Abstract
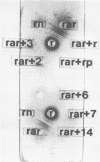
Isolation of a protective subfraction of ribosomes from Streptococcus pneumoniae has been achieved, and the immune response it induces has been investigated. Mice immunized with pneumococcal ribosomes or purified protein extracted from the ribosomal preparation (2-CE protein) exhibit similar survival rates upon challenge by virulent S. pneumoniae. In contrast, recipients of purified ribosomal ribonucleic acid were never protected against pneumococcal challenge. Serum from mice immunized with pneumococcal ribosomes or 2-CE protein passively immunized syngeneic recipients against pneumococcal challenge, whereas spleen cells from the same donors were unable to transfer immunity. Passive immunization with antiribosome serum could be abrogated by absorption with whole ribosomes, 2-CE protein, or various serotypes of S. pneumoniae (capsular types 2, 3, 6, and 14). Antiribosome serum significantly enhanced clearance of S. pneumoniae from mouse blood in vivo and in vitro. This required phagocytic cells, since antiribosome serum alone, with or without complement, supported growth of S. pneumoniae to an extent comparable to normal serum. The data suggest that the primary immunogen of pneumococcal ribosomes resides in the protein fraction. Further, the immunity induced by the protein fraction is mediated by antibody that appears to function as an opsonin for S. pneumoniae.
Full text
PDF




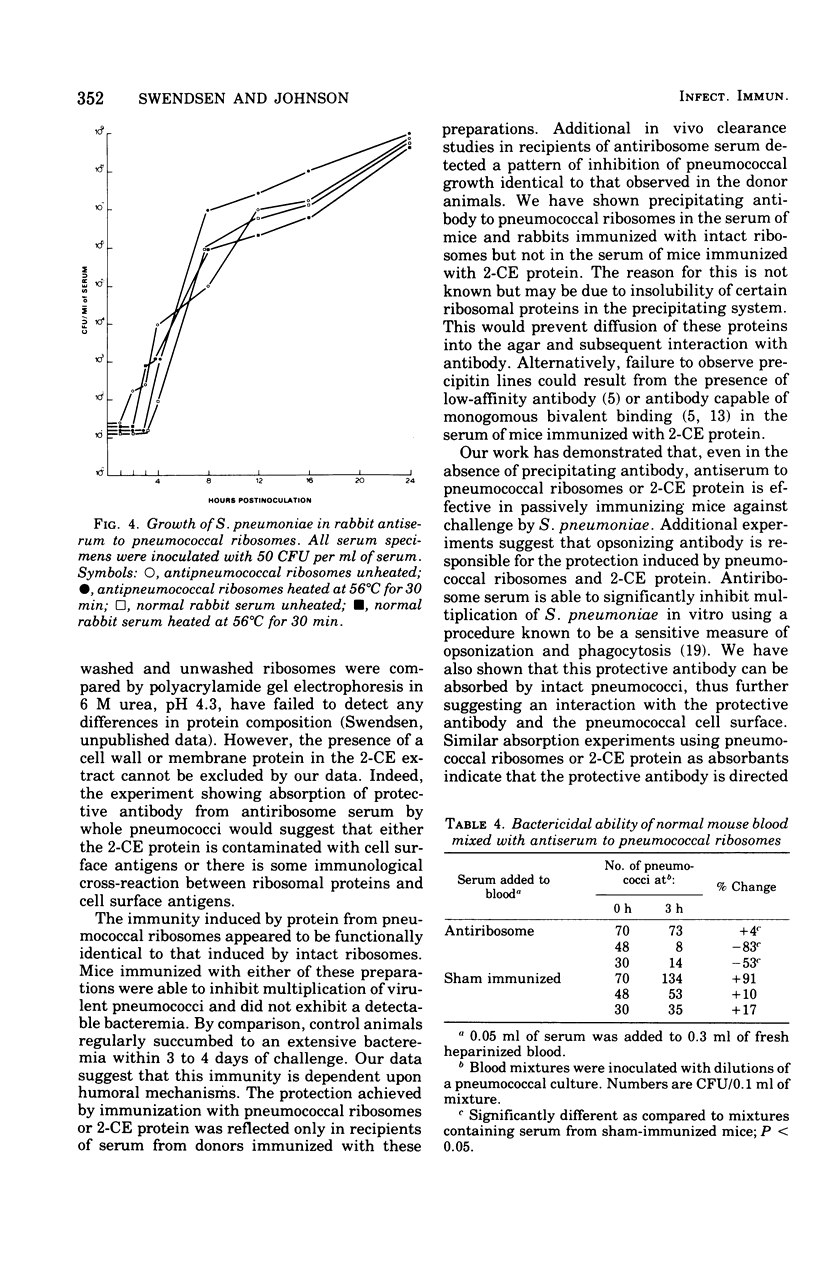


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andron LA I. I., Eigelsbach H. T. Biochemical and immunological properties of ribonucleic acid-rich extracts from Francisella tularensis. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):137–142. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.137-142.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araujo F. G., Remington J. S. Protection against Toxoplasma gondii in mice immunized with Toxoplasma cell fractions, RNA and synthetic polyribonucleotides. Immunology. 1974 Oct;27(4):711–721. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casavant C. H., Youmans G. P. The adjuvant activity of mycobacterial RNA preparations and synthetic polynucleotides for induction of delayed hypersensitivity to purified protein derivative in guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):1014–1022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K. Evidence for O antigens as the antigenic determinants in "ribosomal" vaccines prepared from Salmonella. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):364–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.364-377.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., Houba V. Immunological reactions with chromic chloride-treated erythrocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1973 Aug;3(1):87–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(73)90071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feit C., Tewari R. P. Immunogenicity of Ribosomal Preparations from Yeast Cells of Histoplasma capsulatum. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1091–1097. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1091-1097.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogel S., Sypherd P. S. Extraction and isolation of individual ribosomal proteins from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):358–364. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.358-364.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornick C. L., Karush F. The interaction of hapten-coupled bacteriophage phi-X-174 with antihapten antibody. Isr J Med Sci. 1969 Mar-Apr;5(2):163–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Gregory B., Naylor J., Actor P. Isolation of protective somatic antigen from Vibrio cholerae (Ogawa) ribosomal preparations. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):156–161. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.156-161.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. Ribosomal vaccines. II. Specificity of the immune response to ribosomal ribonucleic acid and protein isolated from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):395–400. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.395-400.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klun C. L., Youmans G. P. The effect of lymphocyte supernatant fluids on the intracellular growth of virulent tubercle bacilli. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1973 Mar;13(3):263–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G. The requirements for specific sRNA binding by ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):90–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Differentiation of group A streptococci with a common R antigen into three serological types, with special reference to the bactericidal test. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):525–544. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU T. Y., GOTSCHLICH E. C. The chemical composition of pneumococcal C-polysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jun;238:1928–1934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R. J., Youmans G. P. Demonstration in tissue culture of lymphocyte-mediated immunity to tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):600–603. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.600-603.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalla W. O., Johnson W. Immunogenicity of ribosomal vaccines isolated from group A, type 14 Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1195–1202. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1195-1202.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P., Larsen B., Johnson W., Galask R. P. Bacterial growth inhibition by amniotic fluid. III. Demonstration of the variability of bacterial growth inhibition by amniotic fluid with a new plate-count technique. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Aug 1;122(7):809–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Bigley N. J. Detection of delayed hypersensitivity in mice injected with ribonucleic acid-protein fractions of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):384–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.384-389.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Bigley N. J. Ribonucleic acid-protein fractions of virulent Salmonella typhimurium as protective immunogens. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):377–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.377-383.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Wysocki J. A., Bruun J. N., De Courcy S. J., Jr, Blakemore W. S., Mudd S. Efficacy of ribosomal preparations from Pseudomonas aeruginosa to protect against intravenous Pseudomonas challenge in mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1974 Jan;15(1):22–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. W., Weiss E. Response of mice to injection of ribosomal fraction from group B Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):355–363. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.355-363.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. C., Eisenstein T. K. Biological properties of an immunogenic pneumococcal subcellular preparation. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):750–757. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.750-757.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. C., Snyder I. S. Protection against pneumococcal infection by a ribosomal preparation. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):16–23. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.16-23.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Berry L. J. Cell-mediated resistance induced with immunogenic preparations of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):381–387. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.381-387.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J. Isolation and partial characterization of an immunogenic moiety obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):140–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.140-148.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R. Purification of immunogenically active ribonucleic acid preparations of Salmonella typhimurium: molecular-sieve and anion-exchange chromatography. Infect Immun. 1972 Mar;5(3):269–282. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.3.269-282.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller D. L., Sjogren R. E. Chemical heterogeneity of ribosomal protein of Escherichia coli examined by electrofocusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 31;200(3):508–521. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcockson J. The use of sodium perchlorate in deproteinization during the preparation of nucleic acids. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;135(3):559–561. doi: 10.1042/bj1350559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston S. H., Berry L. J. Antibacterial immunity induced by ribosomal vaccines. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Jul;8(1):13–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston S., Berry L. J. Immunity induced by ribosomal extracts from Staphylococcus aureus. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Jul;8(1):66–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS A. S., YOUMANS G. P. IMMUNOGENIC ACTIVITY OF A RIBOSOMAL FRACTION OBTAINED FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1291–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1291-1298.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Effect of trypsin and ribonuclease on the immunogenic activity of ribosomes and ribonucleic acid isolated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2146–2154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2146-2154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Immunogenic mycobacterial ribosomal and ribonucleic Acid preparations: chemical and physical characteristics. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):659–668. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.659-668.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]