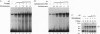Abstract
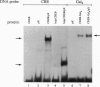
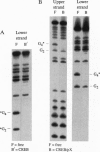
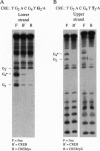
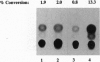
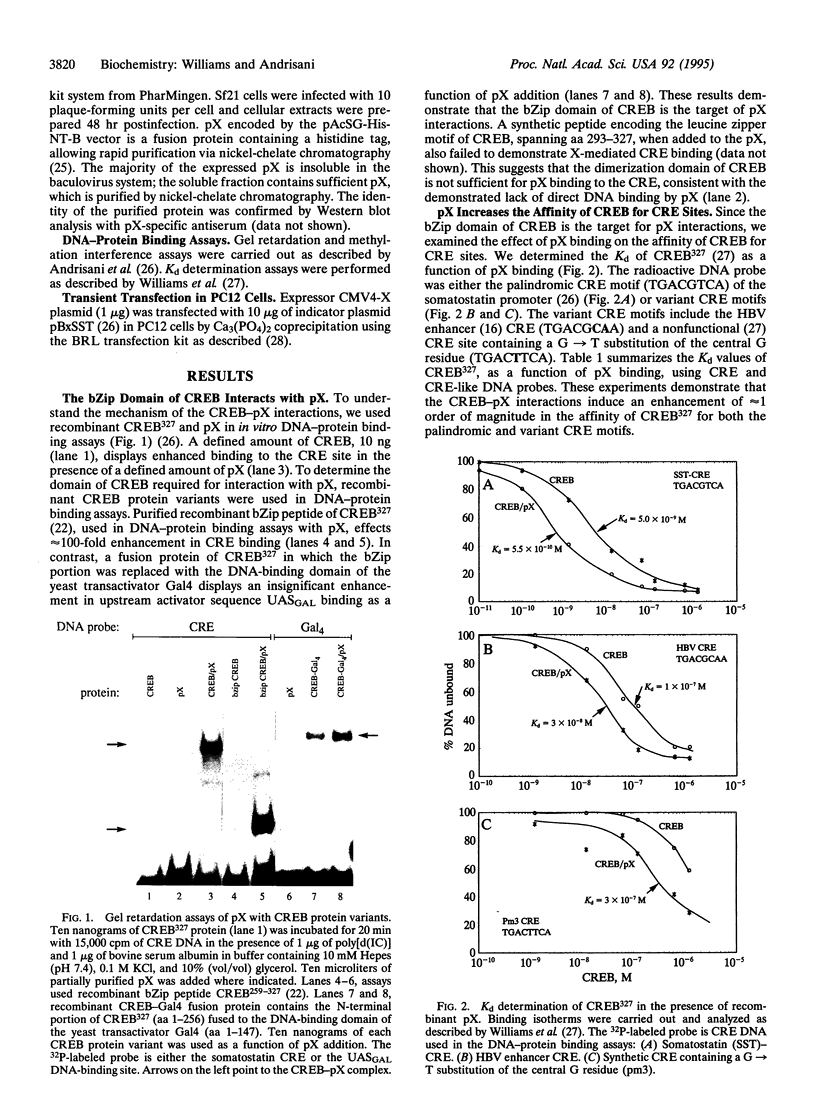
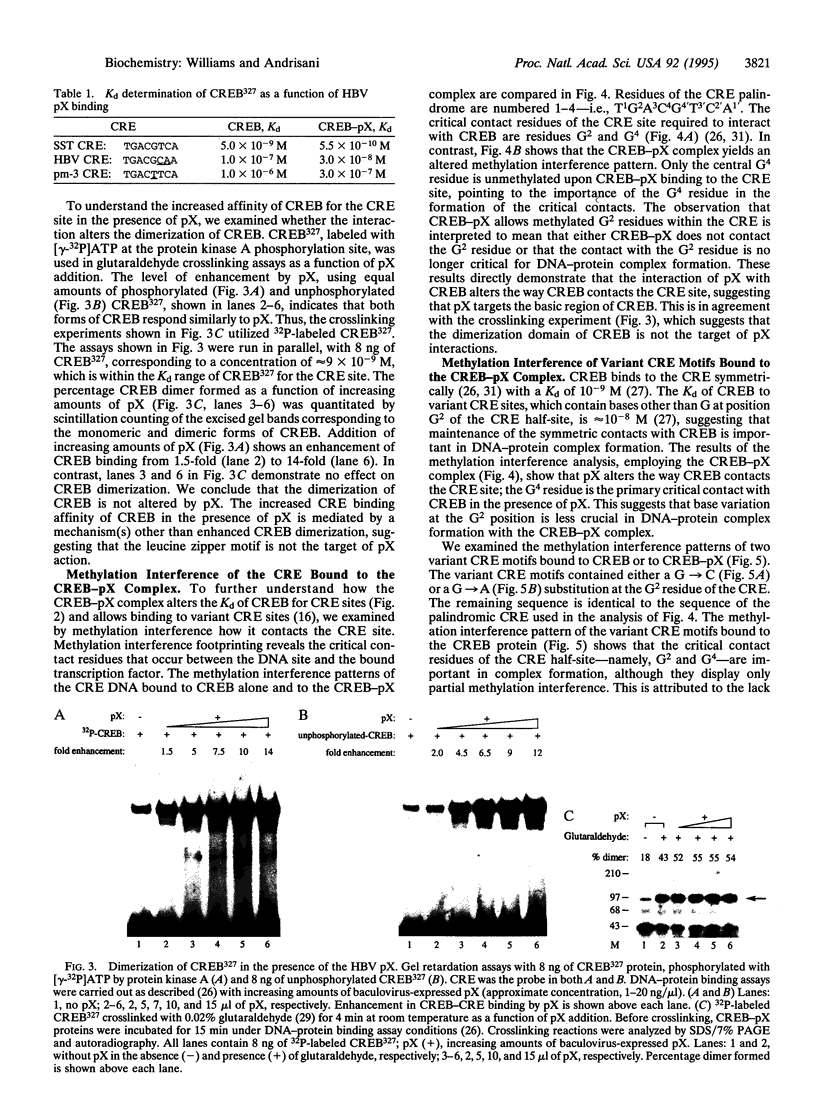
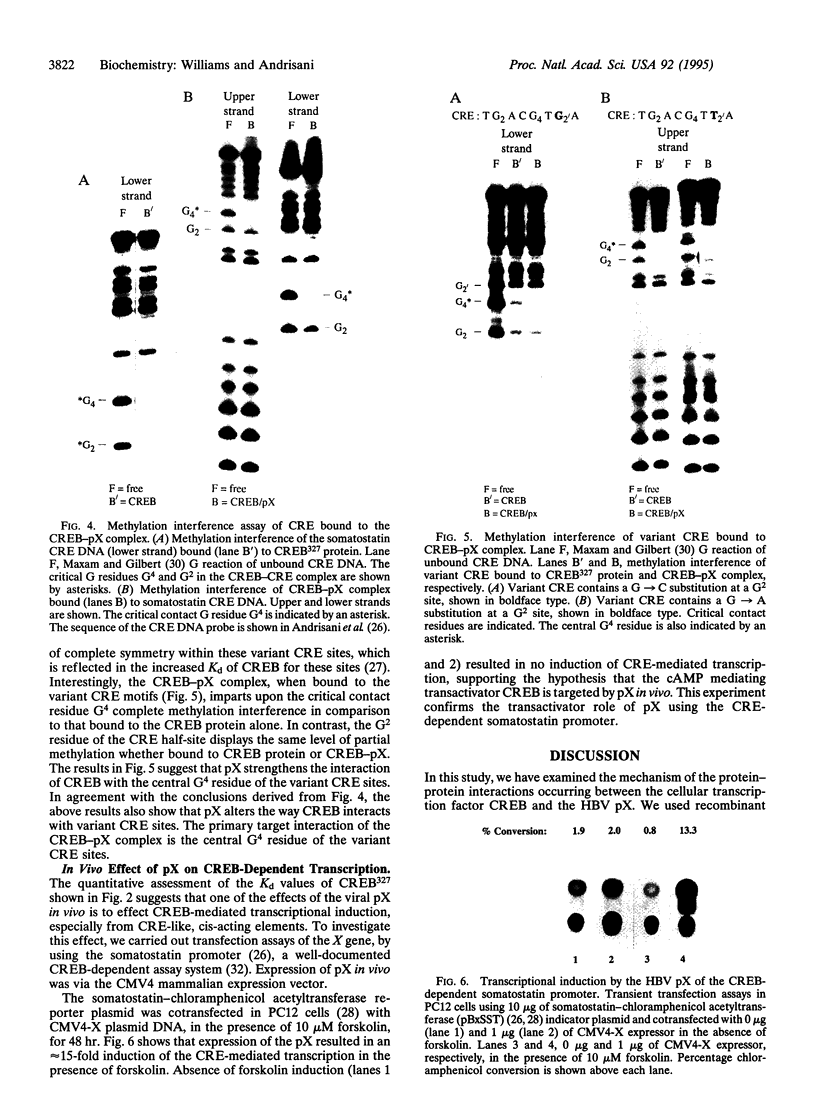
The X gene product encoded by the hepatitis B virus, termed pX, is a promiscuous transactivator of a variety of viral and cellular genes under the control of diverse cis-acting elements. Although pX does not appear to directly bind DNA, pX-responsive elements include the NF-kappa B, AP-1, and CRE (cAMP response element) sites. Direct protein-protein interactions occur between viral pX and the CRE-binding transcription factors CREB and ATF. Here we examine the mechanism of the protein-protein interactions occurring between CREB and pX by using recombinant proteins and in vitro DNA-binding assays. We demonstrate that pX interacts with the basic region-leucine zipper domain of CREB but not with the DNA-binding domain of the yeast transactivator protein Gal4. The interaction between CREB and pX increases the affinity of CREB for the CRE site by an order of magnitude, although pX does not alter the rate of CREB dimerization. Methylation interference footprinting reveals differences between the CREB DNA and CREB-pX DNA complexes. These experiments demonstrate that pX titers the way CREB interacts with the CRE DNA and suggest that the basic, DNA-binding region of CREB is the target of pX. Transfection assays in PC12 cells with the CREB-dependent somatostatin promoter demonstrate a nearly 15-fold transcriptional induction after forskolin stimulation in the presence of pX. These results support the significance of the CREB-pX protein-protein interactions in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Luk D., Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Expression and purification of the leucine zipper and DNA-binding domains of Fos and Jun: both Fos and Jun contact DNA directly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1032–1036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrisani O. M., Dixon J. E. Involvement of lysine residues 289 and 291 of the cAMP-responsive element-binding protein in the recognition of the cAMP-responsive element. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21444–21450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrisani O. M., Pot D. A., Zhu Z., Dixon J. E. Three sequence-specific DNA-protein complexes are formed with the same promoter element essential for expression of the rat somatostatin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1947–1956. