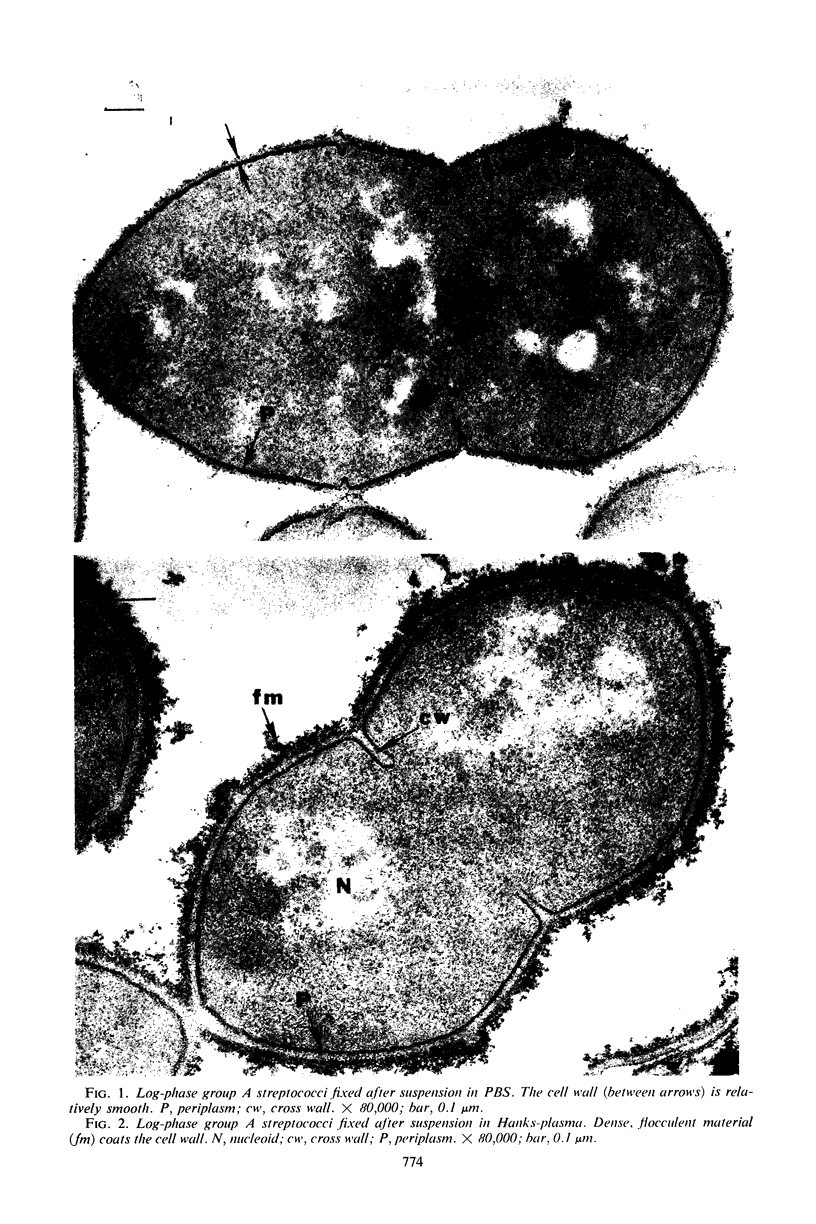
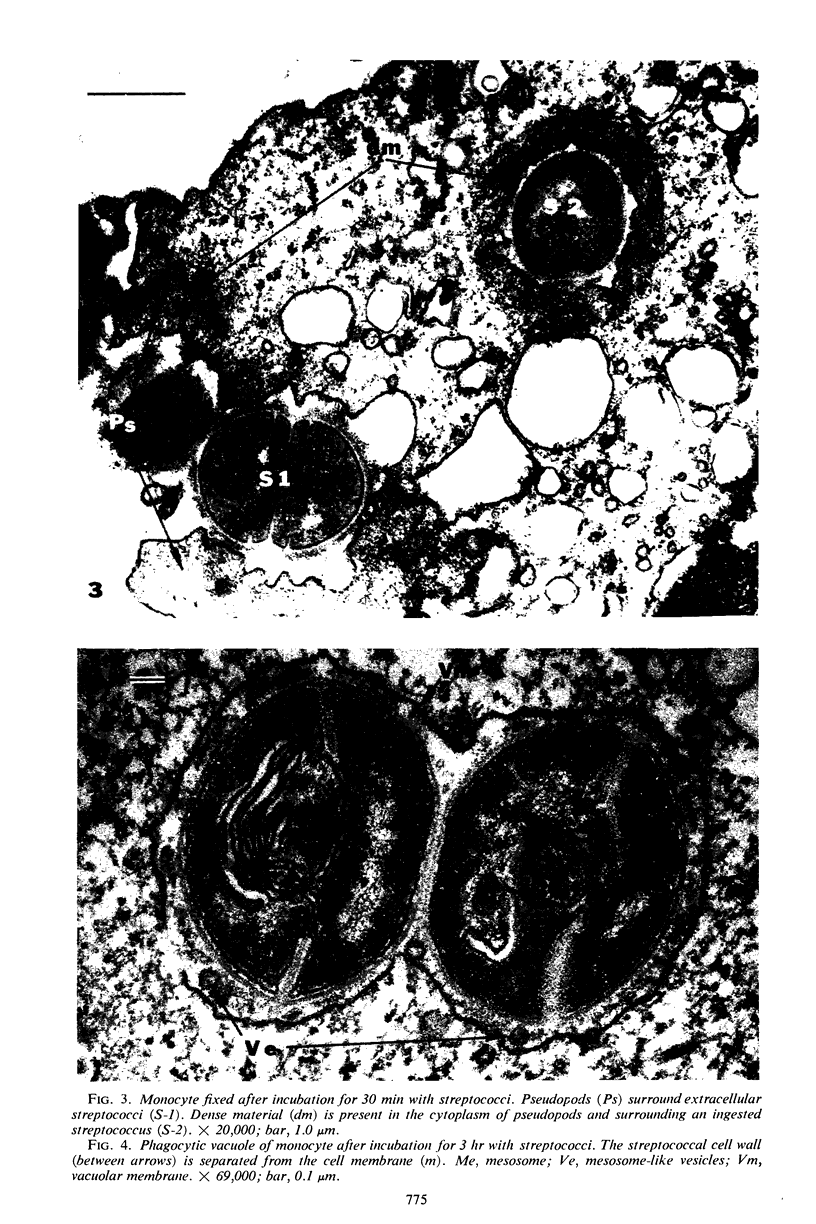
Abstract
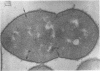
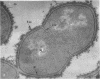
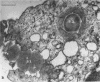
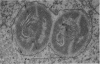
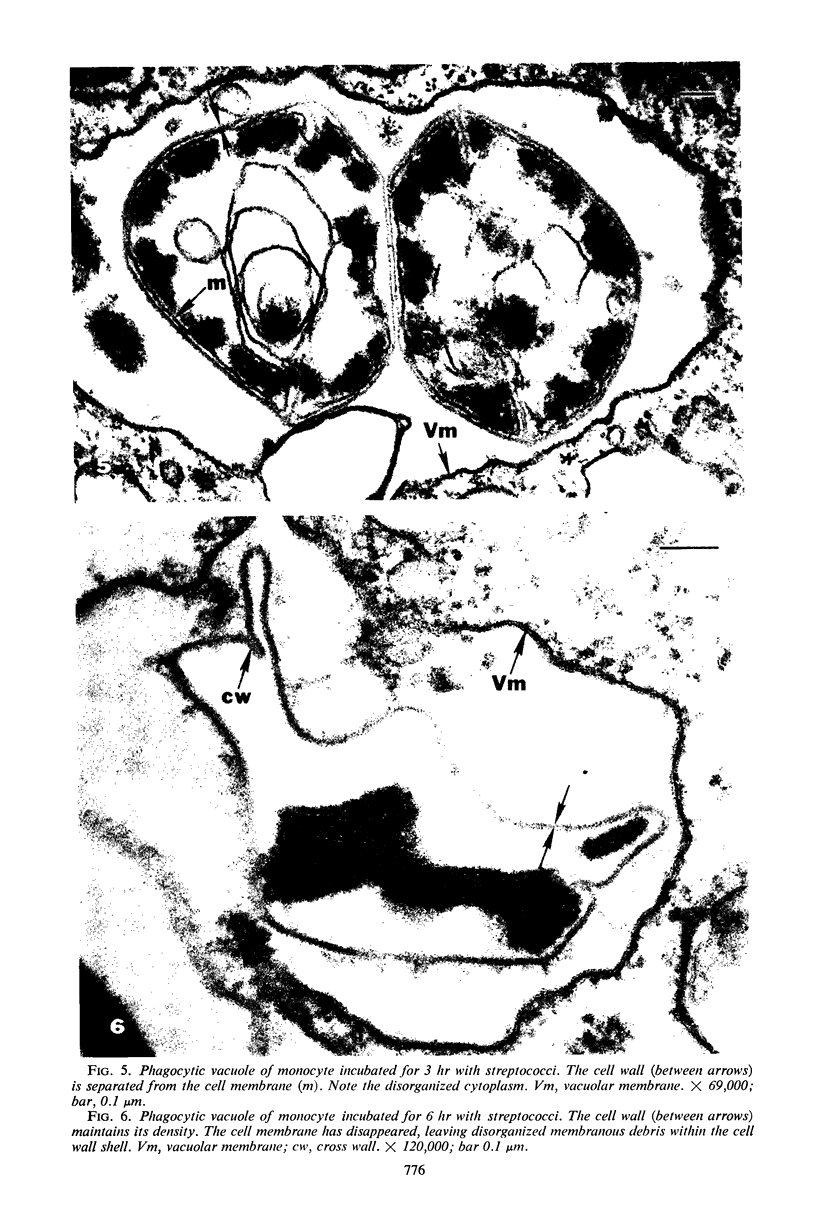
Group A streptococci were added to cultures of isolated human blood monocytes. The bacteria were readily sequestered within phagocytic vacuoles after being coated with flocculent material, apparently derived from the plasma-containing medium. Progressive lysis of intravacuolar streptococci was observed, characterized by plasmolysis, internal disruption, and eventual plasma membrane dissolution. However, the cell walls remained essentially identical to those of nonphagocytized streptococci, showing no signs of dissolution within the limited in vitro survival time of the monocytes. These results indicate that streptococcal cell walls may persist in migrating human phagocytes in vivo and may be deposited in body tissues. This cell wall material, known to be toxic to animal tissues, may be an important determinant in the pathogenesis of poststreptococcal sequelae in man.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayoub E. M., Wannamaker L. W. The fate of group A streptococci following phagocytosis. In vitro phagocytic studies of isotope-labeled streptococci. J Immunol. 1967 Dec;99(6):1099–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayoub E. M., White J. G. Intraphagocytic degradation of group A streptococci: electron microsopic studies. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):728–736. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.728-736.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A. The fate of bacteria within phagocytic cells. I. The degradation of isotopically labeled bacteria by polymorphonuclear leucocytes and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1963 Jan 1;117:27–42. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE R. M., HAHN J. J. Cell wall replication in Streptococcus pyogenes. Science. 1962 Mar 2;135(3505):722–724. doi: 10.1126/science.135.3505.