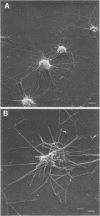
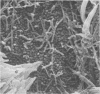
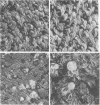
Abstract
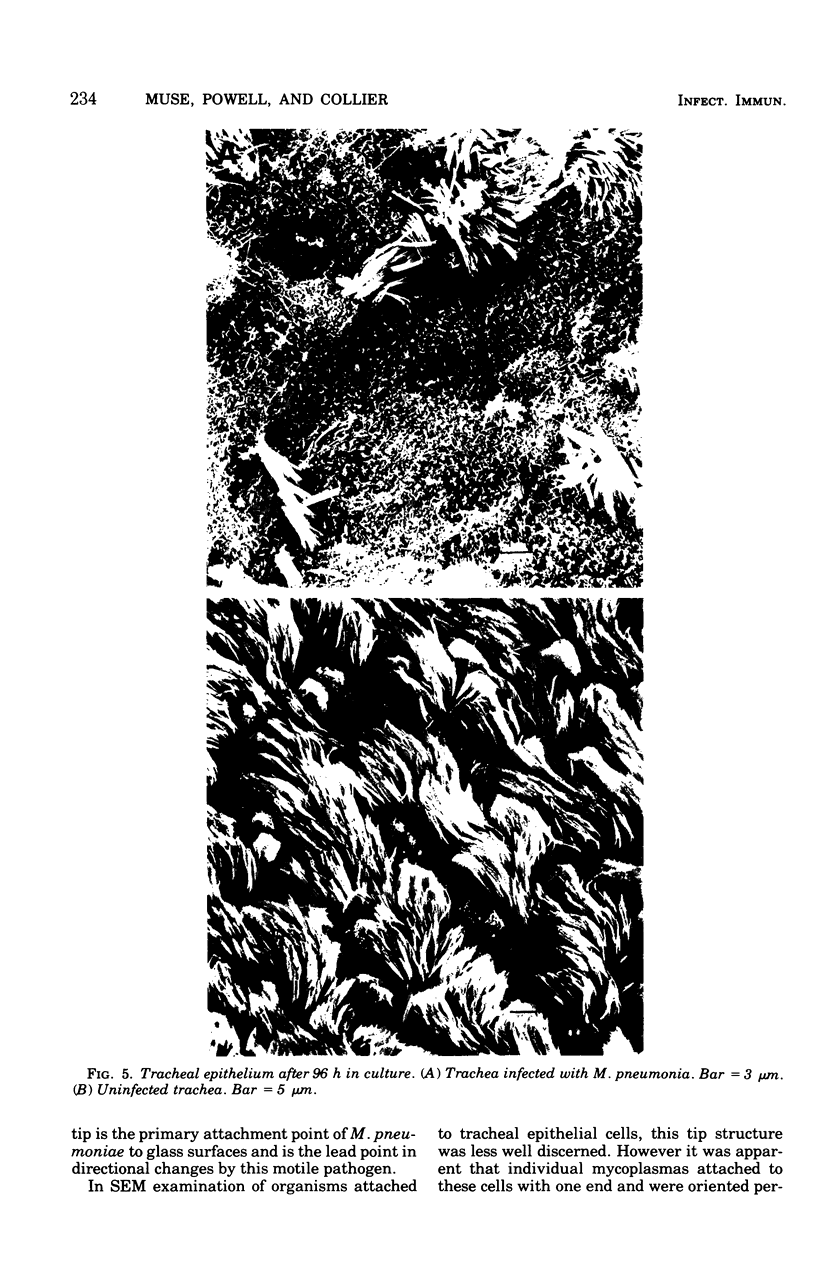
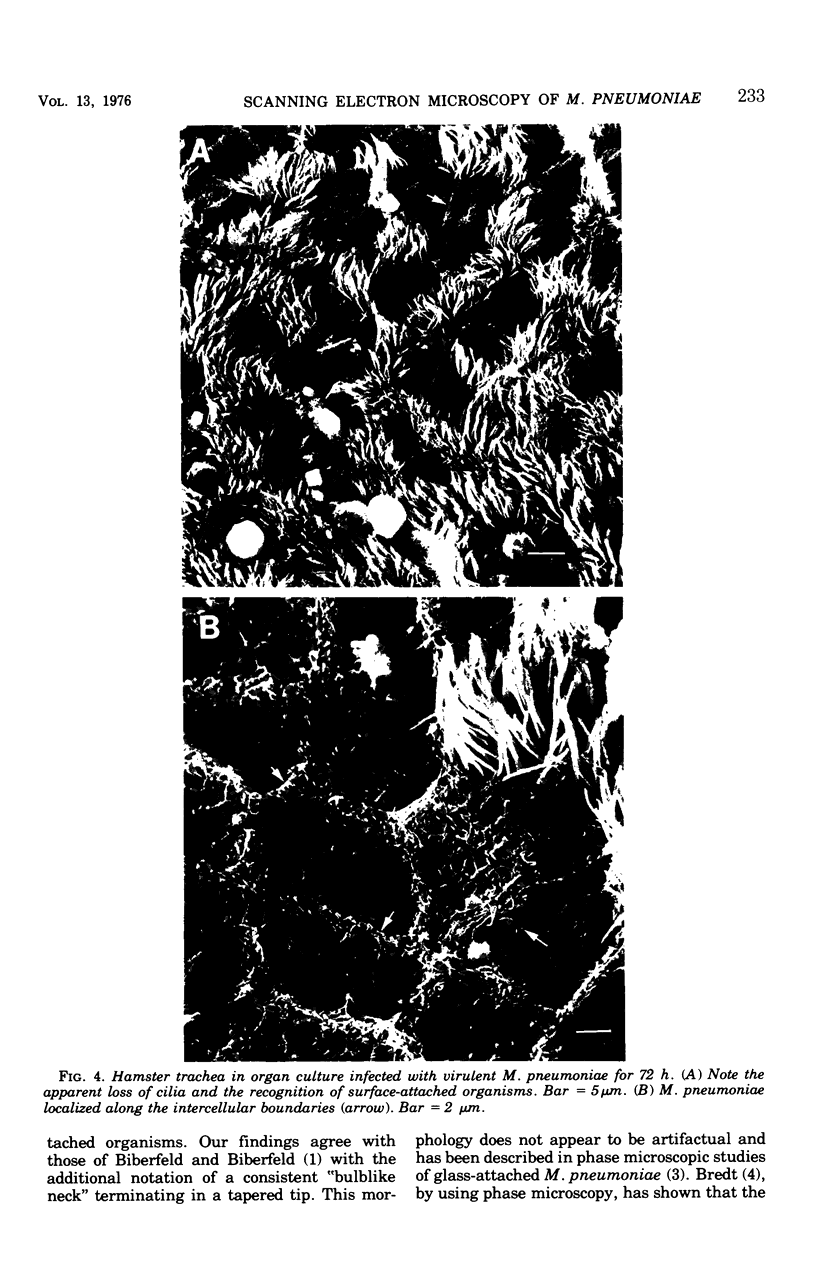
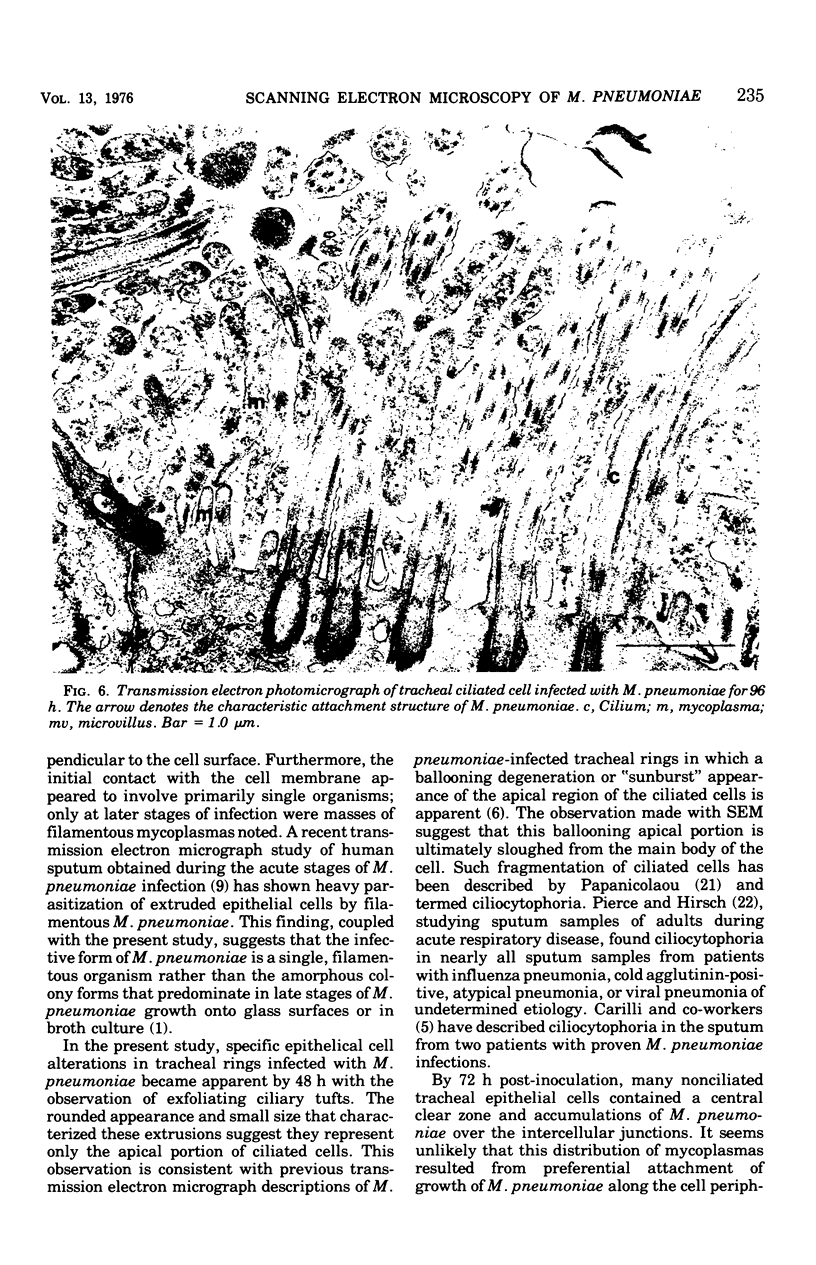
Hamster tracheal rings in organ culture were inoculated with a virulent strain of Mycoplasma pneumoniae and examined by scanning electron microscopy. A progressive increase in epithelial cell injury was detected from 48 to 96 h post-inoculation and was characterized by apparent loss of the apical portion of ciliated cells. M. pneumoniae attaching to the epithelial cell surfaces could be identified by comparison with the surface morphology of mycoplasmas grown on glass cover slips.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biberfeld G., Biberfeld P. Ultrastructural features of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):855–861. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.855-861.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt W. Growth morphology of Mycoplasma pneumoniae strain FH on glass surface. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jun;128(2):338–340. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carilli A. D., Gohd R. S., Brown D. A cytologic study of chronic bronchitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 May;101(5):696–699. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.101.5.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Appearance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in lungs of experimentally infected hamsters and sputum from patients with natural disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Dec;110(6):765–773. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.6P1.