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrisani O. M., Zhu Z. N., Pot D. A., Dixon J. E. In vitro transcription directed from the somatostatin promoter is dependent upon a purified 43-kDa DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2181–2185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Levy R., Faktor O., Berger I., Shaul Y. Cellular factors that interact with the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1804–1809. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbran J. L., Roach P. J., Fiol C. J., Dixon J. E., Andrisani O. M., Corbin J. D. cAMP-dependent protein kinase, but not the cGMP-dependent enzyme, rapidly phosphorylates delta-CREB, and a synthetic delta-CREB peptide. Biochem Cell Biol. 1992 Oct-Nov;70(10-11):1277–1282. doi: 10.1139/o92-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgrove R., Simon G., Ganem D. Transcriptional activation of homologous and heterologous genes by the hepatitis B virus X gene product in cells permissive for viral replication. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4019–4026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4019-4026.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross J. C., Wen P., Rutter W. J. Transactivation by hepatitis B virus X protein is promiscuous and dependent on mitogen-activated cellular serine/threonine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8078–8082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiol C. J., Williams J. S., Chou C. H., Wang Q. M., Roach P. J., Andrisani O. M. A secondary phosphorylation of CREB341 at Ser129 is required for the cAMP-mediated control of gene expression. A role for glycogen synthase kinase-3 in the control of gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32187–32193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P. CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90503-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Viral transactivation. Pleiotropy and henchman X. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):687–688. doi: 10.1038/361687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Yun Y., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein: structure based on a cloned placental cDNA. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameel S., Siddiqui A., Maguire H. F., Rao K. V. Hepatitis B virus X protein produced in Escherichia coli is biologically functional. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3963–3966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3963-3966.