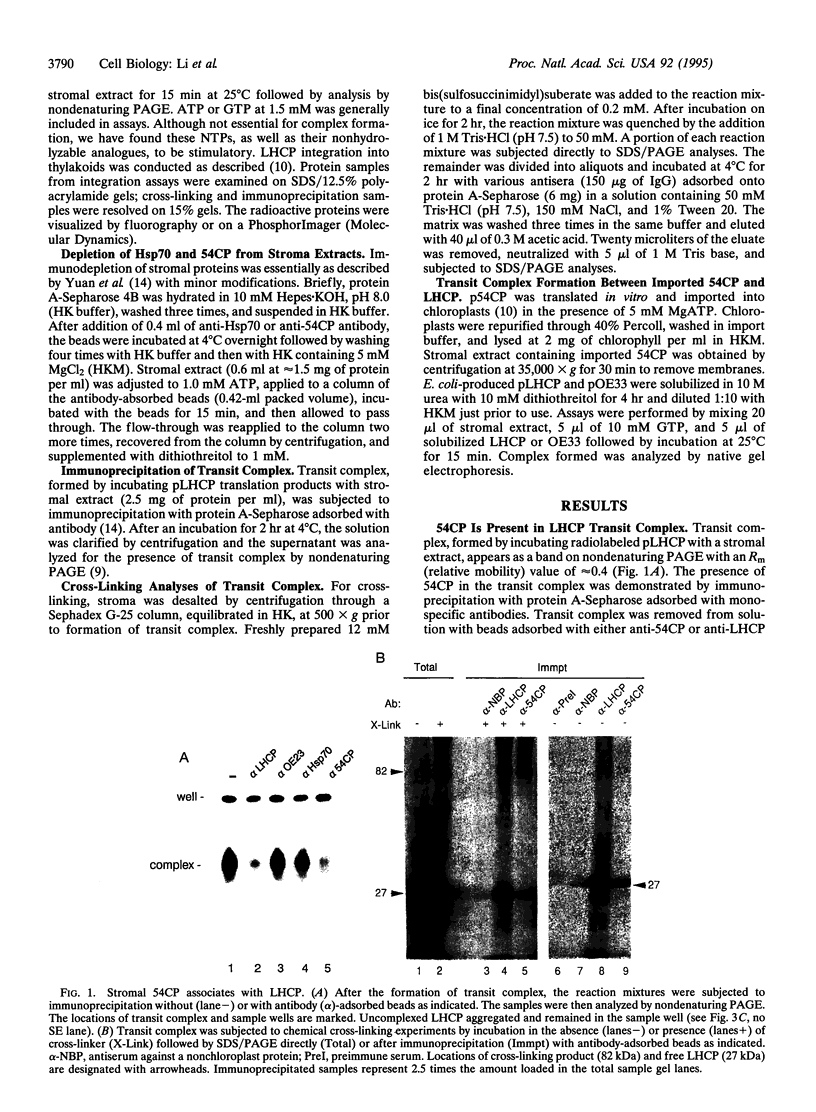
Abstract
The mechanisms involved in the integration of proteins into the thylakoid membrane are largely unknown. However, many of the steps of this process for the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein (LHCP) have been described and reconstituted in vitro. LHCP is synthesized as a precursor in the cytosol and posttranslationally imported into chloroplasts. Upon translocation across the envelope membranes, the N-terminal transit peptide is cleaved, and the apoprotein is assembled into a soluble "transit complex" and then integrated into the thylakoid membrane via three transmembrane helices. Here we show that 54CP, a chloroplast homologue of the 54-kDa subunit of the mammalian signal recognition particle (SRP54), is essential for transit complex formation, is present in the complex, and is required for LHCP integration into the thylakoid membrane. Our data indicate that 54CP functions posttranslationally as a molecular chaperone and potentially pilots LHCP to the thylakoids. These results demonstrate that one of several pathways for protein routing to the thylakoids is homologous to the SRP pathway and point to a common evolutionary origin for the protein transport systems of the endoplasmic reticulum and the thylakoid membrane.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auchincloss A. H., Alexander A., Kohorn B. D. Requirement for three membrane-spanning alpha-helices in the post-translational insertion of a thylakoid membrane protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10439–10446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Poritz M. A., Strub K., Hoben P. J., Brenner S., Walter P. Model for signal sequence recognition from amino-acid sequence of 54K subunit of signal recognition particle. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):482–486. doi: 10.1038/340482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Ettinger W. F., Theg S. M. Protein-specific energy requirements for protein transport across or into thylakoid membranes. Two lumenal proteins are transported in the absence of ATP. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2688–2696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Henry R., Li C., Yuan J. Multiple pathways for protein transport into or across the thylakoid membrane. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4105–4114. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06094.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K. Import of proteins into chloroplasts. Membrane integration of a thylakoid precursor protein reconstituted in chloroplast lysates. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14804–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douwe de Boer A., Weisbeek P. J. Chloroplast protein topogenesis: import, sorting and assembly. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 13;1071(3):221–253. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90015-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J. Molecular chaperones: the plant connection. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):954–959. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4983.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin A. E., Hoffman N. E. Characterization of a chloroplast homologue of the 54-kDa subunit of the signal recognition particle. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):22175–22180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry R., Kapazoglou A., McCaffery M., Cline K. Differences between lumen targeting domains of chloroplast transit peptides determine pathway specificity for thylakoid transport. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10189–10192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman N. E., Franklin A. E. Evidence for a stromal GTP requirement for the integration of a chlorophyll a/b-binding polypeptide into thylakoid membranes. Plant Physiol. 1994 May;105(1):295–304. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.1.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Adam Z., Hoffman N. E. Deletion Mutants of Chlorophyll a/b Binding Proteins Are Efficiently Imported into Chloroplasts but Do Not Integrate into Thylakoid Membranes. Plant Physiol. 1992 May;99(1):247–255. doi: 10.1104/pp.99.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klösgen R. B., Brock I. W., Herrmann R. G., Robinson C. Proton gradient-driven import of the 16 kDa oxygen-evolving complex protein as the full precursor protein by isolated thylakoids. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Mar;18(5):1031–1034. doi: 10.1007/BF00019226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko K., Cashmore A. R. Targeting of proteins to the thylakoid lumen by the bipartite transit peptide of the 33 kd oxygen-evolving protein. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3187–3194. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubben T. H., Donaldson G. K., Viitanen P. V., Gatenby A. A. Several proteins imported into chloroplasts form stable complexes with the GroEL-related chloroplast molecular chaperone. Plant Cell. 1989 Dec;1(12):1223–1230. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.12.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luirink J., High S., Wood H., Giner A., Tollervey D., Dobberstein B. Signal-sequence recognition by an Escherichia coli ribonucleoprotein complex. Nature. 1992 Oct 22;359(6397):741–743. doi: 10.1038/359741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luirink J., ten Hagen-Jongman C. M., van der Weijden C. C., Oudega B., High S., Dobberstein B., Kusters R. An alternative protein targeting pathway in Escherichia coli: studies on the role of FtsY. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2289–2296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06511.