Abstract
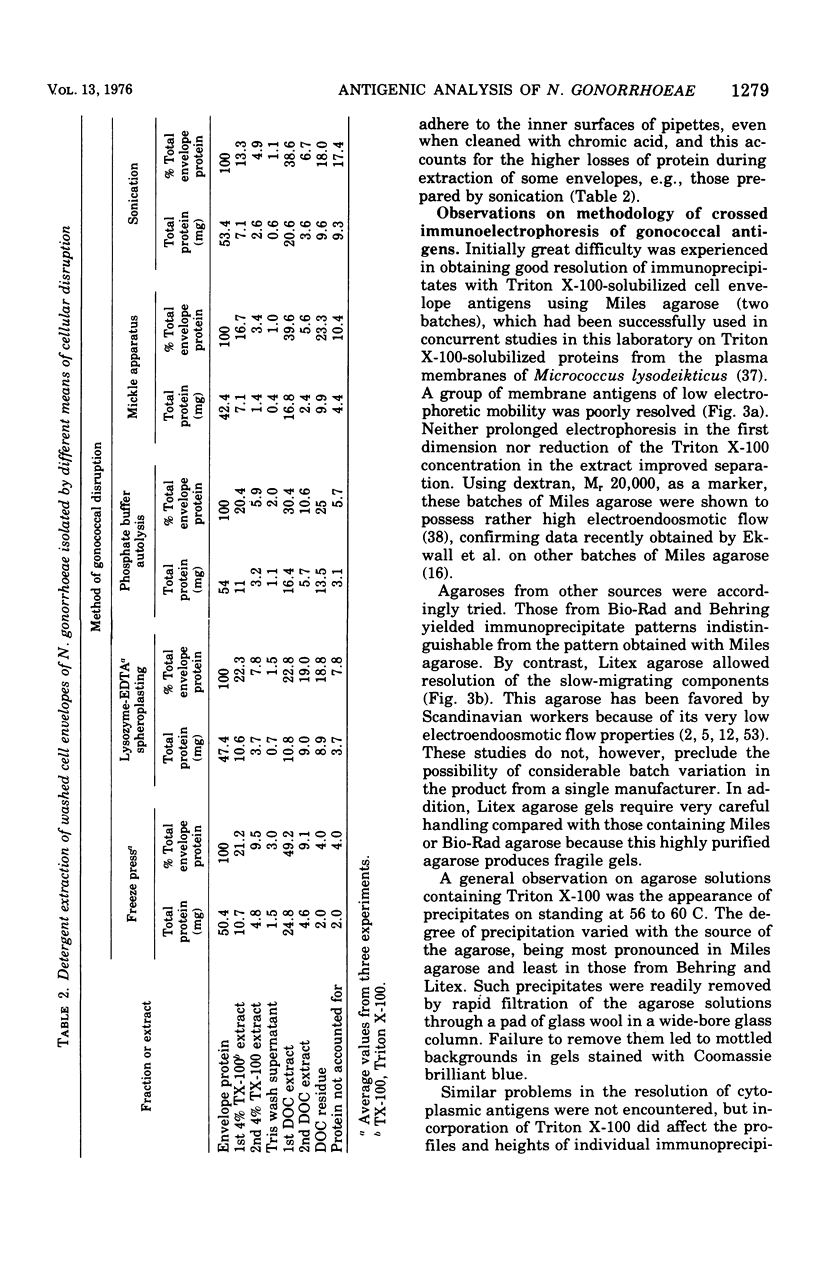
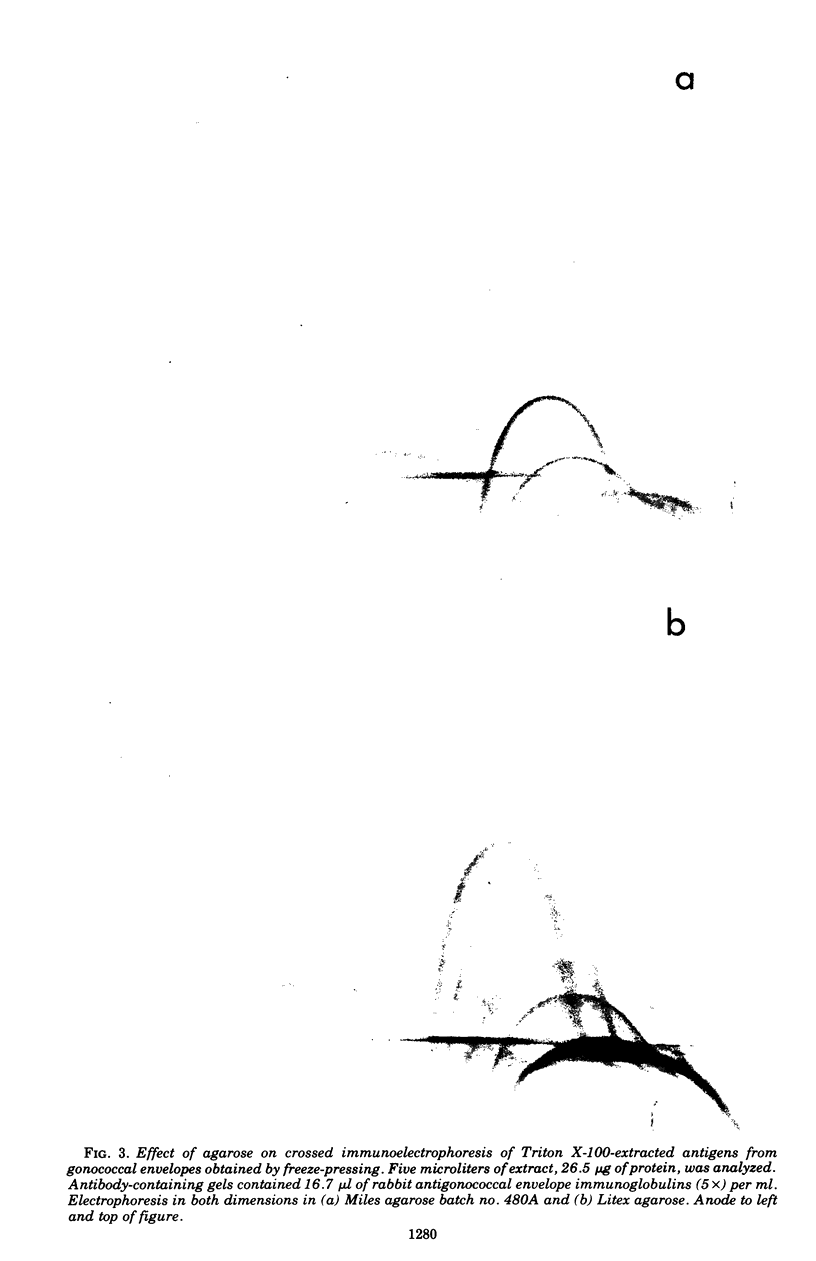
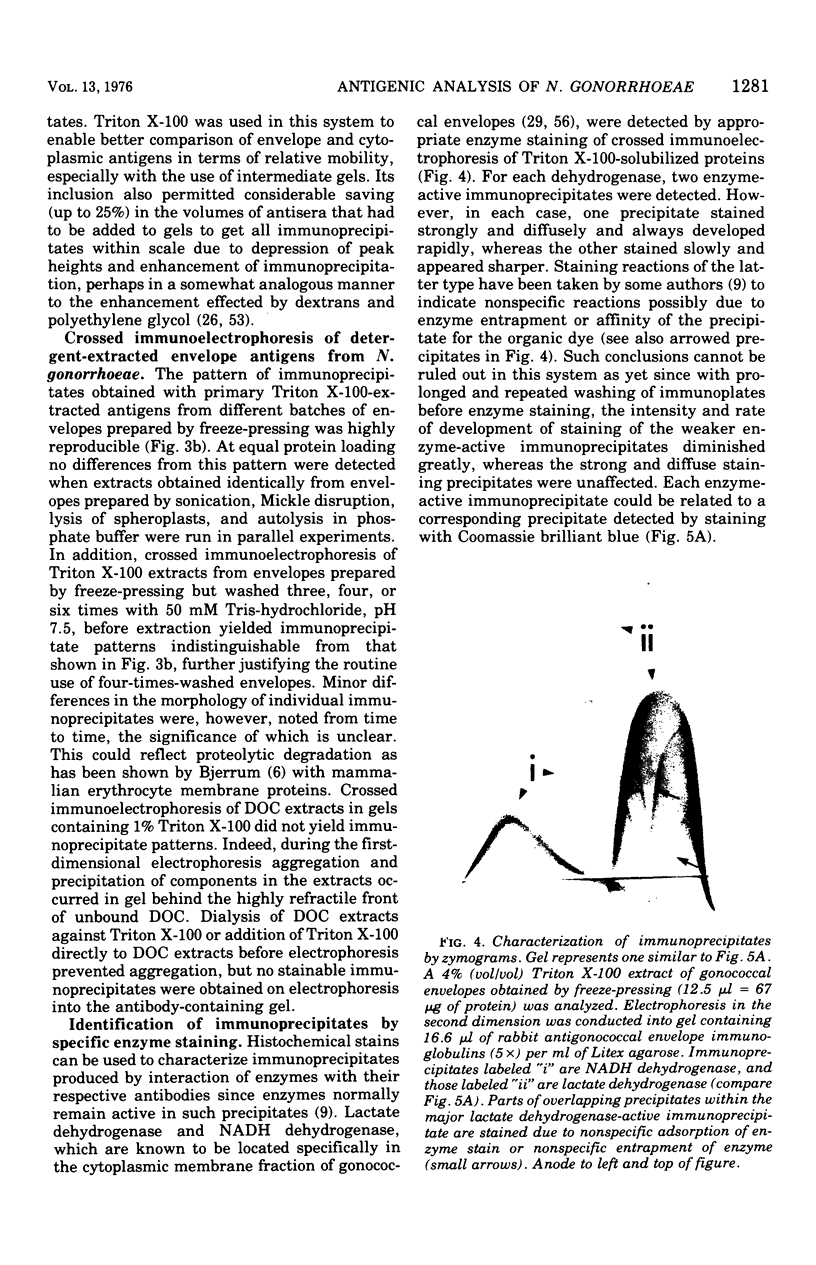
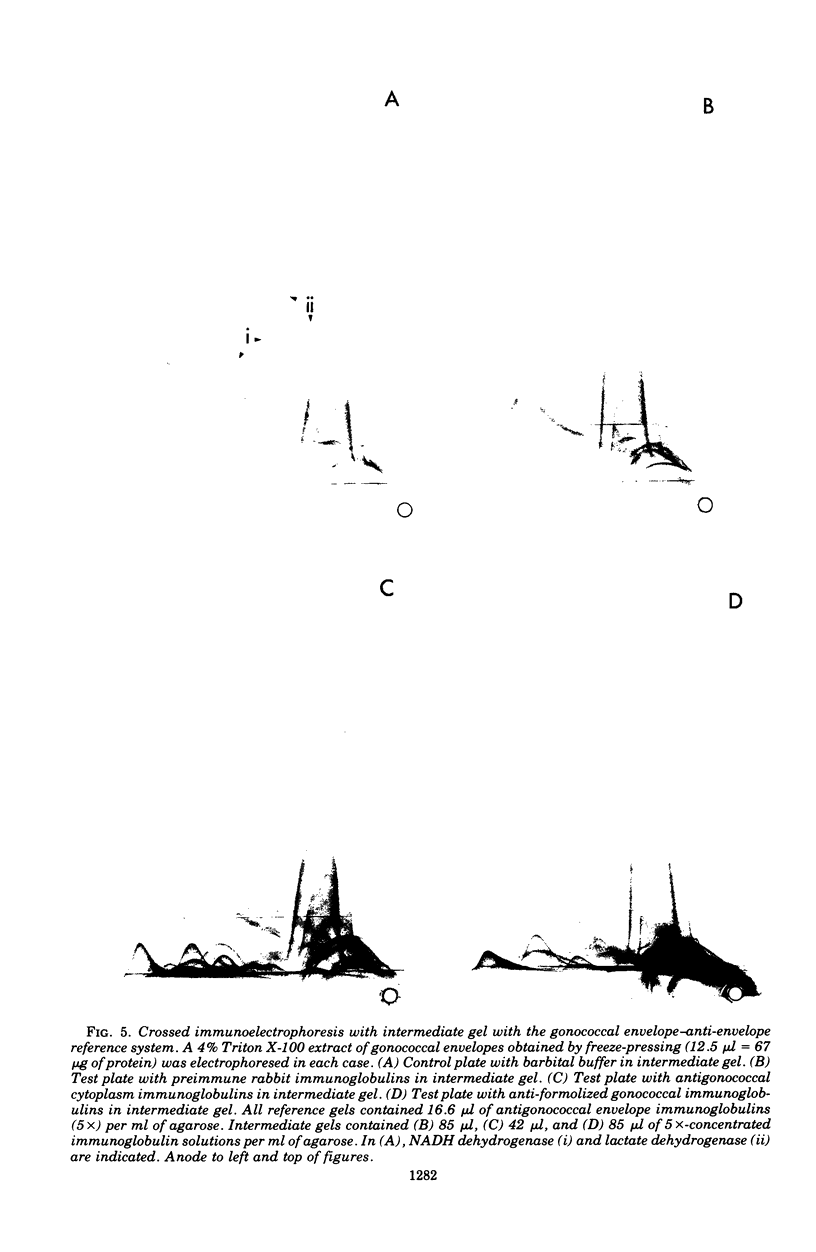
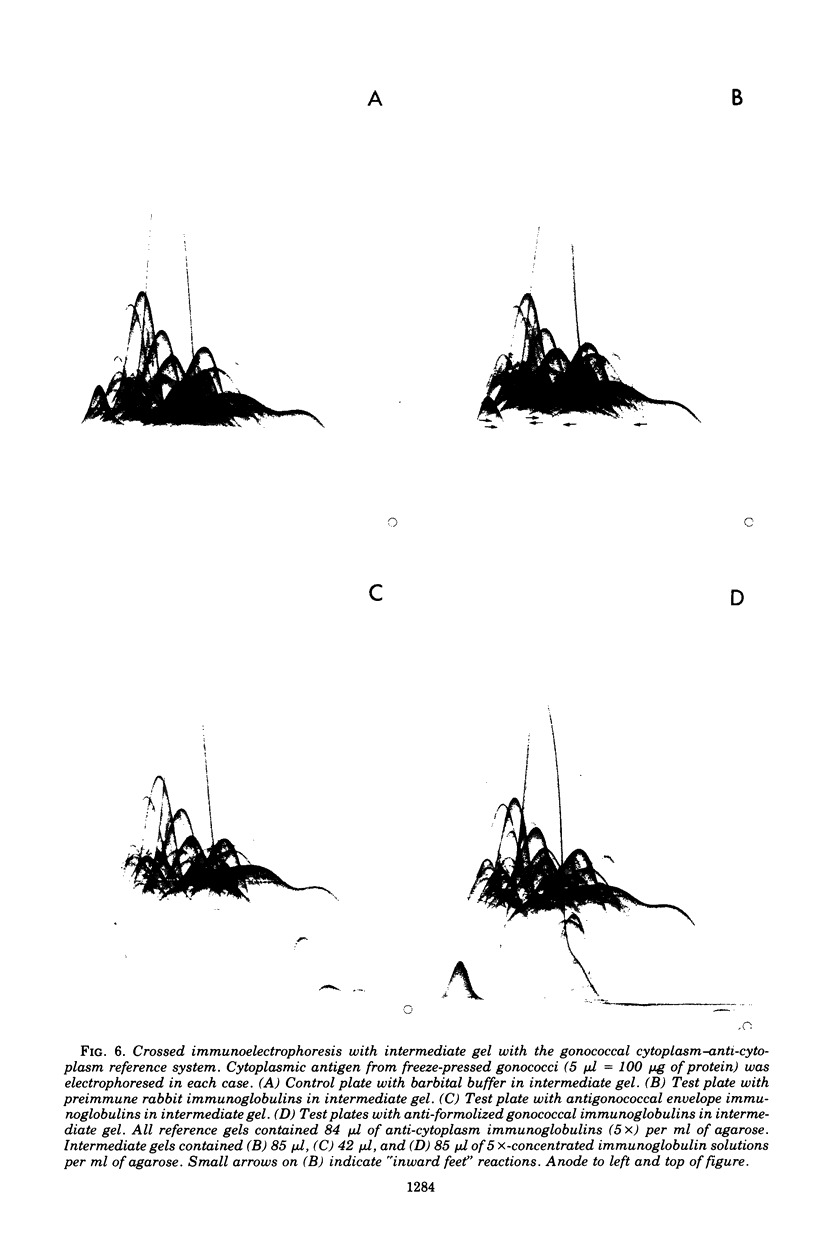
Crossed immunoelectrophoresis was used to study two complex antigenic preparations from Neisseria gonorrhoeae, one of cytoplasmic origin and the other derived by Triton X-100 extraction of isolated washed gonococcal envelopes, with the aim of developing suitable reference antigen-antibody systems that could be subsequently used to investigate the immune response to gonococcal infection and to monitor envelope preparations for cytoplasmic contamination. A number of parameters were investigated to optimized and standardize antigen preparation, e.g., harvesting and washing of gonococci, methods of bacterial disruption, and washing of envelopes. The effects of Triton X-100 concentration, initial total envelope protein concentration, and the composition, pH, and concentration of buffer on cell envelope extractability were studied to obviate the need to concentrate material before use in crossed immunoelectrophoresis. The electroendoosmotic properties of agarose were a major determining factor in resolving envelope antigens. From 25 to 30 immunoprecipitates were revealed in the envelope antigen-antibody system; 75 to 80 were revealed in the cytoplasmic sytem. Envelope immunoprecipitates with reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and lactate dehydrogenase activities were identified. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis with intermediate gels revealed the presence of antibodies in a preimmune rabbit antiserum pool to a distinctive fact-moving component in both the envelope and cytoplasmic antigen preparations. The intermediate gel technique also demonstrated that extensive washing of envelope preparations with buffer did not remove cytoplasmic ontamination completely. The method provides a much more sensitive means of monitoring the purity of envelope fractions than the use of single enzy,e markers as indexes of such contamination. The use of rabbit antisera raised to formolized gonococci in intermediate gels indicated that both reference antigen-antibody systems were of potential use in screening immune responses to N. gonorrhoeae.