Abstract
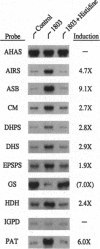
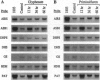
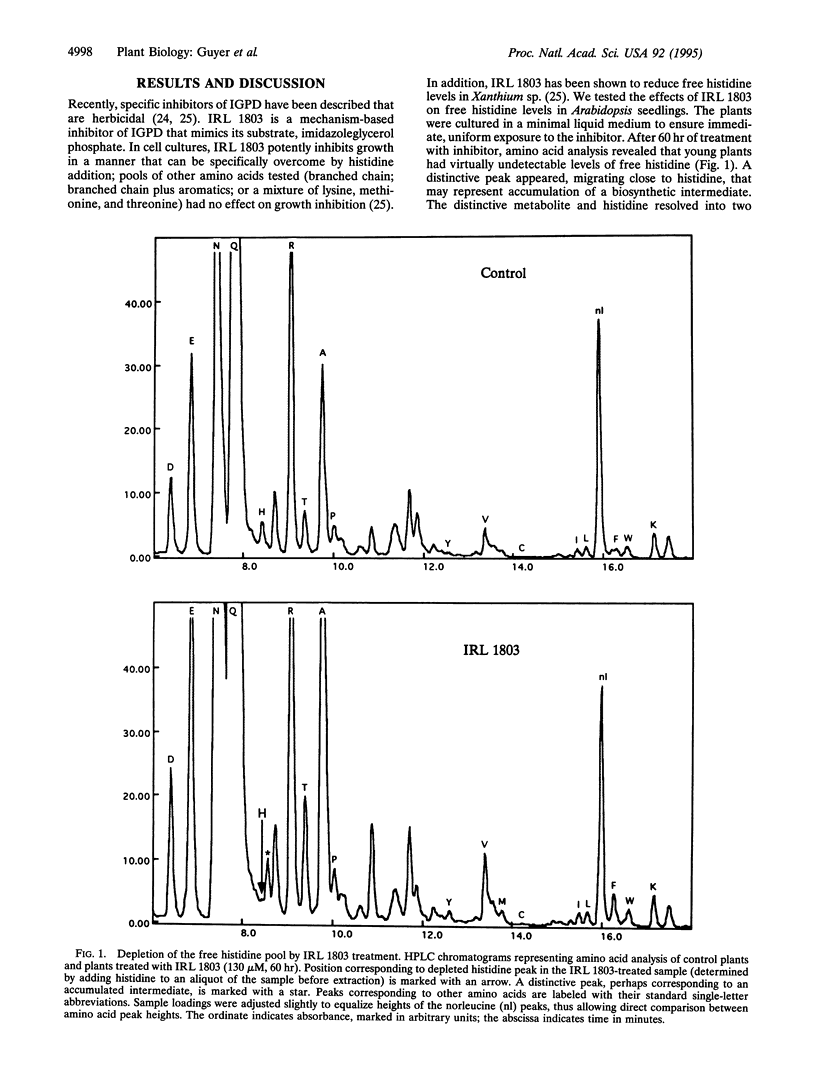
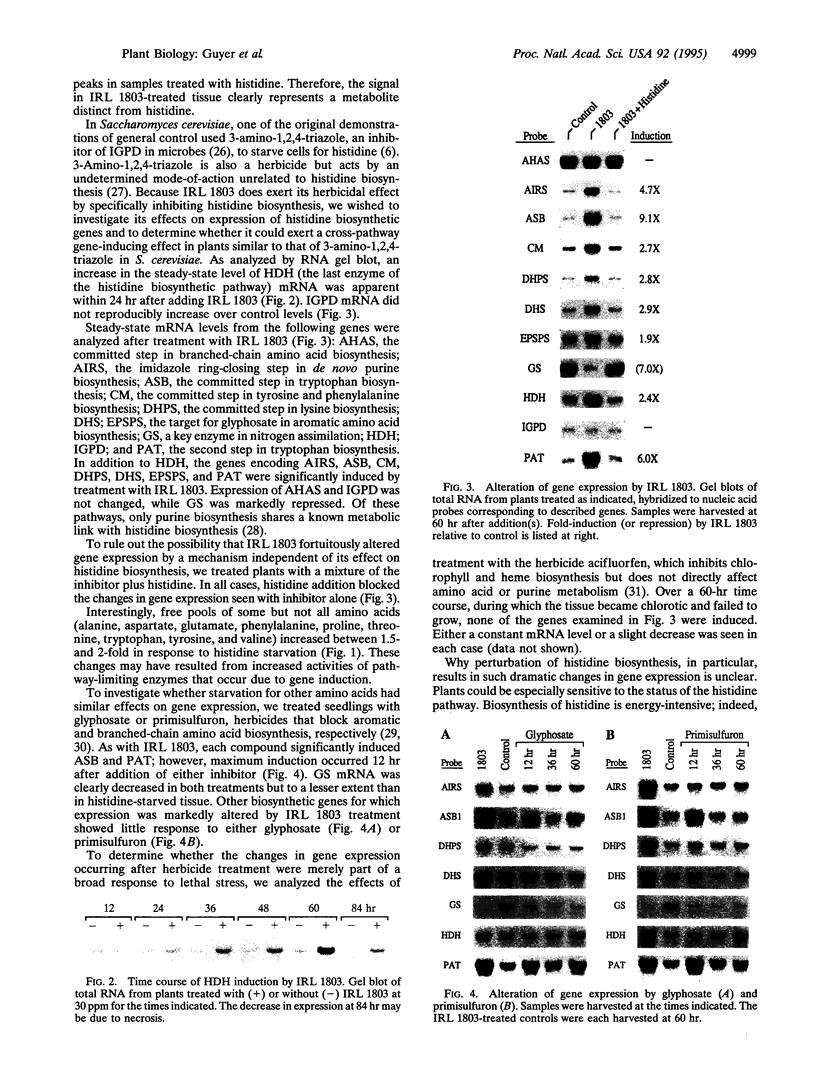
In Arabidopsis thaliana, blocking histidine biosynthesis with a specific inhibitor of imidazoleglycerol-phosphate dehydratase caused increased expression of eight genes involved in the biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids, histidine, lysine, and purines. A decrease in expression of glutamine synthetase was also observed. Addition of histidine eliminated the gene-regulating effects of the inhibitor, demonstrating that the changes in gene expression resulted from histidine-pathway blockage. These results show that plants are capable of cross-pathway metabolic regulation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CARSIOTIS M., LACY A. M. INCREASED ACTIVITY OF TRYPTOPHAN BIOSYNTHETIC ENZYMES IN HISTIDINE MUTANTS OF NEUROSPORA CRASSA. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1472–1477. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1472-1477.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carsiotis M., Jones R. F., Wesseling A. C. Cross-pathway regulation: histidine-mediated control of histidine, tryptophan, and arginine biosynthetic enzymes in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):893–898. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.893-898.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebbole D. J., Paluh J. L., Plamann M., Sachs M. S., Yanofsky C. cpc-1, the general regulatory gene for genes of amino acid biosynthesis in Neurospora crassa, is differentially expressed during the asexual life cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):928–934. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard J., Raesecke H. R., Schmid J., Amrhein N. Cloning and expression in yeast of a higher plant chorismate mutase. Molecular cloning, sequencing of the cDNA and characterization of the Arabidopsis thaliana enzyme expressed in yeast. FEBS Lett. 1993 Nov 15;334(2):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81718-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch D. A., Tommey A. M., Gengenbach B. G., Somers D. A. Direct genetic selection of a maize cDNA for dihydrodipicolinate synthase in an Escherichia coli dapA- auxotroph. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):287–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00282478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S. Bacterial regulation: global regulatory networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:415–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.002215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heim D. R., Larrinua I. M. Primary Site of Action of Amitrole in Arabidopsis thaliana Involves Inhibition of Root Elongation but Not of Histidine or Pigment Biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1989 Nov;91(3):1226–1231. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.3.1226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton J. L., Kearney P. C., Ames B. N. Mode of action of the herbicide, 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole(amitrole): inhibition of an enzyme of histidine biosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Dec;112(3):544–547. