Abstract
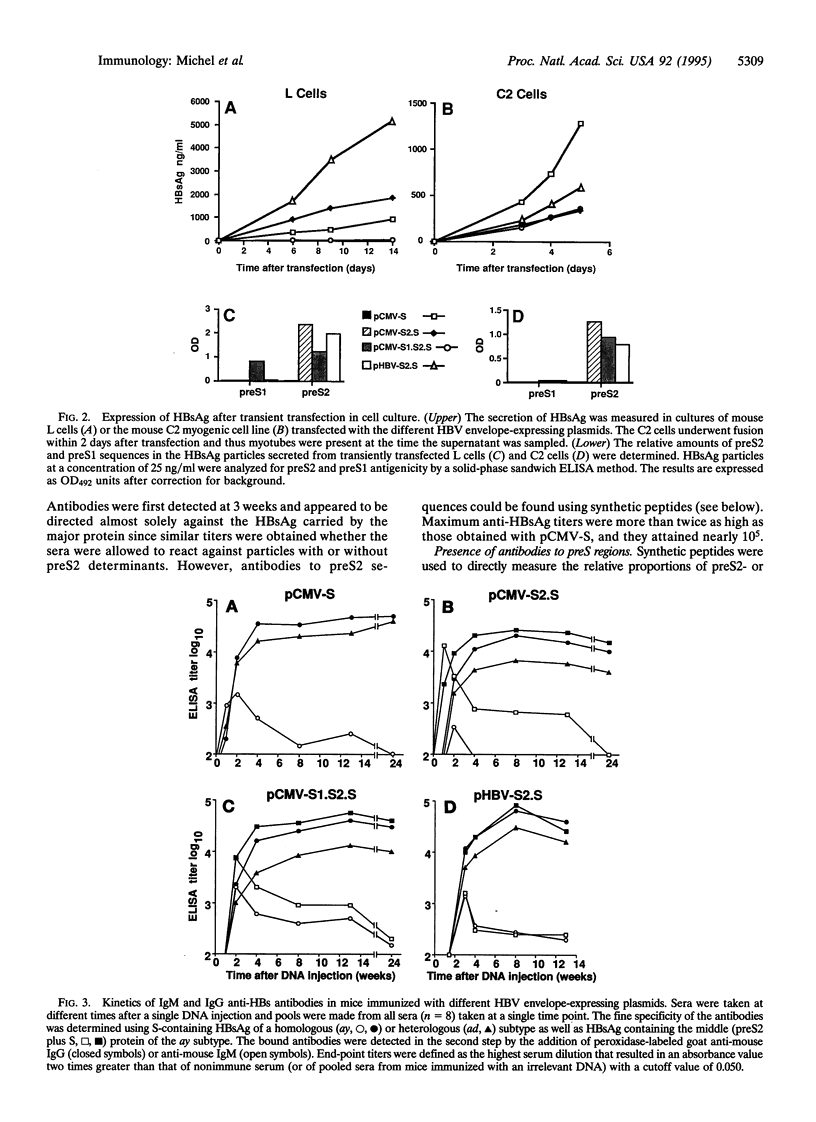
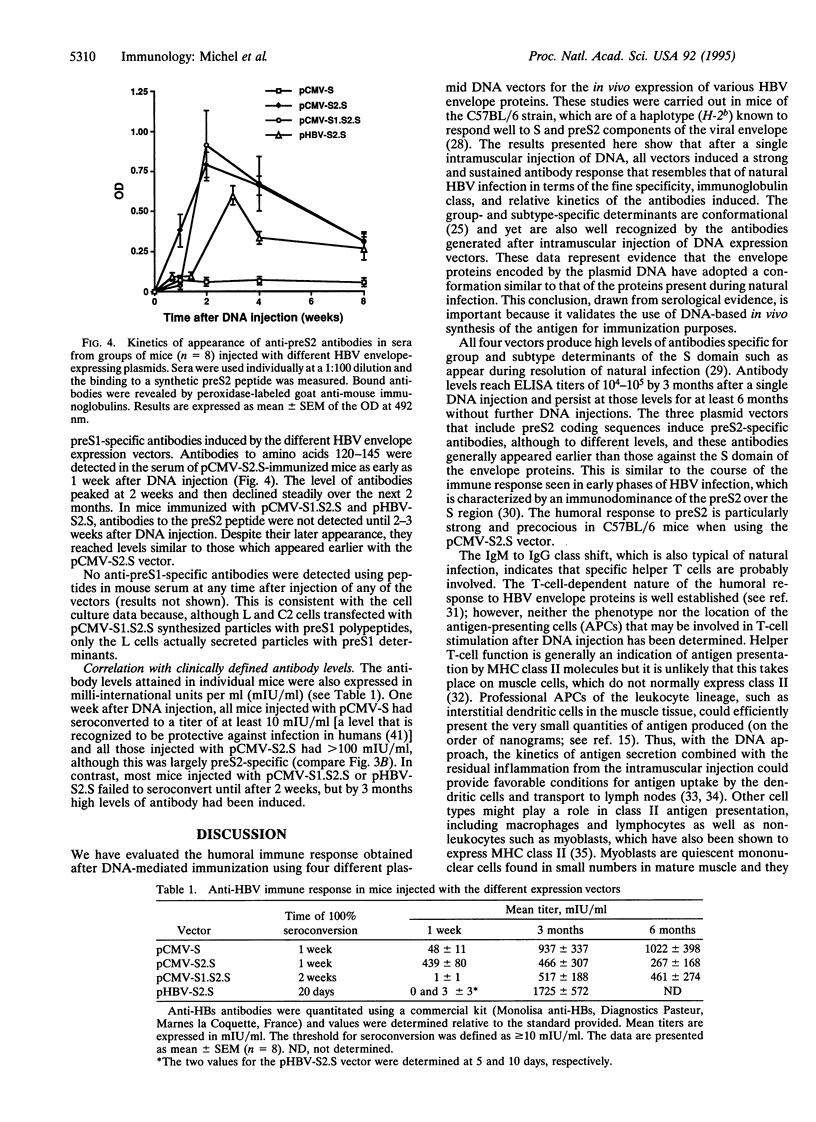
Intramuscular injection of plasmid DNA expression vectors encoding the three envelope proteins of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) induced humoral responses in C57BL/6 mice specific to several antigenic determinants of the viral envelope. The first antibodies appeared within 1-2 weeks after injection of DNA and included antibodies of the IgM isotype. Over the next few weeks, an IgM to IgG class switch occurred, indicating helper T-lymphocyte activity. Peak IgG titers were reached by 4-8 weeks after a single DNA injection and were maintained for at least 6 months without further DNA injections. The antibodies to the envelope proteins reacted with group- and subtype-specific antigenic determinants of the HBV surface antigen (HBsAg). Expression vectors encoding the major (S) and middle (preS2 plus S) envelope proteins induced antibodies specific to the S protein and preS2 domain, and preS2 antibodies were prominent at early time points. In general, the expression vectors induced humoral responses in mice that mimic those observed in humans during the course of natural HBV infection.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti A., Cavalletto D., Pontisso P., Chemello L., Tagariello G., Belussi F. Antibody response to pre-S2 and hepatitis B virus induced liver damage. Lancet. 1988 Jun 25;1(8600):1421–1424. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92237-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austyn J. M. Antigen uptake and presentation by dendritic leukocytes. Semin Immunol. 1992 Aug;4(4):227–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budkowska A., Dubreuil P., Poynard T., Marcellin P., Loriot M. A., Maillard P., Pillot J. Anti-pre-S responses and viral clearance in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 1992 Jan;15(1):26–31. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budkowska A., Riottot M. M., Dubreuil P., Lazizi Y., Brechot C., Sobczak E., Petit M. A., Pillot J. Monoclonal antibody recognizing pre-S(2) epitope of hepatitis B virus: characterization of pre-S(2) epitope and anti-pre-S(2) antibody. J Med Virol. 1986 Oct;20(2):111–125. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890200204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. J., Zamb T. J., Babiuk L. A. Bovine herpesvirus 1: immune responses in mice and cattle injected with plasmid DNA. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5664–5667. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5664-5667.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis H. L., Demeneix B. A., Quantin B., Coulombe J., Whalen R. G. Plasmid DNA is superior to viral vectors for direct gene transfer into adult mouse skeletal muscle. Hum Gene Ther. 1993 Dec;4(6):733–740. doi: 10.1089/hum.1993.4.6-733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis H. L., Michel M. L., Mancini M., Schleef M., Whalen R. G. Direct gene transfer in skeletal muscle: plasmid DNA-based immunization against the hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Vaccine. 1994 Dec;12(16):1503–1509. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(94)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis H. L., Michel M. L., Whalen R. G. DNA-based immunization induces continuous secretion of hepatitis B surface antigen and high levels of circulating antibody. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Nov;2(11):1847–1851. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.11.1847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois M. F., Pourcel C., Rousset S., Chany C., Tiollais P. Excretion of hepatitis B surface antigen particles from mouse cells transformed with cloned viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4549–4553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fynan E. F., Robinson H. L., Webster R. G. Use of DNA encoding influenza hemagglutinin as an avian influenza vaccine. