Abstract
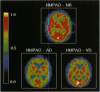
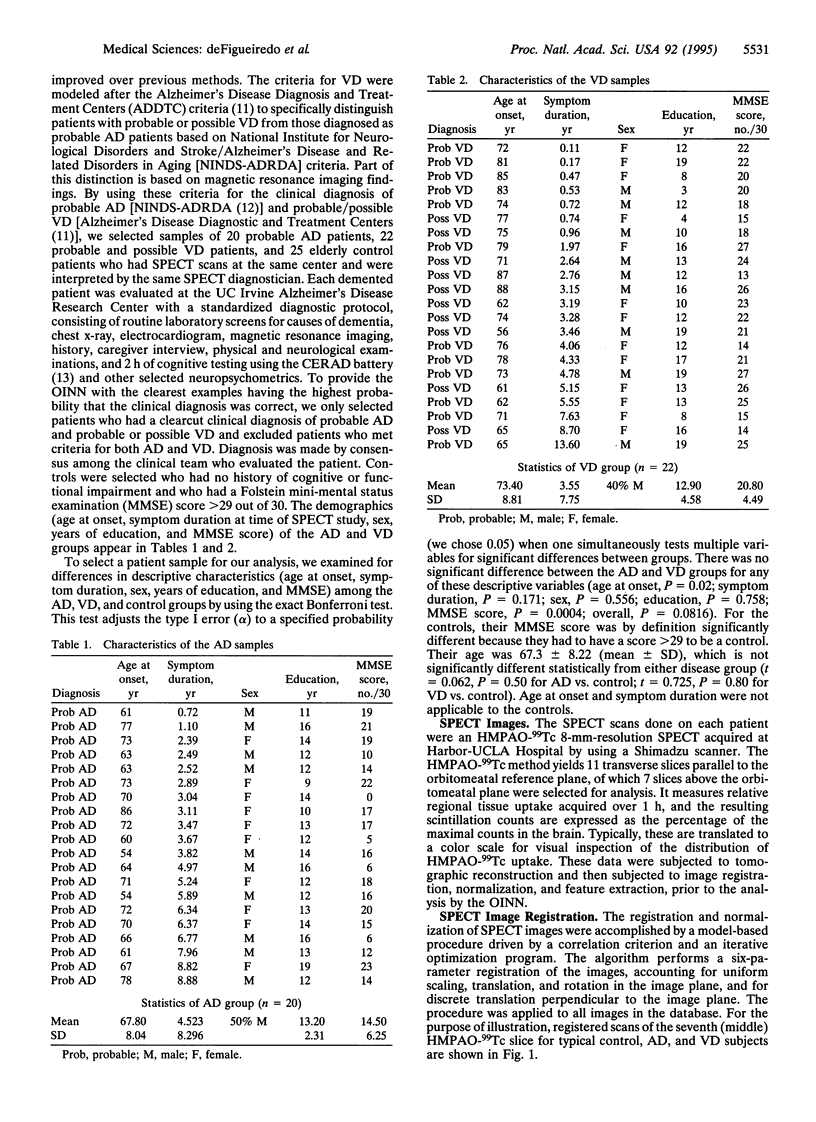
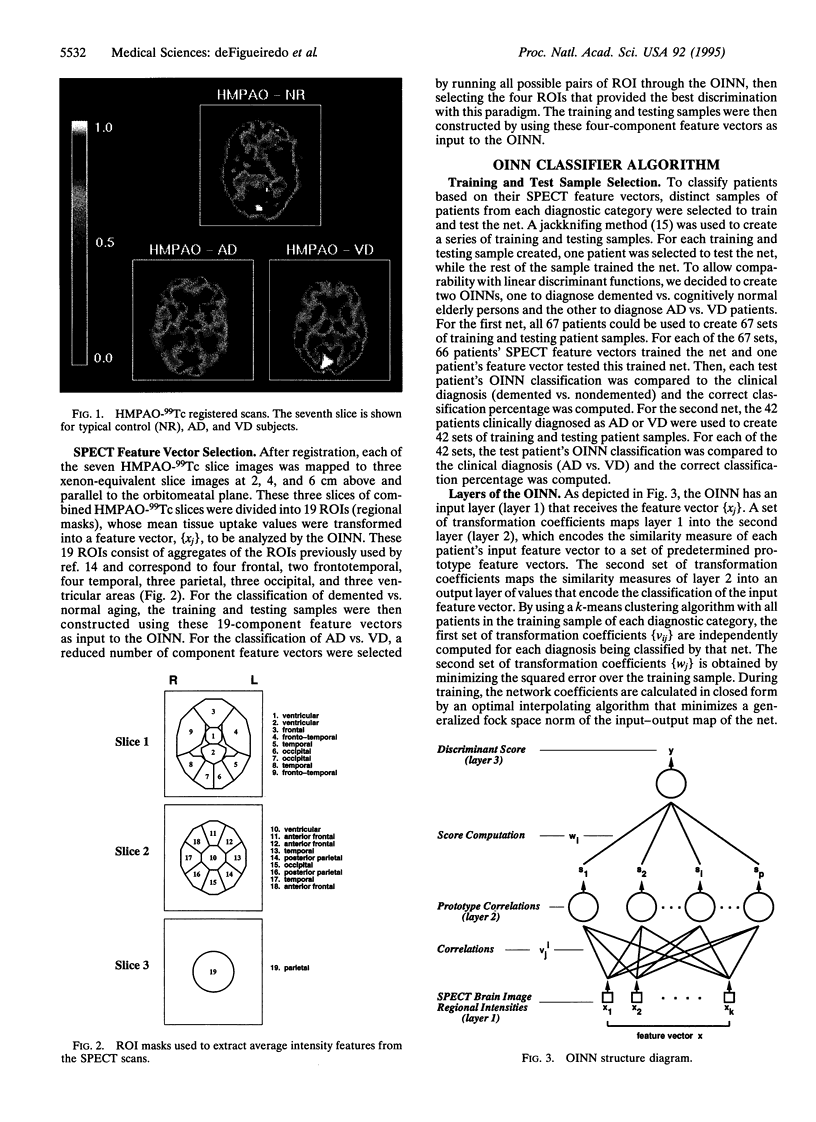
Single photon emission with computed tomography (SPECT) hexamethylphenylethyleneamineoxime technetium-99 images were analyzed by an optimal interpolative neural network (OINN) algorithm to determine whether the network could discriminate among clinically diagnosed groups of elderly normal, Alzheimer disease (AD), and vascular dementia (VD) subjects. After initial image preprocessing and registration, image features were obtained that were representative of the mean regional tissue uptake. These features were extracted from a given image by averaging the intensities over various regions defined by suitable masks. After training, the network classified independent trials of patients whose clinical diagnoses conformed to published criteria for probable AD or probable/possible VD. For the SPECT data used in the current tests, the OINN agreement was 80 and 86% for probable AD and probable/possible VD, respectively. These results suggest that artificial neural network methods offer potential in diagnoses from brain images and possibly in other areas of scientific research where complex patterns of data may have scientifically meaningful groupings that are not easily identifiable by the researcher.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chui H. C., Victoroff J. I., Margolin D., Jagust W., Shankle R., Katzman R. Criteria for the diagnosis of ischemic vascular dementia proposed by the State of California Alzheimer's Disease Diagnostic and Treatment Centers. Neurology. 1992 Mar;42(3 Pt 1):473–480. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.3.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. C., Gray L., Albert M., Wilkinson W., Hughes J., Heyman A., Gado M., Kumar A. J., Destian S., Lee C. The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease (CERAD). Part III. Reliability of a standardized MRI evaluation of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1992 Sep;42(9):1676–1680. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.9.1676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettlin T. M., Staehelin H. B., Kischka U., Ulrich J., Scollo-Lavizzari G., Wiggli U., Seiler W. O. Computed tomography, electroencephalography, and clinical features in the differential diagnosis of senile dementia. A prospective clinicopathologic study. Arch Neurol. 1989 Nov;46(11):1217–1220. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1989.00520470081031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell H. G., Sharp P. F., Besson J. A., Crawford J. R., Ebmeier K. P., Davidson J., Smith F. W. Differential diagnosis in dementia using the cerebral blood flow agent 99mTc HM-PAO: a SPECT study. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1987 May-Jun;11(3):398–402. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198705000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg G., Podreka I., Suess E., Deecke L. The cerebral localization of neuropsychological impairment in Alzheimer's disease: a SPECT study. J Neurol. 1989 Mar;236(3):131–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00314327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman A., Fillenbaum G. G., Mirra S. S. Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease (CERAD): clinical, neuropsychological, and neuropathological components. Aging (Milano) 1990 Dec;2(4):415–424. doi: 10.1007/BF03323962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. J. Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata K., Tachibana H., Sugita M., Fukuchi M. A comparative I-123 IMP SPECT study in Binswanger's disease and Alzheimer's disease. Clin Nucl Med. 1993 Apr;18(4):329–336. doi: 10.1097/00003072-199304000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazee A. M., Eskin T. A., Lapham L. W., Gabriel K. R., McDaniel K. D., Hamill R. W. Clinicopathologic correlates in Alzheimer disease: assessment of clinical and pathologic diagnostic criteria. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1993 Fall;7(3):152–164. doi: 10.1097/00002093-199307030-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Launes J., Sulkava R., Erkinjuntti T., Nikkinen P., Lindroth L., Liewendahl K., Iivanainen M. 99Tcm-HMPAO SPECT in suspected dementia. Nucl Med Commun. 1991 Sep;12(9):757–765. doi: 10.1097/00006231-199109000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardo J. V., Fox P. T., Raichle M. E. Localization of a human system for sustained attention by positron emission tomography. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):61–64. doi: 10.1038/349061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riege W. H., Metter E. J. Cognitive and brain imaging measures of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1988 Jan-Feb;9(1):69–86. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(88)80027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shedlack K. J., Hunter R., Wyper D., McLuskie R., Fink G., Goodwin G. M. The pattern of cerebral activity underlying verbal fluency shown by split-dose single photon emission tomography (SPET or SPECT) in normal volunteers. Psychol Med. 1991 Aug;21(3):687–696. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700022327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. W., Besson J. A., Gemmell H. G., Sharp P. F. The use of technetium-99m-HM-PAO in the assessment of patients with dementia and other neuropsychiatric conditions. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1988 Dec;8(6):S116–S122. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1988.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]