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr, Denny F. W. Mycoplasma pneumoniae in hamster tracheal organ culture: immunofluorescent and electron microscopic studies. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Feb;136(2):569–573. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier A. M., Clyde W. A. Relationships Between Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Human Respiratory Epithelium. Infect Immun. 1971 May;3(5):694–701. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.5.694-701.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAJANI A. S., CLYDE W. A., Jr, DENNY F. W. EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE (EATON'S AGENT). J Exp Med. 1965 Jun 1;121:1071–1086. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.6.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlgren S. E., Dalen H., Dalhamm T. Ultrastructural observations on chemically induced inflammation in guinea pig trachea. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1972;11(3):211–223. doi: 10.1007/BF02889400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny F. W., Clyde W. A., Jr, Glezen W. P. Mycoplasma pneumoniae disease: clinical spectrum, pathophysiology, epidemiology, and control. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jan;123(1):74–92. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.1.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Alterations in the metabolism of hamster tracheas in organ culture after infection by virulent Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):704–710. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.704-710.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Pollack J. D., Klainer A. S. Scanning-beam electron microscopy of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):499–502. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.499-502.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbiris D., Dreifus L. S., Linhart J. W. Complete heart block occurring during cardiac catheterization in patients with preexisting bundle branch block. Chest. 1974 Jan;65(1):95–97. doi: 10.1378/chest.65.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman R. P., Clyde W. A., Jr The interrelationship of virulence, cytadsorption, and peroxide formation in Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Sep;131(4):1163–1167. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-34061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell J. A., Tyler W. S. Scanning electron microscopy of the surface morphology of mammalian lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Mar;103(3):313–328. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPANICOLAOU G. N. Degenerative changes in ciliated cells exfoliating from the bronchial epithelium as a cytologic criterion in the diagnosis of diseases of the lung. N Y State J Med. 1956 Sep 1;56(17):2647–2650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIERCE C. H., HIRSCH J. G. Ciliocytophthoria: relationship to viral respiratory infections of humans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Jul;98(3):489–492. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. A., Clyde W. A., Jr Opsonin-reversible resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to in vitro phagocytosis by alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):540–550. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.540-550.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. E., Boyde A. Organ cultures of respiratory epithelium infected with rhinovirus or parainfluenza virus studied in a scanning electron microscope. Infect Immun. 1972 Jul;6(1):68–76. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.1.68-76.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]