Abstract
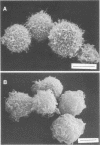
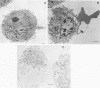
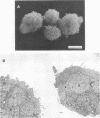
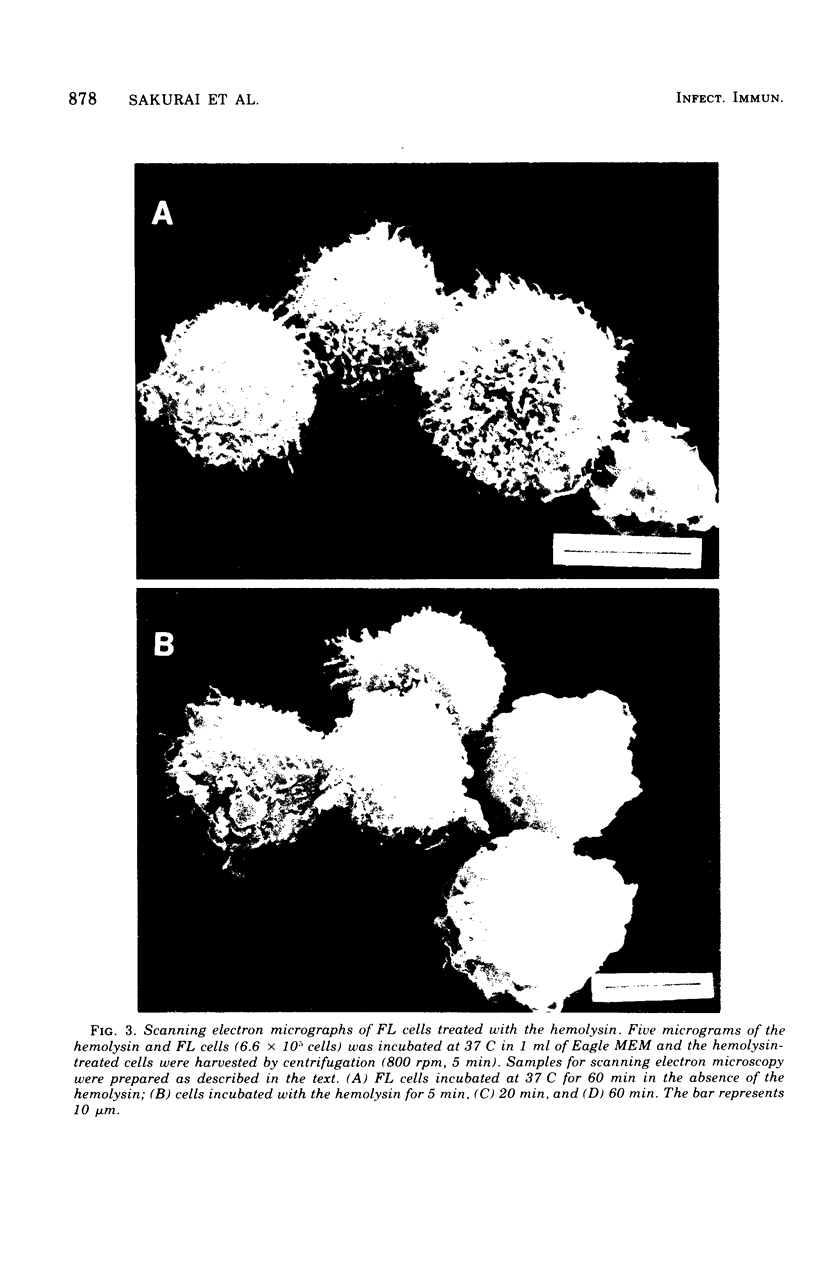
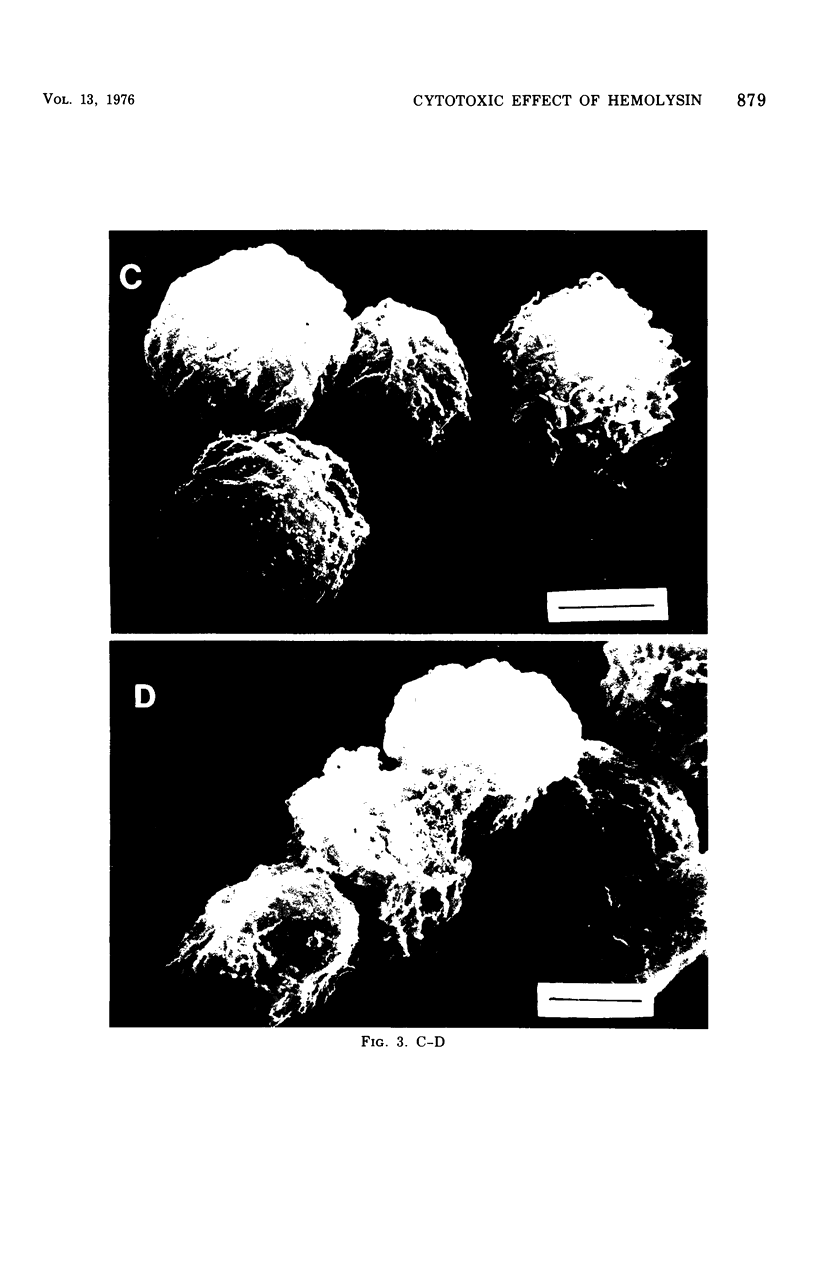
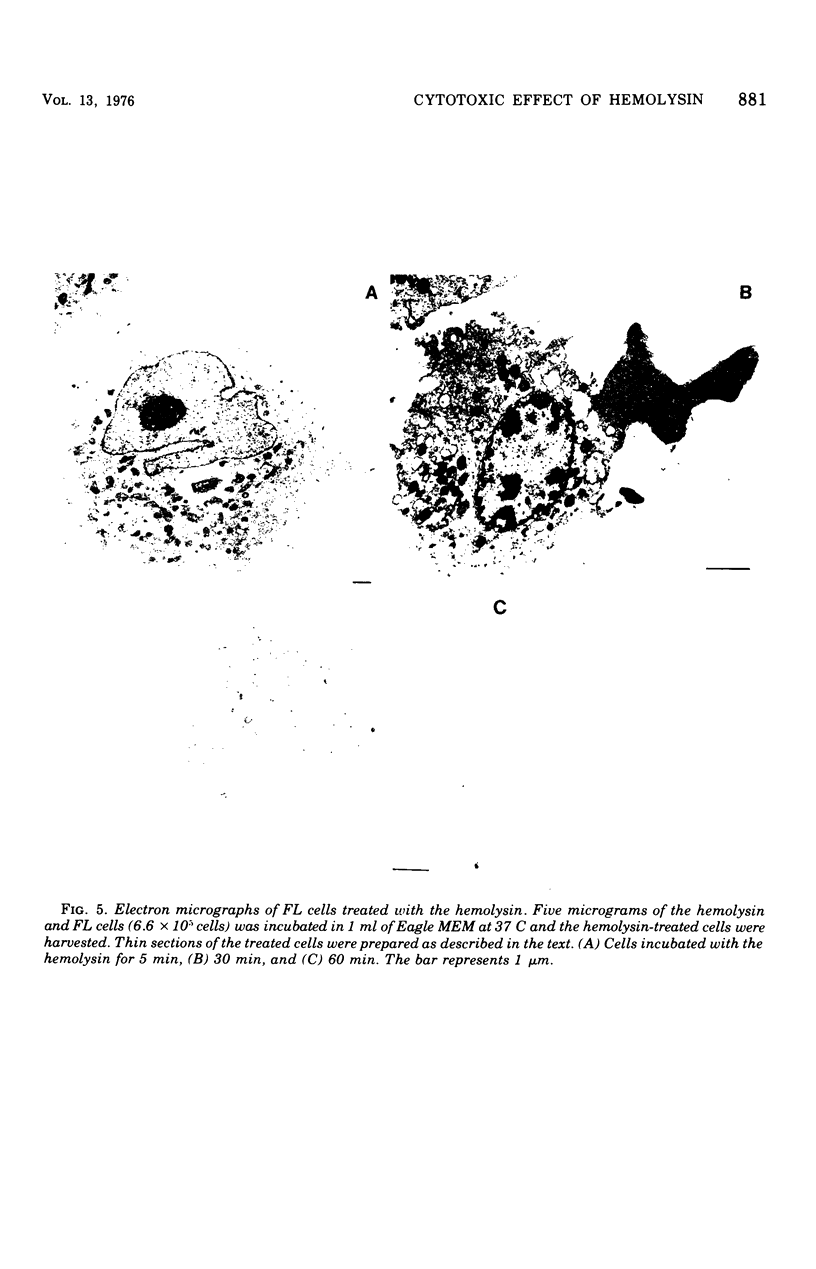
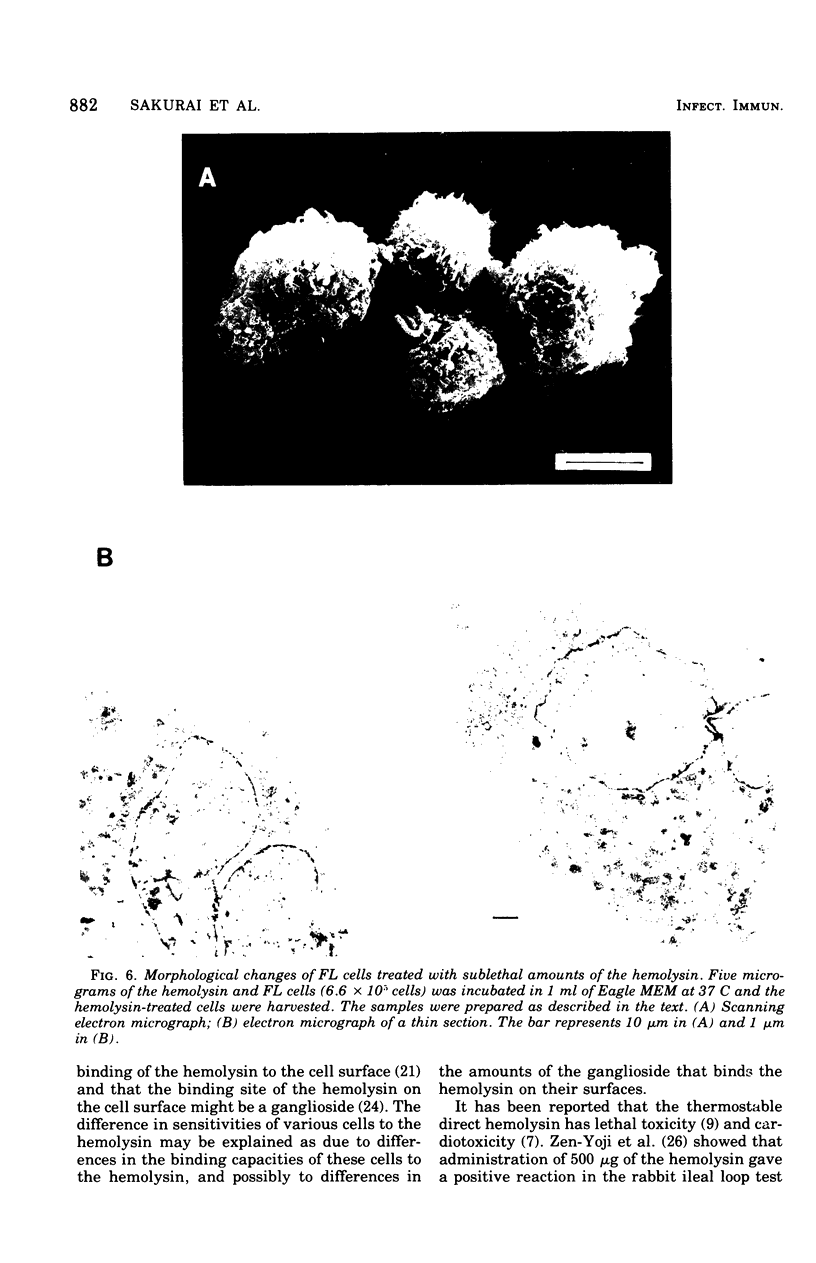
The thermostable direct hemolysin produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus showed cytotoxic activity on FL cells derived from human amniotic membrane. Scanning electron micrographs of the whole cells showed that the microvilli on the cell surface decreased in number and changed in shape on treatment with the hemolysin. Most of the microvilli disappeared before death of the cells, as judged from the results of staining the cells with trypan blue and measuring release of alkaline phosphatase from the cells. Electron micrographs of thin sections ofthe cells showed that the cytoplasm of the cells was not significantly affected by treatment with sublethal amounts of hemolysin, even when the microvilli on the cell surface were significantly affected. Lethal amounts of hemolysin affected the cytoplasm and caused disarovilli on the cell surface are affected by treatment with the hemolysin before cytoxic effects develop.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernheimer A. W. Cytolytic toxins of bacterial origin. The nature and properties of cytolytic proteins are discussed with emphasis on staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Science. 1968 Feb 23;159(3817):847–851. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3817.