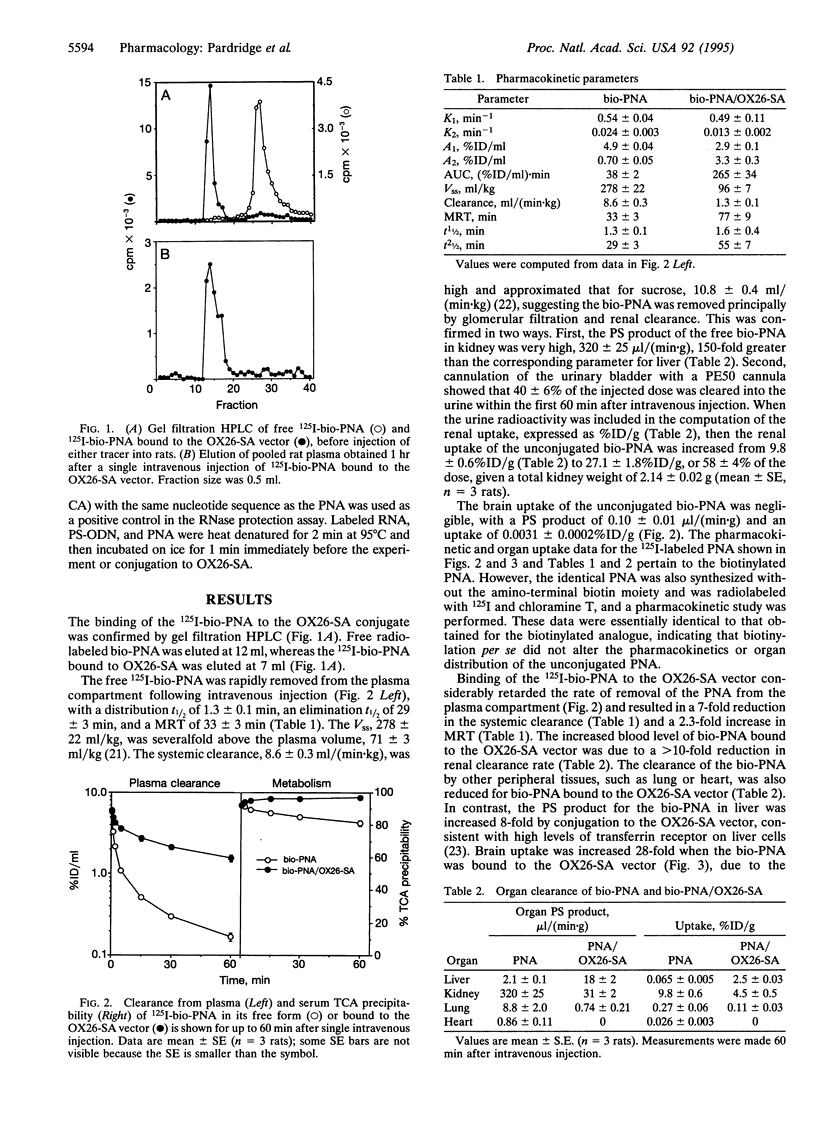
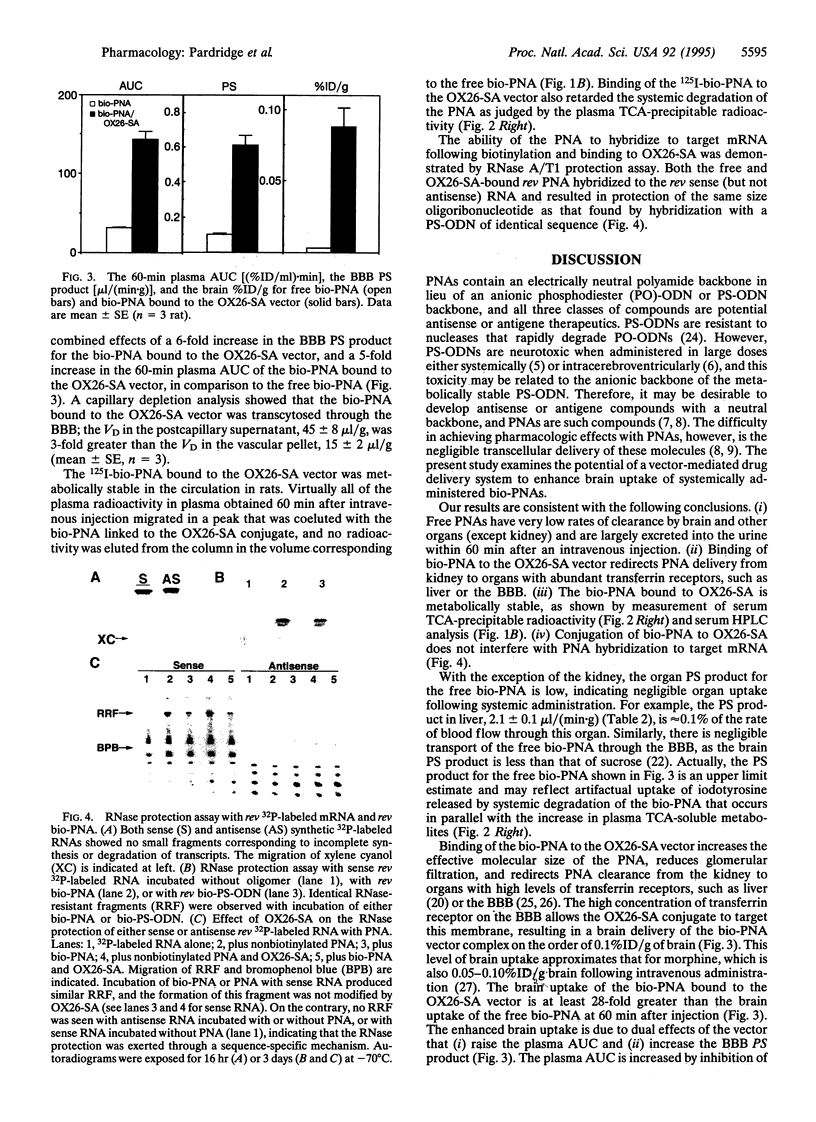
Abstract
Polyamide ("peptide") nucleic acids (PNAs) are molecules with antigene and antisense effects that may prove to be effective neuropharmaceuticals if these molecules are enabled to undergo transport through the brain capillary endothelial wall, which makes up the blood-brain barrier in vivo. The model PNA used in the present studies is an 18-mer that is antisense to the rev gene of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and is biotinylated at the amino terminus and iodinated at a tyrosine residue near the carboxyl terminus. The biotinylated PNA was linked to a conjugate of streptavidin (SA) and the OX26 murine monoclonal antibody to the rat transferrin receptor. The blood-brain barrier is endowed with high transferrin receptor concentrations, enabling the OX26-SA conjugate to deliver the biotinylated PNA to the brain. Although the brain uptake of the free PNA was negligible following intravenous administration, the brain uptake of the PNA was increased at least 28-fold when the PNA was bound to the OX26-SA vector. The brain uptake of the PNA bound to the OX26-SA vector was 0.1% of the injected dose per gram of brain at 60 min after an intravenous injection, approximating the brain uptake of intravenously injected morphine. The PNA bound to the OX26-SA vector retained the ability to bind to synthetic rev mRNA as shown by RNase protection assays. In summary, the present studies show that while the transport of PNAs across the blood-brain barrier is negligible, delivery of these potential neuropharmaceutical drugs to the brain may be achieved by coupling them to vector-mediated peptide-drug delivery systems.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya S. K., Guo C., Josephs S. F., Wong-Staal F. Trans-activator gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III). Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):69–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2990040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickel U., Yoshikawa T., Landaw E. M., Faull K. F., Pardridge W. M. Pharmacologic effects in vivo in brain by vector-mediated peptide drug delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2618–2622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boado R. J., Pardridge W. M. Complete inactivation of target mRNA by biotinylated antisense oligodeoxynucleotide-avidin conjugates. Bioconjug Chem. 1994 Sep-Oct;5(5):406–410. doi: 10.1021/bc00029a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanvey J. C., Peffer N. J., Bisi J. E., Thomson S. A., Cadilla R., Josey J. A., Ricca D. J., Hassman C. F., Bonham M. A., Au K. G. Antisense and antigene properties of peptide nucleic acids. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1481–1485. doi: 10.1126/science.1279811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie S., Kishimoto T., Tavassoli M. Desialation of transferrin by rat liver endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):508–513. doi: 10.1172/JCI113625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferies W. A., Brandon M. R., Hunt S. V., Williams A. F., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. Transferrin receptor on endothelium of brain capillaries. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):162–163. doi: 10.1038/312162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang Y. S., Boado R. J., Pardridge W. M. Pharmacokinetics and organ clearance of a 3'-biotinylated, internally [32P]-labeled phosphodiester oligodeoxynucleotide coupled to a neutral avidin/monoclonal antibody conjugate. Drug Metab Dispos. 1995 Jan;23(1):55–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang Y. S., Pardridge W. M. Brain delivery of biotin bound to a conjugate of neutral avidin and cationized human albumin. Pharm Res. 1994 Sep;11(9):1257–1264. doi: 10.1023/a:1018982125649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang Y. S., Pardridge W. M. Use of neutral avidin improves pharmacokinetics and brain delivery of biotin bound to an avidin-monoclonal antibody conjugate. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Apr;269(1):344–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisziewicz J., Sun D., Metelev V., Zamecnik P., Gallo R. C., Agrawal S. Long-term treatment of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells with antisense oligonucleotide phosphorothioates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3860–3864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. E., Egholm M., Berg R. H., Buchardt O. Peptide nucleic acids (PNAs): potential antisense and anti-gene agents. Anticancer Drug Des. 1993 Feb;8(1):53–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. E., Egholm M., Berg R. H., Buchardt O. Sequence-selective recognition of DNA by strand displacement with a thymine-substituted polyamide. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1497–1500. doi: 10.1126/science.1962210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. E., Egholm M., Buchardt O. Peptide nucleic acid (PNA). A DNA mimic with a peptide backbone. Bioconjug Chem. 1994 Jan-Feb;5(1):3–7. doi: 10.1021/bc00025a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H., Hyman S., Braun L., Oldendorf S. Z. Blood-brain barrier: penetration of morphine, codeine, heroin, and methadone after carotid injection. Science. 1972 Dec 1;178(4064):984–986. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4064.984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M., Eisenberg J., Yang J. Human blood-brain barrier transferrin receptor. Metabolism. 1987 Sep;36(9):892–895. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M., Kang Y. S., Buciak J. L. Transport of human recombinant brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) through the rat blood-brain barrier in vivo using vector-mediated peptide drug delivery. Pharm Res. 1994 May;11(5):738–746. doi: 10.1023/a:1018940732550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatyszek M. A., Jarmolowski A., Augustyniak J. Iodo-Gen-mediated radioiodination of nucleic acids. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;172(2):356–359. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90455-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi G., Pan Y. X., Cheng J., Pasternak G. W. Blockade of morphine analgesia by an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide against the mu receptor. Life Sci. 1994;54(21):PL375–PL379. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samii A., Bickel U., Stroth U., Pardridge W. M. Blood-brain barrier transport of neuropeptides: analysis with a metabolically stable dermorphin analogue. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jul;267(1 Pt 1):E124–E131. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1994.267.1.E124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Cheng Y. C. Antisense oligonucleotides as therapeutic agents--is the bullet really magical? Science. 1993 Aug 20;261(5124):1004–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.8351515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Pilowsky P., Minson J., Arnolda L., Llewellyn-Smith I. J., Chalmers J. c-fos antisense in rostral ventral medulla reduces arterial blood pressure. Am J Physiol. 1994 Apr;266(4 Pt 2):R1418–R1422. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1994.266.4.R1418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlestedt C. Antisense oligonucleotide strategies in neuropharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Feb;15(2):42–46. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlestedt C., Pich E. M., Koob G. F., Yee F., Heilig M. Modulation of anxiety and neuropeptide Y-Y1 receptors by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Science. 1993 Jan 22;259(5094):528–531. doi: 10.1126/science.8380941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitesell L., Geselowitz D., Chavany C., Fahmy B., Walbridge S., Alger J. R., Neckers L. M. Stability, clearance, and disposition of intraventricularly administered oligodeoxynucleotides: implications for therapeutic application within the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4665–4669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