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A. Antigenically distinct populations of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: isolation and characterization of the responsible determinants. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):619–625. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsen N. H., Harboe M., Closs O., Godal T. BCG antibody profiles in tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):952–958. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.952-958.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsen N. H. Quantitative immunoelectrophoretic methods as tools for a polyvalent approach to standardization in the immunochemistry of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):949–960. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.949-960.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bog-Hansen T. C. Crossed immuno-affinoelectrophoresis. An analytical method to predict the result of affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):480–488. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Swanson J., Holmes K. K., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Quantitative determination of antibody to gonococcal pili. Changes in antibody levels with gonococcal infection. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2896–2909. doi: 10.1172/JCI107486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carifo K., Catlin B. W. Neisseria gonorrhoeae auxotyping: differentiation of clinical isolates based on growth responses on chemically defined media. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):223–230. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.223-230.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson D., Thyresson N., Falk V., Barr J. Serologic investigation of the immune response in various types of gonogoccal infection. Acta Derm Venereol. 1972;52(6):467–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. H., Salton M. R. Some properties of a D-alanine carboxypeptidase in envelope fractions of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1065–1069. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1065-1069.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faur Y. C., Weisburd M. H., Wilson M. E., May P. S. A new medium for the isolation of pathogenic Neisseria (NYC medium). I. Formulation and comparisons with standard media. Health Lab Sci. 1973 Apr;10(2):44–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Nachbar M. S., Salton M. R. Immunological properties of Micrococcus lysodeikticus membranes. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):86–92. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.86-92.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geizer I. Studies on serotyping of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975 Jul;232(2-3):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler B. H., Young F. E. Autolysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):385–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.385-392.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N., Axelsen N. H. Identification and quantitation of precipitins against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis by means of crossed immunoelectrophoresis with intermediate gel. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Jun;81(3):298–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg K., Nord C. E., Wadström T. Serological studies of Actinomyces israelii by crossed immunoelectrophoresis: taxonomic and diagnostic applications. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):398–403. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.398-403.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg K., Nord C. E., Wadström T. Serological studies of actionomyces israelii by crossed immunoelectrophoresis: standard antigen-antibody system for A. israelii. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):387–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.387-397.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyslop N. G., Cochrane D. G. Effects of dextrans on immunoprecipitation in agar and in low-temperature-gelling agarose gels. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Dec;6(1-2):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson K. E., Hjertén S. Localization of the Tween 20-soluble membrane proteins of Acholeplasma laidlawii by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Gotschlich E. C. Isolation and characterization of the outer membrane of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):250–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.250-257.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson P., Hanson L. A., Kaijser B. Immunodiffusion studies on some Proteus strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Dec;81(6):641–649. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Bartenstein L. Factors affecting autolysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Apr;145(4):1418–1421. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-38025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz E., Nachbar M. S., Schor M. T., Salton M. R. Adenosinetriphosphatase of Micrococcus lysodeikticus: selective release and relationship to membrane structure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Aug 13;32(3):539–546. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90696-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G., Coutinho A., Persson U. Mechanism of b-lymphocyte activation: failure to obtain evidence of a direct role of the Ig receptors in the triggering process. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(1):37–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norins L. C. The case for gonococcal serology. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):677–679. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny P., Turner W. H. Immunological heterogeneity of pili of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jul;89(1):87–92. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Salton M. R. Antigenic and enzymatic architecture of Micrococcus lysodeikticus membranes established by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3711–3715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. B., Daoust V. The lipopolysaccharides of Neisseria gonorrhoeae colony types 1 and 4. Can J Biochem. 1975 May;53(5):623–629. doi: 10.1139/o75-084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftell M., Blomberg F. Enzyme polymorphism in rat-liver microsomes and plasma membranes. 2. An immunochemical comparison of enzyme-active antigens solubilized by detergents, papain or phospholipases. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Nov 1;49(1):31–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. B., Wright G. L., Jr, Affronti L. F., Reich M. Characterization and comparison of mycobacterial antigens by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):564–573. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.564-573.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmale J. D., Danielsson D. G., Smith J. F., Lee L., Peacock W. L., Jr Isolation of an antigen of Neisseria gonorrhoeae involved in the human immune response to gonococcal infection. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):469–471. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.469-471.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Examination of the protein composition of the cell envelope of Escherichia coli by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):882–889. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.882-889.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. P., Shapiro B. M. Immunological properties of membrane fractions from wild type and dnaA mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 9;356(3):331–349. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svendsen J., Axelsen N. H. A modified antigen--antibody crossed electrophoresis characterizing the specificity and titre of human precipiting against Candida albicans. J Immunol Methods. 1972 Jan;1(2):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(72)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Sparks E., Young D., King G. Studies on Gonococcus infection. X. Pili and leukocyte association factor as mediators of interactions between gonococci and eukaryotic cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1352–1361. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1352-1361.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirkill C. E., Kenny G. E. Serological comparison of five arginine-utilizing Mycoplasma species by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):624–632. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.624-632.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thunberg A. L., Kindt T. J. Sequence variability of rabbit antibody light chains. Familial occurrence of n-terminal sequence differences between b4 and b9 light chains. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(2):197–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestergaard B. F. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic characterization of Herpesvirus hominis type 1 and 2 antigens. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Dec;81(6):808–810. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt P. J., Ward M. E., Glynn A. A. A comparison of serological tests for the diagnosis of gonorrhoea. Br J Vener Dis. 1971 Dec;47(6):448–451. doi: 10.1136/sti.47.6.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf-Watz H., Elmros T., Normark S., Bloom G. D. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: outer membrane and peptidoglycan composition of penicillin-sensitive and-resistant strains. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1332–1341. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1332-1341.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]