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston H. M., Roth J. R. Histidine mutants requiring adenine: selection of mutants with reduced hisG expression in Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1979 May;92(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko T., Hashimoto T., Kumpaisal R., Yamada Y. Molecular cloning of wheat dihydrodipicolinate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17451–17455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith B., Dong X. N., Ausubel F. M., Fink G. R. Differential induction of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate synthase genes in Arabidopsis thaliana by wounding and pathogenic attack. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8821–8825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee H. J., Muskopf Y. M., Gasser C. S. Cloning of an Arabidopsis thaliana gene encoding 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase: sequence analysis and manipulation to obtain glyphosate-tolerant plants. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(3):437–442. doi: 10.1007/BF00327194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matringe M., Camadro J. M., Labbe P., Scalla R. Protoporphyrinogen oxidase as a molecular target for diphenyl ether herbicides. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):231–235. doi: 10.1042/bj2600231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur B. J., Chui C. F., Smith J. K. Isolation and characterization of plant genes coding for acetolactate synthase, the target enzyme for two classes of herbicides. Plant Physiol. 1987 Dec;85(4):1110–1117. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.4.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori I., Fonne-Pfister R., Matsunaga Si., Tada S., Kimura Y., Iwasaki G., Mano Ji., Hatano M., Nakano T., Koizumi Si. A Novel Class of Herbicides (Specific Inhibitors of Imidazoleglycerol Phosphate Dehydratase). Plant Physiol. 1995 Mar;107(3):719–723. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai A., Ward E., Beck J., Tada S., Chang J. Y., Scheidegger A., Ryals J. Structural and functional conservation of histidinol dehydrogenase between plants and microbes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4133–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederberger P., Miozzari G., Hütter R. Biological role of the general control of amino acid biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;1(7):584–593. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.7.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niyogi K. K., Last R. L., Fink G. R., Keith B. Suppressors of trp1 fluorescence identify a new arabidopsis gene, TRP4, encoding the anthranilate synthase beta subunit. Plant Cell. 1993 Sep;5(9):1011–1027. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.9.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil S. S. Inhibition of Ornithin Carbamyl Transferase from Bean Plants by the Toxin of Pseudomonas phaseolicola. Plant Physiol. 1970 Nov;46(5):752–753. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.5.