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekulé A. S., Lauer U., Weiss L., Luber B., Hofschneider P. H. Hepatitis B virus transactivator HBx uses a tumour promoter signalling pathway. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):742–745. doi: 10.1038/361742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. M., Koike K., Saito I., Miyamura T., Jay G. HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in transgenic mice. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):317–320. doi: 10.1038/351317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamph W. W., Wamsley P., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Induction of proto-oncogene JUN/AP-1 by serum and TPA. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):629–631. doi: 10.1038/334629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire H. F., Hoeffler J. P., Siddiqui A. HBV X protein alters the DNA binding specificity of CREB and ATF-2 by protein-protein interactions. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.1827531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty A. M., Alexander H., Lerner R. A., Thornton G. B. Antibodies to peptides detect new hepatitis B antigen: serological correlation with hepatocellular carcinoma. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):429–433. doi: 10.1126/science.2981434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natoli G., Avantaggiati M. L., Chirillo P., Costanzo A., Artini M., Balsano C., Levrero M. Induction of the DNA-binding activity of c-jun/c-fos heterodimers by the hepatitis B virus transactivator pX. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):989–998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel L., Abate C., Curran T. Altered protein conformation on DNA binding by Fos and Jun. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):572–575. doi: 10.1038/347572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated by growth factors is related to the oncogene v-jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Hirai S. I., Yaniv M., Bravo R. Transcriptional activation of c-jun during the G0/G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):535–537. doi: 10.1038/334535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago-Rivera Z. I., Williams J. S., Gorenstein D. G., Andrisani O. M. Bacterial expression and characterization of the CREB bZip module: circular dichroism and 2D 1H-NMR studies. Protein Sci. 1993 Sep;2(9):1461–1471. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Mitchell P. J., Yen T. S. Transactivation by the hepatitis B virus X protein depends on AP-2 and other transcription factors. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):72–74. doi: 10.1038/344072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Yen T. S., Peterlin B. M., Ou J. H. Trans-activation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat by the hepatitis B virus X protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8286–8290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Gaynor R., Srinivasan A., Mapoles J., Farr R. W. trans-activation of viral enhancers including long terminal repeat of the human immunodeficiency virus by the hepatitis B virus X protein. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandau D. F., Lee C. H. trans-activation of viral enhancers by the hepatitis B virus X protein. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):427–434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.427-434.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Pourcel C., Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):489–495. doi: 10.1038/317489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Chu K., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B virus X gene activates kappa B-like enhancer sequences in the long terminal repeat of human immunodeficiency virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5168–5172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B virus X gene can transactivate heterologous viral sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2046–2050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Schloemer R. H. Transcriptional trans-activating function of hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3448–3453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3448-3453.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger T., Shaul Y. The X protein of the hepatitis B virus acts as a transcription factor when targeted to its responsive element. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1889–1895. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner S., Green M. R. HTLV-I Tax protein stimulation of DNA binding of bZIP proteins by enhancing dimerization. Science. 1993 Oct 15;262(5132):395–399. doi: 10.1126/science.8211160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. S., Dixon J. E., Andrisani O. M. Binding constant determination studies utilizing recombinant delta CREB protein. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;12(2):183–190. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Zhou Z. Y., Judd A., Cartwright C. A., Robinson W. S. The hepatitis B virus-encoded transcriptional trans-activator hbx appears to be a novel protein serine/threonine kinase. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):687–695. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]