Abstract
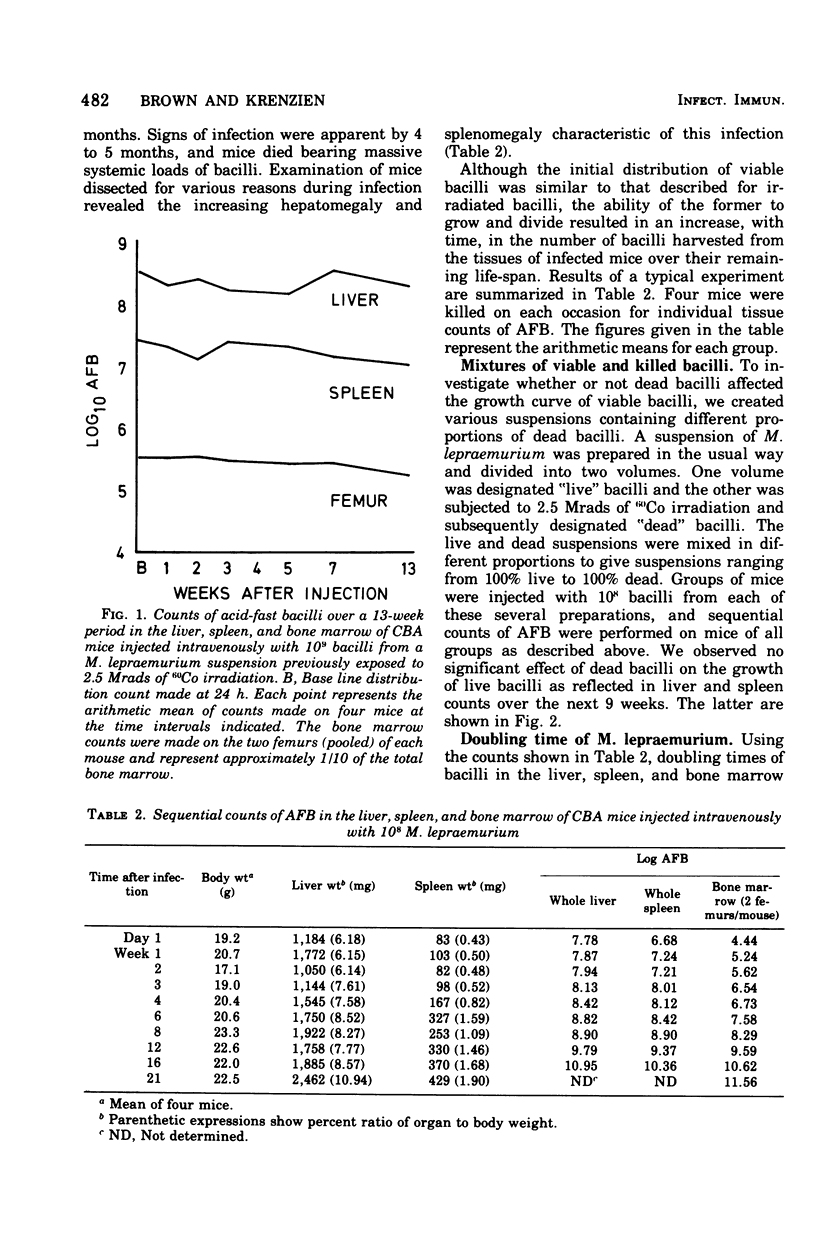
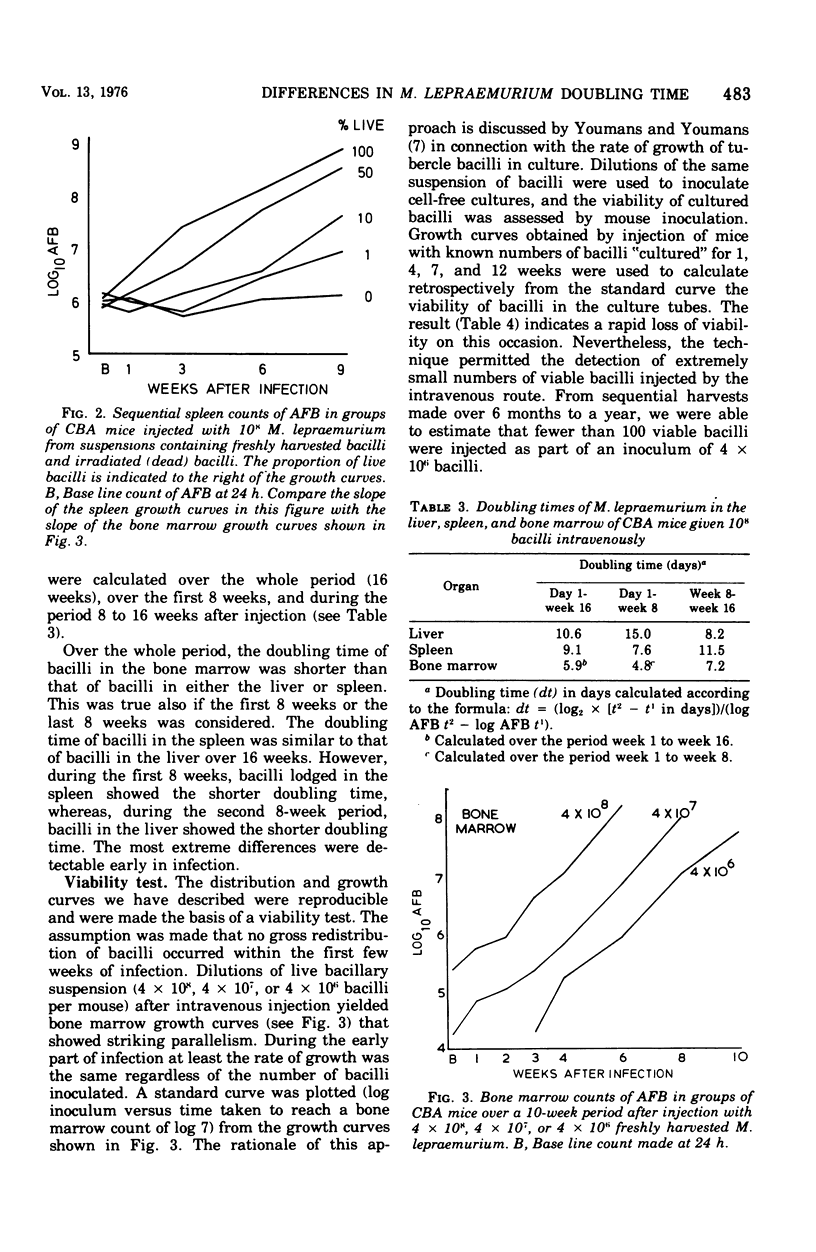
Counts of acid-fast bacilli were made on homogenates of whole liver, whole spleen, and two femurs of CBA mice killed at various time intervals after intravenous infection with Mycobacterium lepraemurium. The growth curves so obtained showed that the bacillus multiplied faster in bone marrow than in liver or spleen. No evidence of redistribution during the early part of infection was obtained. The time of appearance of significant numbers of bacilli (10(7)) in the bone marrow was used to make estimates of viability of M. lepraemurium suspensions. Several applications of the techniques described are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gaugas J., Rees R. J. Enhancing effect of antilymphocytic serum on mycobacterial infections in mice. Nature. 1968 Jul 27;219(5152):408–409. doi: 10.1038/219408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HART P. D., REES R. J. Effect of macrocyclon in acute and chronic pulmonary tuberculous infection in mice as shown by viable and total bacterial counts. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Aug;41:414–421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HART P. D., VALENTINE R. C. GROWTH (WITHOUT MULTIPLICATION) OF MYCOBACTERIUM LEPRAEMURIUM IN CELL-FREE MEDIUM. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jul;32:43–53. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TILL J. E., McCULLOCH E. A. A direct measurement of the radiation sensitivity of normal mouse bone marrow cells. Radiat Res. 1961 Feb;14:213–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans G. P., Youmans A. S. A METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF THE RATE OF GROWTH OF TUBERCLE BACILLI BY THE USE OF SMALL INOCULA. J Bacteriol. 1949 Aug;58(2):247–255. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.2.247-255.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