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;12(9):785–789. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fynan E. F., Webster R. G., Fuller D. H., Haynes J. R., Santoro J. C., Robinson H. L. DNA vaccines: protective immunizations by parenteral, mucosal, and gene-gun inoculations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11478–11482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebels N., Michaelis D., Wekerle H., Hohlfeld R. Human myoblasts as antigen-presenting cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):661–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld R., Engel A. G. The immunobiology of muscle. Immunol Today. 1994 Jun;15(6):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90006-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H. Type B hepatitis: virology, serology and clinical course. Semin Liver Dis. 1981 Feb;1(1):7–14. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1063925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Takai E., Ohnuma H., Kitajima K., Tsuda F., Machida A., Mishiro S., Nakamura T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. A synthetic peptide vaccine involving the product of the pre-S(2) region of hepatitis B virus DNA: protective efficacy in chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9174–9178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzavecchia A. Identifying strategies for immune intervention. Science. 1993 May 14;260(5110):937–944. doi: 10.1126/science.8493532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini M., Hadchouel M., Tiollais P., Pourcel C., Michel M. L. Induction of anti-hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) antibodies in HBsAg producing transgenic mice: a possible way of circumventing "nonresponse" to HBsAg. J Med Virol. 1993 Jan;39(1):67–74. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890390113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. L., Pontisso P., Sobczak E., Malpièce Y., Streeck R. E., Tiollais P. Synthesis in animal cells of hepatitis B surface antigen particles carrying a receptor for polymerized human serum albumin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7708–7712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., McLachlan A., Chisari F. V., Kent S. B., Thorton G. B. Immune response to the pre-S(1) region of the hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg): a pre-S(1)-specific T cell response can bypass nonresponsiveness to the pre-S(2) and S regions of HBsAg. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):315–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R. T- and B-cell recognition of hepatitis B viral antigens. Immunol Today. 1988 Dec;9(12):380–386. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91239-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman G., Herzberg M. Efficient DNA transfection and rapid assay for thymidine kinase activity and viral antigenic determinants. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Mar;7(2):161–170. doi: 10.1007/BF01567655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery D. L., Shiver J. W., Leander K. R., Perry H. C., Friedman A., Martinez D., Ulmer J. B., Donnelly J. J., Liu M. A. Heterologous and homologous protection against influenza A by DNA vaccination: optimization of DNA vectors. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;12(9):777–783. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Adamowicz P., Kent S. B., Riottot M. M., Strick N., Parker K., Offensperger W., Petit M. A., Wahl S., Budkowska A. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for the pre-S2 region of the hepatitis B virus envelope protein. Mol Immunol. 1986 Sep;23(9):991–997. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Parker K., Prince A. M., Strick N., Brotman B., Sproul P. Antibodies to a synthetic peptide from the preS 120-145 region of the hepatitis B virus envelope are virus neutralizing. Vaccine. 