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen R. G., Marshall J. M. A study of phagocytosis in the ameba Chaos chaos. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3):443–457. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A. The structure and function of monocytes and macrophages. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:163–214. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60443-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman S. E., van de Rijn I., Bleiweis A. S. Lysis of grouped and ungrouped streptococci by lysozyme. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):563–569. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.563-569.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont A., Robert A. Electron microscopic study of phagocytosis of Histoplasma capsulatum by hamster peritoneal macrophages. Lab Invest. 1970 Sep;23(3):278–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERHARDT P., JUDGE J. A. POROSITY OF ISOLATED CELL WALLS OF SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE AND BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. J Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:945–951. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.4.945-951.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILL F. A., COLE R. M. THE FATE OF A BACTERIAL ANTIGEN (STREPTOCOCCAL M PROTEIN) AFTER PHAGOCYTOSIS BY MACROPHAGES. J Immunol. 1965 Jun;94:898–915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg I., Gallis H. A., Cole R. M. Group A streptococci: localization in rabbits and guinea pigs following tissue injury. Science. 1969 Nov 28;166(3909):1161–1163. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3909.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Pooley H. M., Shockman G. D. Site of initiation of cellular autolysis in Streptococcus faecalis as seen by electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):504–512. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.504-512.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R. G., Koenig M. G., Goodman J. S., Collins R. D. Phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus by hepatic reticuloendothelial cells. