Abstract
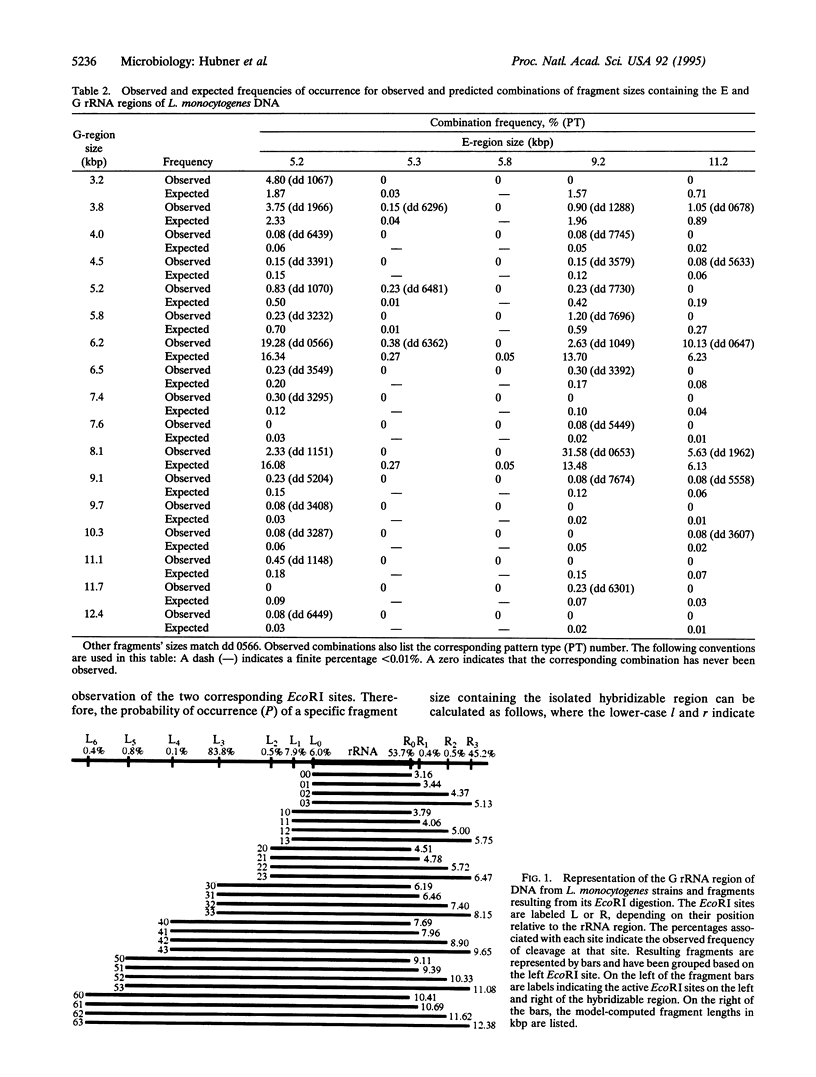
By using taxonomic characters derived from EcoRI restriction endonuclease digestion of genomic DNA and hybridization with a labeled rRNA operon from Escherichia coli, a polymorphic structure of Listeria monocytogenes, characterized by fragments with different frequencies of occurrence, was observed. This structure was expanded by creating predicted patterns through a recursive process of observation, expectation, prediction, and assessment of completeness. This process was applied, in turn, to normalized strain patterns, fragment bands, and positions of EcoRI recognition sites relative to rRNA regions. Analysis of 1346 strains provided observed patterns, fragment sizes, and their frequencies of occurrence in the patterns. Fragment size statistics led to the creation of unobserved combinations of bands, predicted pattern types. The observed fragment bands revealed positions of EcoRI sites relative to rRNA sequences. Each EcoRI site had a frequency of occurrence, and unobserved fragment sizes were postulated on the basis of knowing the restriction site locations. The result of the recursion process applied to the components of the strain data was an extended classification with observed and predicted members.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruce J. L., Hubner R. J., Cole E. M., McDowell C. I., Webster J. A. Sets of EcoRI fragments containing ribosomal RNA sequences are conserved among different strains of Listeria monocytogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):5229–5233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.5229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carriere C., Allardet-Servent A., Bourg G., Audurier A., Ramuz M. DNA polymorphism in strains of Listeria monocytogenes. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jul;29(7):1351–1355. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.7.1351-1355.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel E., Cossart P. Physical map of the Listeria monocytogenes chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(22):7098–7103. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.22.7098-7103.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Yasunaga T., Nishida T. Nucleotide sequence divergence and functional constraint in mRNA evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7328–7332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Measurement of DNA length by gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1979 Dec;100(2):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90235-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. E., Balsdon J. T., Cai J., Collins M. D. Studies on the ribosomal RNA operons of Listeria monocytogenes. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Sep 15;75(2-3):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90407-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster J. A., Bannerman T. L., Hubner R. J., Ballard D. N., Cole E. M., Bruce J. L., Fiedler F., Schubert K., Kloos W. E. Identification of the Staphylococcus sciuri species group with EcoRI fragments containing rRNA sequences and description of Staphylococcus vitulus sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1994 Jul;44(3):454–460. doi: 10.1099/00207713-44-3-454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