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterman T. K., Goodman H. M. The glutamine synthetase gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana: light-regulation and differential expression in leaves, roots and seeds. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Nov;230(1-2):145–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00290662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto J. E., Dyer W. E., Weller S. C., Herrmann K. M. Glyphosate Induces 3-Deoxy-d-arabino-Heptulosonate 7-Phosphate Synthase in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) Cells Grown in Suspension Culture. Plant Physiol. 1988 Aug;87(4):891–893. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.4.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schürch A., Miozzari J., Hütter R. Regulation of tryptophan biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: mode of action of 5-methyl-tryptophan and 5-methyl-tryptophan-sensitive mutants. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1131–1140. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1131-1140.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senecoff J. F., Meagher R. B. Isolating the Arabidopsis thaliana genes for de novo purine synthesis by suppression of Escherichia coli mutants. I. 5'-Phosphoribosyl-5-aminoimidazole synthetase. Plant Physiol. 1993 Jun;102(2):387–399. doi: 10.1104/pp.102.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul O., Galili G. Threonine Overproduction in Transgenic Tobacco Plants Expressing a Mutant Desensitized Aspartate Kinase of Escherichia coli. Plant Physiol. 1992 Nov;100(3):1157–1163. doi: 10.1104/pp.100.3.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden S. L., Durbin R. D. Glutamine synthetase inhibition: possible mode of action of wildfire toxin from Pseudomonas tabaci. Nature. 1968 Jul 27;219(5152):379–380. doi: 10.1038/219379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinrücken H. C., Amrhein N. The herbicide glyphosate is a potent inhibitor of 5-enolpyruvyl-shikimic acid-3-phosphate synthase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 30;94(4):1207–1212. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90547-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada S., Volrath S., Guyer D., Scheidegger A., Ryals J., Ohta D., Ward E. Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding imidazoleglycerolphosphate dehydratase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 1994 Jun;105(2):579–583. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward E. R., Payne G. B., Moyer M. B., Williams S. C., Dincher S. S., Sharkey K. C., Beck J. J., Taylor H. T., Ahl-Goy P., Meins F. Differential Regulation of beta-1,3-Glucanase Messenger RNAs in Response to Pathogen Infection. Plant Physiol. 1991 Jun;96(2):390–397. doi: 10.1104/pp.96.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenbach V. A., Teaney P. W., Hanna W. S., Rayner D. R., Schloss J. V. Herbicidal Activity of an Isopropylmalate Dehydrogenase Inhibitor. Plant Physiol. 1994 Sep;106(1):321–328. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfner M., Yep D., Messenguy F., Fink G. R. Integration of amino acid biosynthesis into the cell cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 5;96(2):273–290. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]