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütcke H., High S., Römisch K., Ashford A. J., Dobberstein B. The methionine-rich domain of the 54 kDa subunit of signal recognition particle is sufficient for the interaction with signal sequences. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1543–1551. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning-Krieg U. C., Scherer P. E., Schatz G. Sequential action of mitochondrial chaperones in protein import into the matrix. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3273–3280. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04891.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michl D., Robinson C., Shackleton J. B., Herrmann R. G., Klösgen R. B. Targeting of proteins to the thylakoids by bipartite presequences: CFoII is imported by a novel, third pathway. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1310–1317. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06383.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. D., Wilhelm H., Gierasch L., Gilmore R., Walter P. GTP binding and hydrolysis by the signal recognition particle during initiation of protein translocation. Nature. 1993 Nov 25;366(6453):351–354. doi: 10.1038/366351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai M., Goto A., Nohara T., Sugita D., Endo T. Identification of the SecA protein homolog in pea chloroplasts and its possible involvement in thylakoidal protein transport. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31338–31341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Cabelli R. J., Jarosik G. P. SecA protein: autoregulated initiator of secretory precursor protein translocation across the E. coli plasma membrane. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):311–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00763170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payan L. A., Cline K. A stromal protein factor maintains the solubility and insertion competence of an imported thylakoid membrane protein. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):603–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. J., Silhavy T. J. The E. coli ffh gene is necessary for viability and efficient protein export. Nature. 1992 Oct 22;359(6397):744–746. doi: 10.1038/359744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport T. A. Transport of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):931–936. doi: 10.1126/science.1332192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. E., Cline K., Stephens L. C., Bacot K. O., Viitanen P. V. Early events in the import/assembly pathway of an integral thylakoid protein. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 26;194(1):33–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson C., Cai D., Hulford A., Brock I. W., Michl D., Hazell L., Schmidt I., Herrmann R. G., Klösgen R. B. The presequence of a chimeric construct dictates which of two mechanisms are utilized for translocation across the thylakoid membrane: evidence for the existence of two distinct translocation systems. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 15;13(2):279–285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson C., Ellis R. J. Transport of proteins into chloroplasts. Partial purification of a chloroplast protease involved in the processing of important precursor polypeptides. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 16;142(2):337–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S., Bauerle C., Hageman J., Keegstra K., Weisbeek P. The role of the transit peptide in the routing of precursors toward different chloroplast compartments. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90657-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. A., Kohorn B. D. Mutations in a signal sequence for the thylakoid membrane identify multiple protein transport pathways and nuclear suppressors. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(2):365–374. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.2.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viitanen P. V., Doran E. R., Dunsmuir P. What is the role of the transit peptide in thylakoid integration of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein? J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15000–15007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmann B., Sakai H., Davis T. A., Wiedmann M. A protein complex required for signal-sequence-specific sorting and translocation. Nature. 1994 Aug 11;370(6489):434–440. doi: 10.1038/370434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L. From the elephant to E. coli: SRP-dependent protein targeting. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):787–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalovsky S., Paulsen H., Michaeli D., Chitnis P. R., Nechushtai R. Involvement of a chloroplast HSP70 heat shock protein in the integration of a protein (light-harvesting complex protein precursor) into the thylakoid membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5616–5619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J., Henry R., Cline K. Stromal factor plays an essential role in protein integration into thylakoids that cannot be replaced by unfolding or by heat shock protein Hsp70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8552–8556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J., Henry R., McCaffery M., Cline K. SecA homolog in protein transport within chloroplasts: evidence for endosymbiont-derived sorting. Science. 1994 Nov 4;266(5186):796–798. doi: 10.1126/science.7973633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zopf D., Bernstein H. D., Walter P. GTPase domain of the 54-kD subunit of the mammalian signal recognition particle is required for protein translocation but not for signal sequence binding. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1113–1121. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]