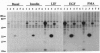
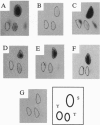
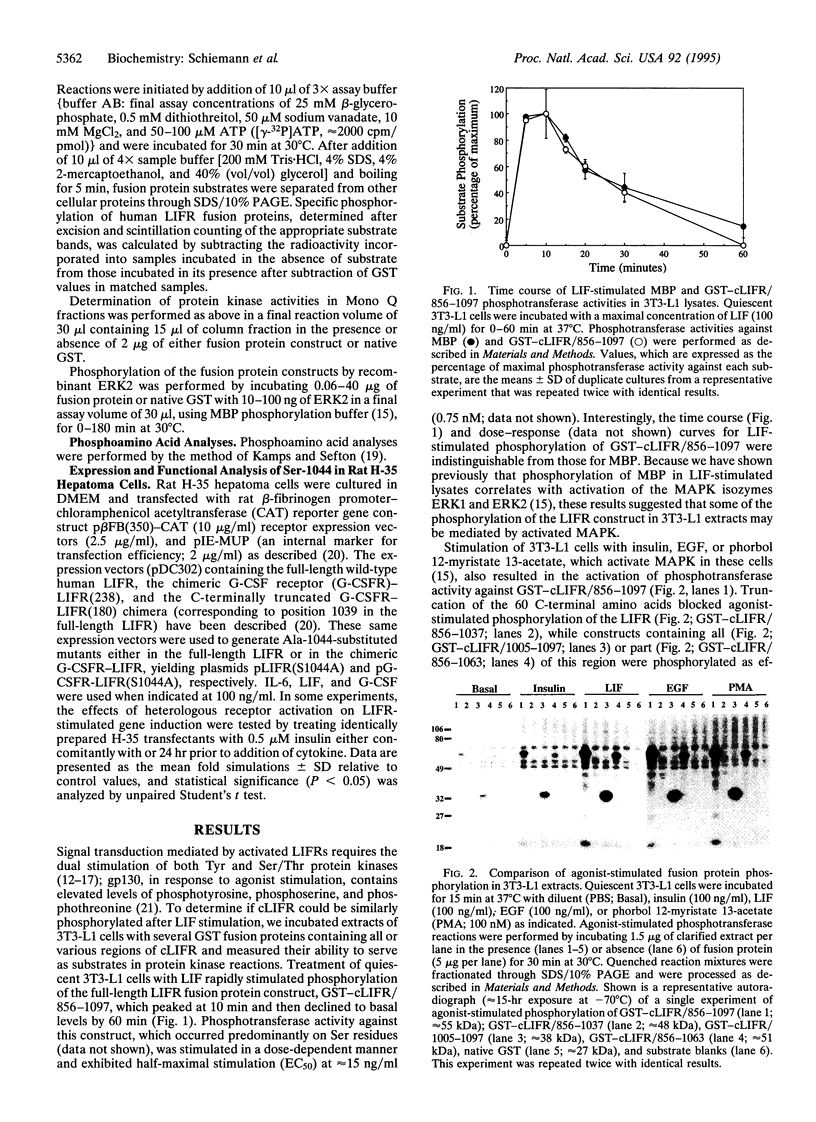
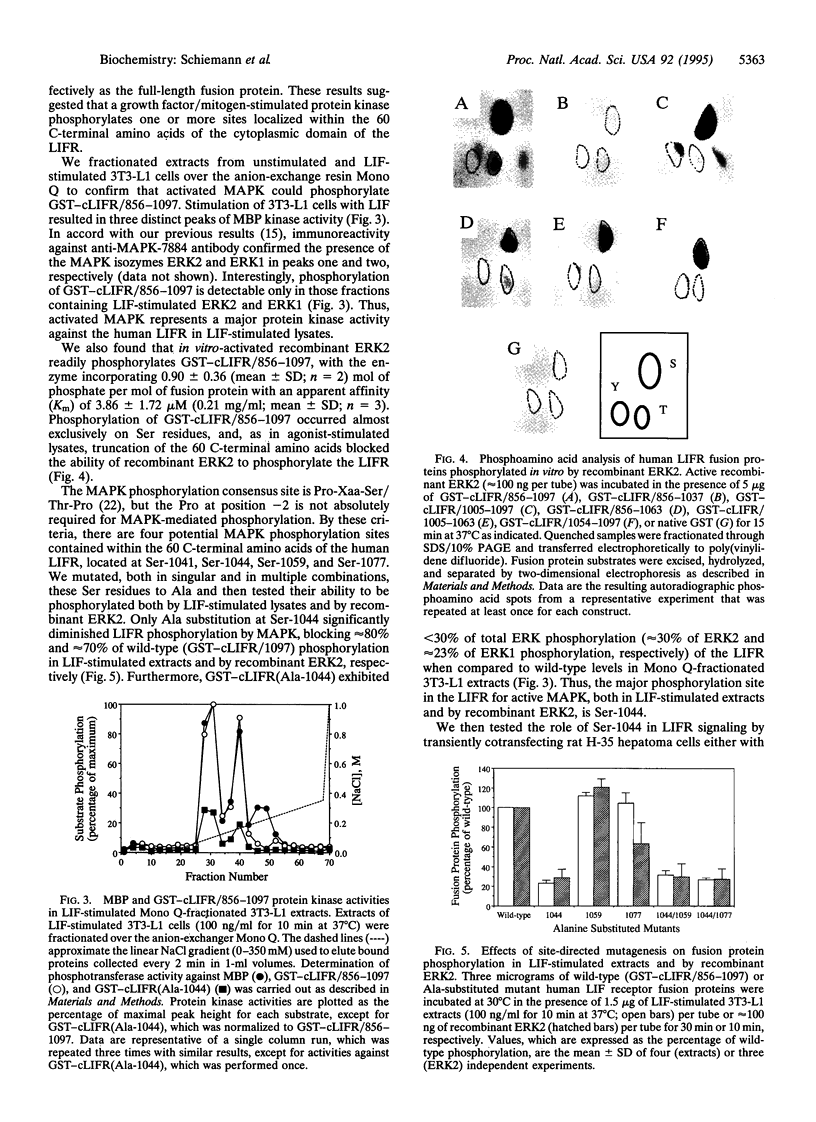
Abstract
We used a bacterially expressed fusion protein containing the entire cytoplasmic domain of the human leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) receptor to study its phosphorylation in response to LIF stimulation. The dose- and time-dependent relationships for phosphorylation of this construct in extracts of LIF-stimulated 3T3-L1 cells were superimposable with those for the stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Indeed, phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic domain of the low-affinity LIF receptor alpha-subunit (LIFR) in Mono Q-fractionated, LIF-stimulated 3T3-L1 extracts occurred only in those fractions containing activated MAPK; Ser-1044 served as the major phosphorylation site in the human LIFR for MAPK both in agonist-stimulated 3T3-L1 lysates and by recombinant extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 in vitro. Expression in rat H-35 hepatoma cells of LIFR or chimeric granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor receptor (G-CSFR)-LIFR mutants lacking Ser-1044 failed to affect cytokine-stimulated expression of a reporter gene under the control of the beta-fibrinogen gene promoter but eliminated the insulin-induced attenuation of cytokine-stimulated gene expression. Thus, our results identify the human LIFR as a substrate for MAPK and suggest a mechanism of heterologous receptor regulation of LIFR signaling occurring at Ser-1044.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez E., Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Latour D. A., Seth A., Abate C., Curran T., Davis R. J. Pro-Leu-Ser/Thr-Pro is a consensus primary sequence for substrate protein phosphorylation. Characterization of the phosphorylation of c-myc and c-jun proteins by an epidermal growth factor receptor threonine 669 protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15277–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Gearing D., Ziegler S. F. Signaling by the cytoplasmic domain of hematopoietin receptors involves two distinguishable mechanisms in hepatic cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 10;269(23):16297–16304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Symes A. J., Comeau M. R., Morella K. K., Wang Y., Friend D., Ziegler S. F., Fink J. S., Gearing D. P. Multiple regions within the cytoplasmic domains of the leukemia inhibitory factor receptor and gp130 cooperate in signal transduction in hepatic and neuronal cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):138–146. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Ziegler S. F., Mosley B., Morella K. K., Pajovic S., Gearing D. P. Reconstitution of the response to leukemia inhibitory factor, oncostatin M, and ciliary neurotrophic factor in hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8414–8417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Neuropoietic cytokines in the hematopoietic fold. