Abstract
Exposure of mononuclear cells from the mouse peritoneal cavity to interferon (IF)-containing mouse sera enhanced phagocytosis of colloidal carbon particles by the cells. The same effect was observed when the cells were exposed to IF-containing cell culture harvest free of serum. The magnitude of this effect of IF-containing preparations paralleled the titer of IF and was not related to the dilution of various IF-containing serum specimens tested. The factor responsible for the enhancing effect was stable at pH 2, inactivated by trypsin, and nonsedimentable at 105,000 × g. Heating at 60 C for 1 hr destroyed it, and its kinetics of heat inactivation paralleled that of the antiviral activity of IF. A period of incubation of phagocytic cells with IF-containing serum was necessary before a maximum level of enhancement was reached, and once established was not removable by repeated washing of cells. The kinetics of the production of the enhancing factor in mice injected with Newcastle disease virus was essentially identical to that of the simultaneous production of IF as measured by antiviral activity. Contrary to the effect of mouse IF preparations, human IF preparation did not enhance the activity of mouse phagocytes. It appears, therefore, that the phagocytosis-enhancing factor falls within the present definition of IF.
Full text
PDF

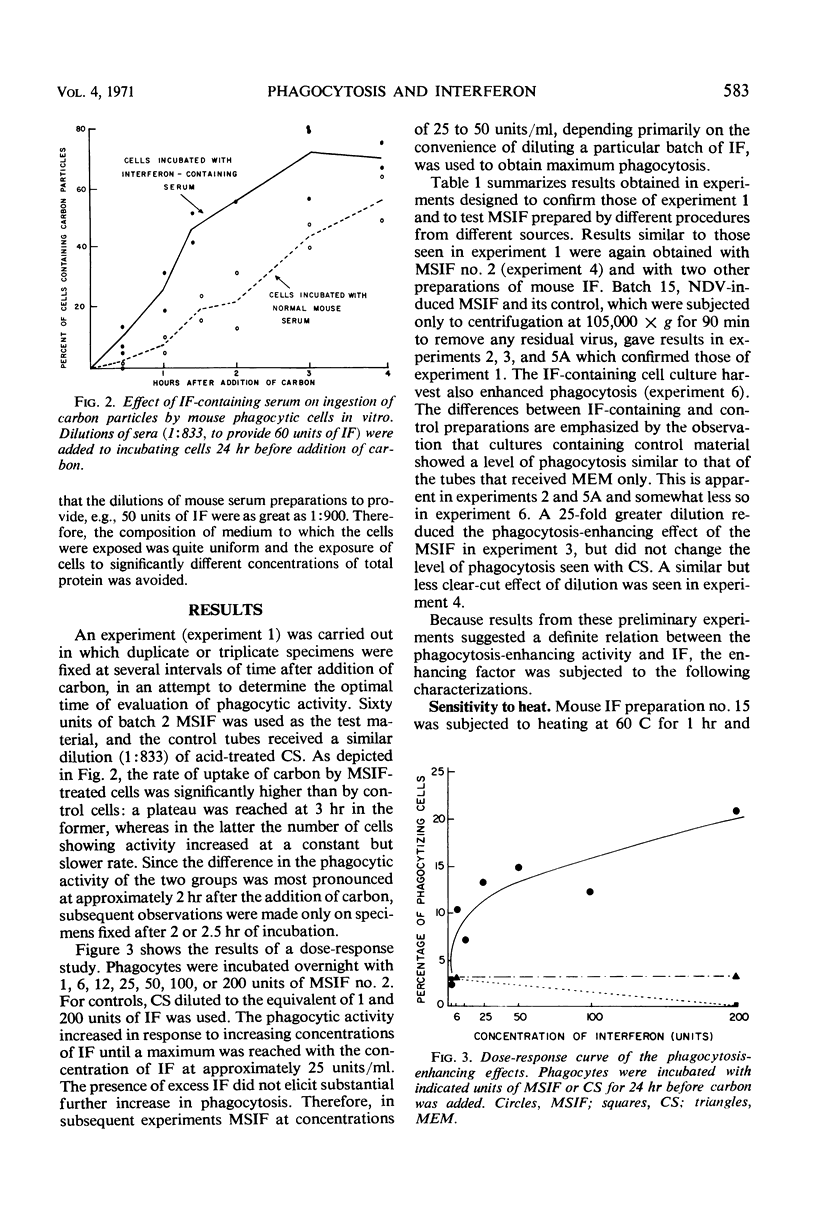
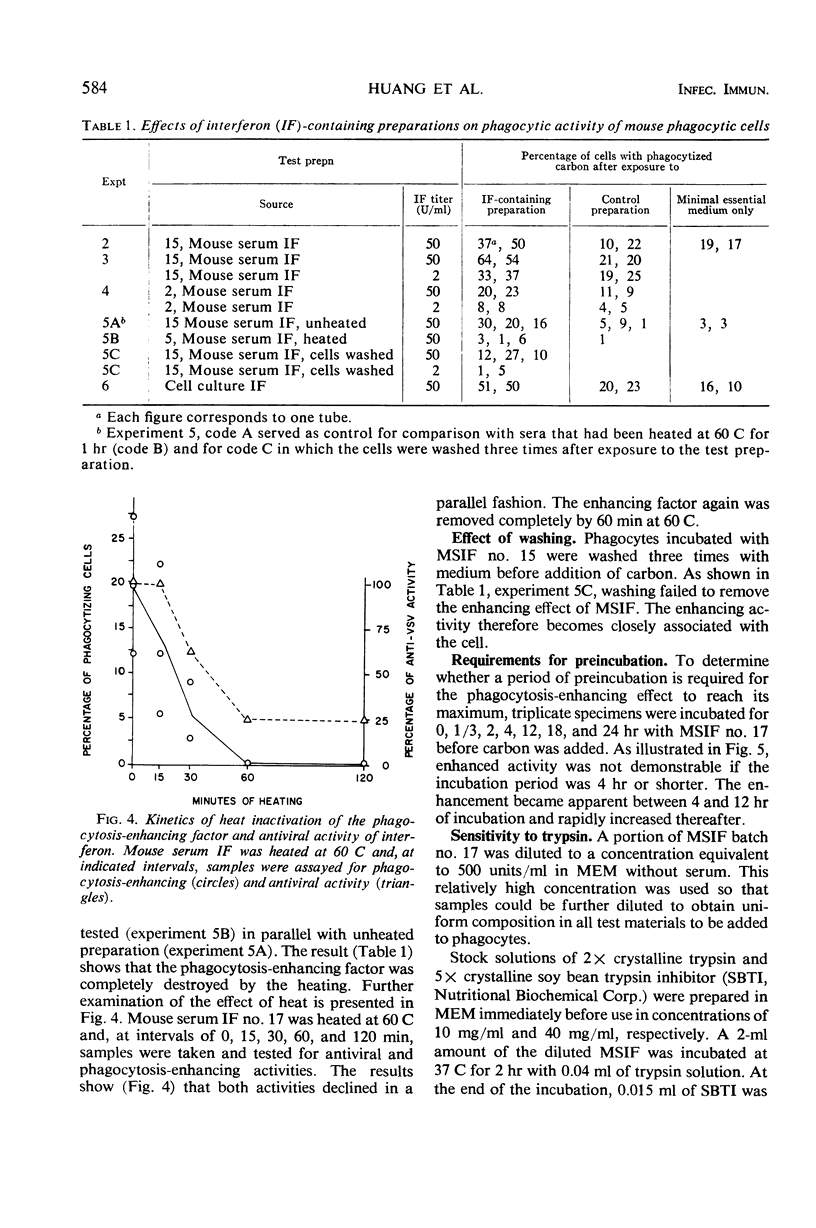
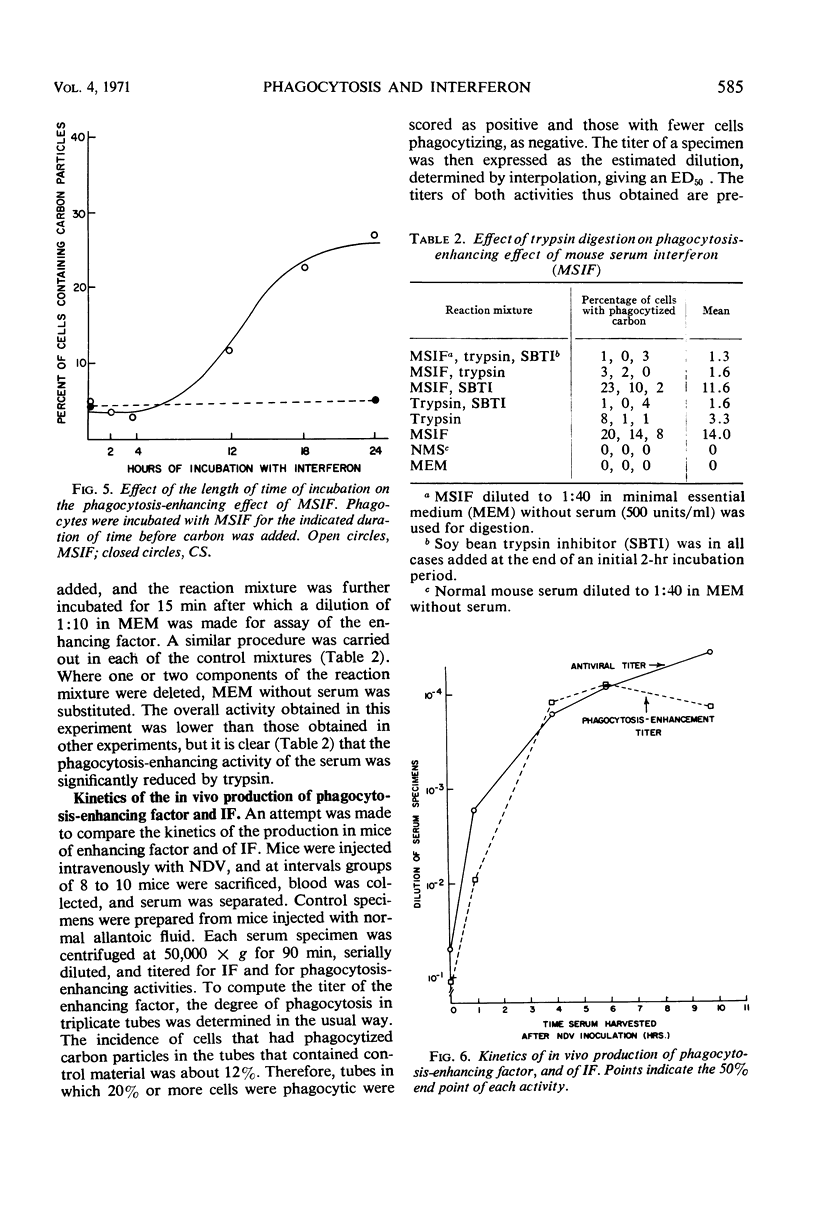


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Desmyter J., Rawls W. E., Melnick J. L. A human interferon that crosses the species line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):69–76. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidalgo B. V., Najjar V. A. The physiological role of the lymphoid system, 3. Leucophilic gamma-globulin and the phagocytic activity of the polymorphonuclear leucocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):957–964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gifford G. E., Tibor A., Peavy D. L. Interferon production in mixed lymphocyte cell cultures. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):164–166. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.164-166.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow L. A. Leukocytes and interferon in the host response to viral infections. II. Enhanced interferon response of leukocytes from immune animals. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2185–2191. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2185-2191.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. A., Cooperband S. R., Kibrick S. Immune specific induction of interferon production in cultures of human blood lymphocytes. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1415–1417. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Brouty-Boyé D., Thomas M. T., Macieira-Coelho A. Interferon and cell division. I. Inhibition of the multiplication of mouse leukemia L 1210 cells in vitro by interferon preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1052–1058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. Y., Gordon F. B. Production of interferon in mice: effect of altered gaseous environments. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Oct;16(10):1551–1556. doi: 10.1128/am.16.10.1551-1556.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahiel R. I., Nussenzweig R. S., Vilcek J., Vanderberg J. Protective effect of interferon inducers on Plasmodium berghei malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1969 Nov;18(6):823–835. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1969.18.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahiel R. I., Vilcek J., Nussenzweig R., Vanderberg J. Interferon inducers protect mice against plasmodium berghei malaria. Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazar J., Gillmore J. D., Gordon F. B. Effect of Interferon and Interferon Inducers on Infections with a Nonviral Intracellular Microorganism, Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):825–832. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.825-832.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Salb J. M. Molecular basis of interferon action: inhibition of viral RNA translation. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):502–516. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordhorst C. H., Reinicke V., Schonne E. In ovo inhibition by concentrated chick interferon of the growth of TRIC agents. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967 May;63(5 Suppl):1107–1109. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(67)94090-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najjar V. A., Nishioka K. "Tuftsin": a natural phagocytosis stimulating peptide. Nature. 1970 Nov 14;228(5272):672–673. doi: 10.1038/228672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxman M. N., Levin M. J. Interferon and transcription of early virus-specific RNA in cells infected with simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):299–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pindak F. F. Protection of mice against bacterial infection by interferon inducers. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):271–273. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.271-273.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Merigan T. C. Synthetic polyanions protect mice against intracellular bacterial infection. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):361–363. doi: 10.1038/226361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz W. W., Huang K. Y., Gordon F. B. Role of interferon in experimental mouse malaria. Nature. 1968 Nov 16;220(5168):709–710. doi: 10.1038/220709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. Inhibition of interferon action by actinomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:447–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. J., Craighead J. E. Infection of adult mouse macrophages in vitro with cytomegalovirus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Dec;129(3):690–694. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. J., Waitz J. A., Came P. E. Induction of resistance to bacterial infections of mice with poly I-poly C. Nature. 1970 Apr 11;226(5241):170–170. doi: 10.1038/226170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]