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1969 Nov;21(5):406–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANTOR F. S. FATE OF STREPTOCOCCAL M PROTEIN AFTER EXPOSURE TO PLASMIN AND HUMAN LEUKOCYTES. Yale J Biol Med. 1964 Feb;36:259–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. Autolytic release and osmotic properties of protoplasts from Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):184–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORTH R. J., MACKANESS G. B. ELECTRON MICROSCOPICAL OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERITONEAL MACROPHAGES OF NORMAL MICE AND MICE IMMUNISED WITH LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. I. STRUCTURE OF NORMAL MACROPHAGES AND THE EARLY CYTOPLASMIC RESPONSE TO THE PRESENCE OF INGESTED BACTERIA. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Dec;44:601–607. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohanian S. H., Schwab J. H., Cromartie W. J. Relation of rheumatic-like cardiac lesions of the mouse to localization of group A streptococcal cell walls. J Exp Med. 1969 Jan 1;129(1):37–49. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohanian S. H., Schwab J. H. Persistence of group a streptococcal cell walls related to chronic inflammation of rabbit dermal connective tissue. J Exp Med. 1967 Jun 1;125(6):1137–1148. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.6.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E., BIRCHANDERSEN A., MAALOE O. Etude au microscope électronique de plasmas contenant de l'acide désoxyribonucliéique. I. Les nucléoides des bactéries en croissance active. Z Naturforsch B. 1958 Sep;13B(9):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranhand J. M., Leonard C. G., Cole R. M. Autolytic activity associated with competent group H streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):257–268. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.257-268.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles N., Zilberstein Z., Kraus S., Arad G., Kaufstein M., Ginsburg I. Persistence of group A streptococci labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate in inflammatory sites in the heart and muscle of mice and rabbits. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jun;131(2):525–530. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLADE H. D., SLAMP W. C. Studies on Streptococcus pyogenes. V. Biochemical and microscopic aspects of cell lysis and digestion by enzymes from Streptomyces albus. J Bacteriol. 1960 Jan;79:103–112. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.1.103-112.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H. Biological properties of streptococcal cell-wall particles. I. Determinants of the chronic nodular lesion of connective tissue. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1405–1411. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1405-1411.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H., Cromartie W. J., Ohanian S. H., Craddock J. G. Association of experimental chronic arthritis with the persistence of group A streptococcal cell walls in the articular tissue. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1728–1735. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1728-1735.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D., Martin J. T. Autolytic enzyme system of Streptococcus faecalis. IV. Electron microscopic observations of autolysin and lysozyme action. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1803–1810. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1803-1810.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Hsu K. C., Gotschlich E. C. Electron microscopic studies on streptococci. I. M antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Nov 1;130(5):1063–1091. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.5.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON A. T., WILEY G. G., BRUNO P. Fate of non-virulent group A streptococci phagocytized by human and mouse neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1957 Dec 1;106(6):777–786. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.6.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiri N., Bentwich Z., Boss J. H., Ginsburg I., Harris T. N. Organ Lesions Produced in Rabbits by Group a Streptococci and Some of their Extracellular Products. Am J Pathol. 1967 Sep;51(3):351–371. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]