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):197–208. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90258-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos S. P., Baumann H. Insulin is a prominent modulator of the cytokine-stimulated expression of acute-phase plasma protein genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1789–1797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Aldrich T. H., Valenzuela D. M., Wong V. V., Furth M. E., Squinto S. P., Yancopoulos G. D. The receptor for ciliary neurotrophic factor. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.1648265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Comeau M. R., Friend D. J., Gimpel S. D., Thut C. J., McGourty J., Brasher K. K., King J. A., Gillis S., Mosley B. The IL-6 signal transducer, gp130: an oncostatin M receptor and affinity converter for the LIF receptor. Science. 1992 Mar 13;255(5050):1434–1437. doi: 10.1126/science.1542794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Thut C. J., VandeBos T., Gimpel S. D., Delaney P. B., King J., Price V., Cosman D., Beckmann M. P. Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor is structurally related to the IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2839–2848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Murakami M., Saito M., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1149–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90411-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton D. J., Gough N. M. Leukemia inhibitory factor: a biological perspective. J Cell Biochem. 1991 May;46(1):21–26. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240460105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton D. J. LIF: lots of interesting functions. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Feb;17(2):72–76. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90505-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Nye S. H., Boulton T. G., Davis S., Taga T., Li Y., Birren S. J., Yasukawa K., Kishimoto T., Anderson D. J. CNTF and LIF act on neuronal cells via shared signaling pathways that involve the IL-6 signal transducing receptor component gp130. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1121–1132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90634-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Acid and base hydrolysis of phosphoproteins bound to immobilon facilitates analysis of phosphoamino acids in gel-fractionated proteins. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jan;176(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Modrell B., Aruffo A., Marken J. S., Taga T., Yasukawa K., Murakami M., Kishimoto T., Shoyab M. Interleukin-6 signal transducer gp130 mediates oncostatin M signaling. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16763–16766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord K. A., Abdollahi A., Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., Brugge J. S., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Leukemia inhibitory factor and interleukin-6 trigger the same immediate early response, including tyrosine phosphorylation, upon induction of myeloid leukemia differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4371–4379. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Hibi M., Nakagawa N., Nakagawa T., Yasukawa K., Yamanishi K., Taga T., Kishimoto T. IL-6-induced homodimerization of gp130 and associated activation of a tyrosine kinase. Science. 1993 Jun 18;260(5115):1808–1810. doi: 10.1126/science.8511589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Narazaki M., Hibi M., Yawata H., Yasukawa K., Hamaguchi M., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Critical cytoplasmic region of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130 is conserved in the cytokine receptor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11349–11353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Charest D. L., Mordret G. P., Siow Y. L., Palaty C., Campbell D., Charlton L., Samiei M., Sanghera J. S. Networking with mitogen-activated protein kinases. Mol Cell Biochem. 1993 Nov;127-128:157–169. doi: 10.1007/BF01076767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann W. P., Nathanson N. M. Involvement of protein kinase C during activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade by leukemia inhibitory factor. Evidence for participation of multiple signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6376–6382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Boulton T. G., Farruggella T., Ip N. Y., Davis S., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Silvennoinen O., Barbieri G., Pellegrini S. Association and activation of Jak-Tyk kinases by CNTF-LIF-OSM-IL-6 beta receptor components. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8272873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma B., Bird T. A., Friend D. J., Gearing D. P., Dower S. K. Oncostatin M and leukemia inhibitory factor trigger overlapping and different signals through partially shared receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):6215–6222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K., Taga T., Hirata Y., Yawata H., Kawanishi Y., Seed B., Taniguchi T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Cloning and expression of the human interleukin-6 (BSF-2/IFN beta 2) receptor. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):825–828. doi: 10.1126/science.3136546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin T., Yang Y. C. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and ribosomal S6 protein kinases are involved in signaling pathways shared by interleukin-11, interleukin-6, leukemia inhibitory factor, and oncostatin M in mouse 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3731–3738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]