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuve R. M., Alouf J. E., Delaunay A., Raynaud M. Cytotoxic effects in vitro of highly purified streptolysin O on mouse macrophages cultured in a serum-free medium. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1150–1153. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1150-1153.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG I., GROSSOWICZ N. Effect of streptococcal haemolysins on Ehrlich ascites tumour cells. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1960 Jul;80:111–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladstone G. P., Yoshida A. The cytopathic action of purified staphylococcal delta-hemolysin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1967 Feb;48(1):11–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H. E., ZUBAY G. Preferential staining of nucleic acid-containing structures for electron microscopy. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Nov;11:273–296. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashino K., Kudo S., Yamamura Y., Honda T., Sakurai J. Possible identity between the hepatoma alkaline phosphatase and an isozyme of human amniotic membrane (FL cells). Clin Chim Acta. 1975 May 1;60(3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Goshima K., Takeda Y., Sugino Y., Miwatani T. Demonstration of the cardiotoxicity of the thermostable direct hemolysin (lethal toxin) produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):163–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.163-171.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Taga S., Takeda T., Hasibuan M. A., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Identification of lethal toxin with the thermostable direct hemolysin produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and some physicochemical properties of the purified toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):133–139. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.133-139.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeljaszewicz J., Szmigielski S., Korbecki M., Zak C. Histochemical demonstration of changes in enzymatic activity of KB cells produced by staphylococcal alpha and beta hemolysins. J Infect Dis. 1965 Dec;115(5):421–428. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.5.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King E. J., Armstrong A. R. A CONVENIENT METHOD FOR DETERMINING SERUM AND BILE PHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY. Can Med Assoc J. 1934 Oct;31(4):376–381. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLIMANS W. F., DAVIS E. V., GLOVER F. L., RAKE G. W. The submerged culture of mammalian cells; the spinner culture. J Immunol. 1957 Nov;79(5):428–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwatani T., Sakurai J., Yoshihara A., Takeda Y. Isolation and partial purification of thermolabile direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Biken J. 1972 Jun;15(2):61–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto Y., Kato T., Obara Y., Akiyama S., Takizawa K., Yamai S. In vitro hemolytic characteristic of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: its close correlation with human pathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1147–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1147-1149.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai J., Bahavar M. A., Jinguji Y., Miwatani T. Interaction of thermostable direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus with human erythrocytes. Biken J. 1975 Dec;18(4):187–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai J., Matsuzaki A., Miwatani T. Purification and characterization of thermostable direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):775–780. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.775-780.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai J., Matsuzaki A., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Existence of two distinct hemolysins in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):777–780. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.777-780.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda R., Honda T., Sakural J., Otomo N. Inhibition of hemolytic activity of the thermostable direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus by ganglioside. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):931–933. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.931-933.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zen-Yoji H., Hitokoto H., Morozumi S., Le Clair R. A. Purification and characterization o;f a hemolysin produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jun;123(6):665–667. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.6.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]