1986 Mar;4(1):35–37. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(86)80001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N., Taylor P., Stevens C. E. Hepatitis B virus contains pre-S gene-encoded domains. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):154–156. doi: 10.1038/315154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. L., Nath N., Gavilanes F. Structure of hepatitis B surface antigen. Correlation of subtype with amino acid sequence and location of the carbohydrate moiety. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10414–10420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Hunt L. A., Webster R. G. Protection against a lethal influenza virus challenge by immunization with a haemagglutinin-expressing plasmid DNA. Vaccine. 1993;11(9):957–960. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(93)90385-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedegah M., Hedstrom R., Hobart P., Hoffman S. L. Protection against malaria by immunization with plasmid DNA encoding circumsporozoite protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):9866–9870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda S., North D. L., Lakich M. M., Russell S. D., Whalen R. G. A possible regulatory role for conserved promoter motifs in an adult-specific muscle myosin gene from mouse. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16957–16967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe C. J. Outsize peptides bulge out of the groove. Immunol Today. 1993 Feb;14(2):51–52. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90057-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Pourcel C., Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):489–495. doi: 10.1038/317489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmer J. B., Donnelly J. J., Parker S. E., Rhodes G. H., Felgner P. L., Dwarki V. J., Gromkowski S. H., Deck R. R., DeWitt C. M., Friedman A. Heterologous protection against influenza by injection of DNA encoding a viral protein. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1745–1749. doi: 10.1126/science.8456302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B., Boyer J., Srikantan V., Coney L., Carrano R., Phan C., Merva M., Dang K., Agadjanan M., Gilbert L. DNA inoculation induces neutralizing immune responses against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in mice and nonhuman primates. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;12(9):799–805. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B., Ugen K. E., Srikantan V., Agadjanyan M. G., Dang K., Refaeli Y., Sato A. I., Boyer J., Williams W. V., Weiner D. B. Gene inoculation generates immune responses against human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4156–4160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Davis H. L. DNA-mediated immunization and the energetic immune response to hepatitis B surface antigen. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995 Apr;75(1):1–12. doi: 10.1006/clin.1995.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Harris J. B., Butler-Browne G. S., Sesodia S. Expression of myosin isoforms during notexin-induced regeneration of rat soleus muscles. Dev Biol. 1990 Sep;141(1):24–40. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang Z. Q., Spitalnik S., Tran M., Wunner W. H., Cheng J., Ertl H. C. Vaccination with a plasmid vector carrying the rabies virus glycoprotein gene induces protective immunity against rabies virus. Virology. 1994 Feb 15;199(1):132–140. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankauckas M. A., Morrow J. E., Parker S. E., Abai A., Rhodes G. H., Dwarki V. J., Gromkowski S. H. Long-term anti-nucleoprotein cellular and humoral immunity is induced by intramuscular injection of plasmid DNA containing NP gene. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;12(9):771–776. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]