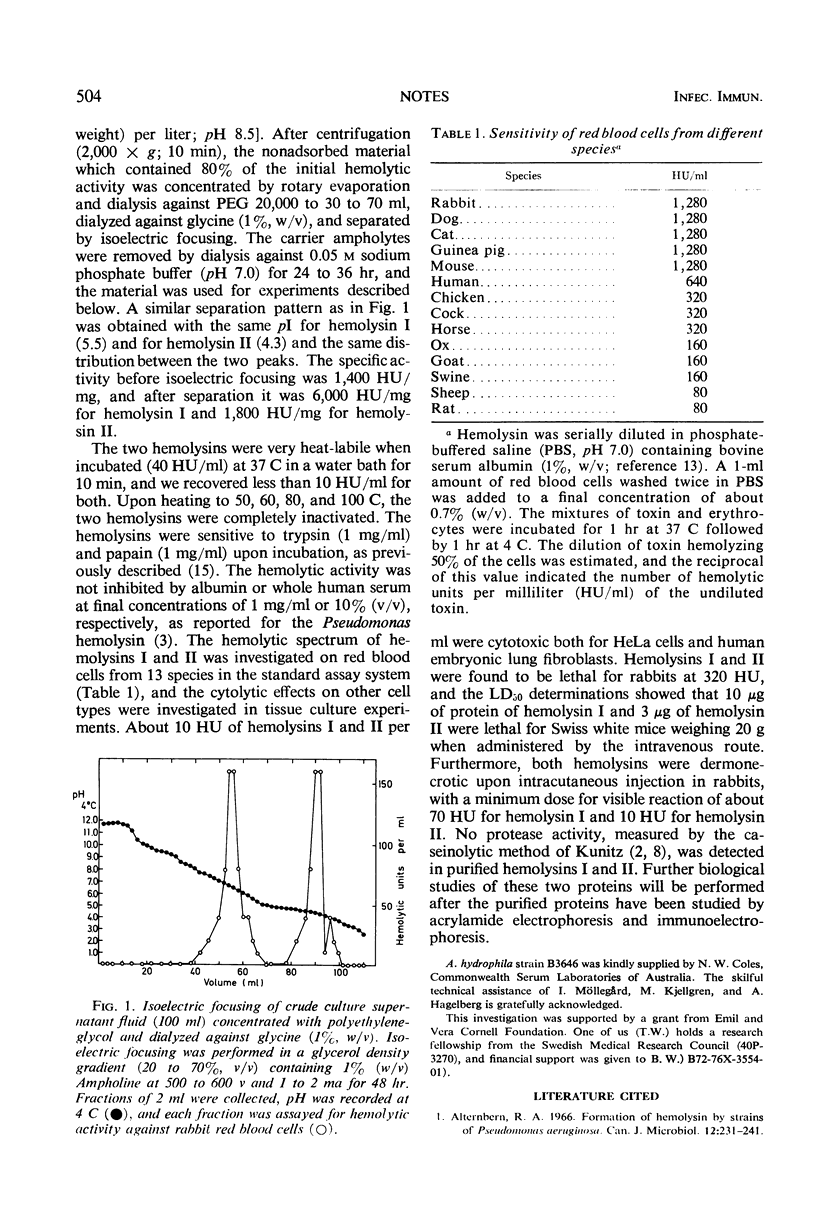
Two hemolytic proteins (hemolysin I and II) with isoelectric points of 5.5 and 4.3 were purified by isoelectric focusing from the culture supernatant fluid of Aeromonas hydrophila. The purified hemolysins were unstable after dialysis and upon heating at 37 C and were inactivated by proteolytic enzymes. The two hemolysins were lethal for mice in a dose of 10 μg (hemolysin I) and 3 μg (hemolysin II) and showed similar hemolytic spectra on red cells of different species. Both were also cytotoxic for HeLa cells and human fibroblasts and gave dermonecrosis in rabbits.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvidson S., Holme T., Wadström T. Formation of bacteriolytic enzymes in batch and continuous culture of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):227–233. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.227-233.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERK R. S. PARTIAL PURIFICATION OF THE EXTRACELLULAR HEMOLYSIN OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:559–565. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.559-565.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASELITZ F. H., GUENTHER R. [Hemolysin studies with Aeromonas strains]. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1960 Sep;180:30–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney S. A., Jones R. J. Biological and immunochemical properties of culture filtrates of virulent and avirulent strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Br J Exp Pathol. 1968 Oct;49(5):395–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurioka S., Liu P. V. Effect of the hemolysin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on phosphatides and on phospholipase c activity. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):670–674. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.670-674.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. 3. Identity of the lethal toxins produced in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1966 Oct;116(4):481–489. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinke G., Barum J., Rosenberg B., Berk R. In Vivo Studies with the Partially Purified Protease (Elastase) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):583–589. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.583-589.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesterberg O., Wadström T., Vesterberg K., Svensson H., Malmgren B. Studies on extracellular PROTEINS FROM Staphylococcus aureus. I. Separation and characterization of enzymes and toxins by isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 11;133(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90547-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Graevenitz A., Mensch A. H. The genus aeromonas in human bacteriology report of 30 cases and review of the literature. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 1;278(5):245–249. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802012780504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T. Bacteriolytic enzymes from Staphylococcus aureus. Properties of the endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):745–752. doi: 10.1042/bj1200745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T. Studies on extracellular proteins from Staphylococcus aureus. IV. Separation of alpha-toxin by isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 21;168(2):228–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


