Abstract
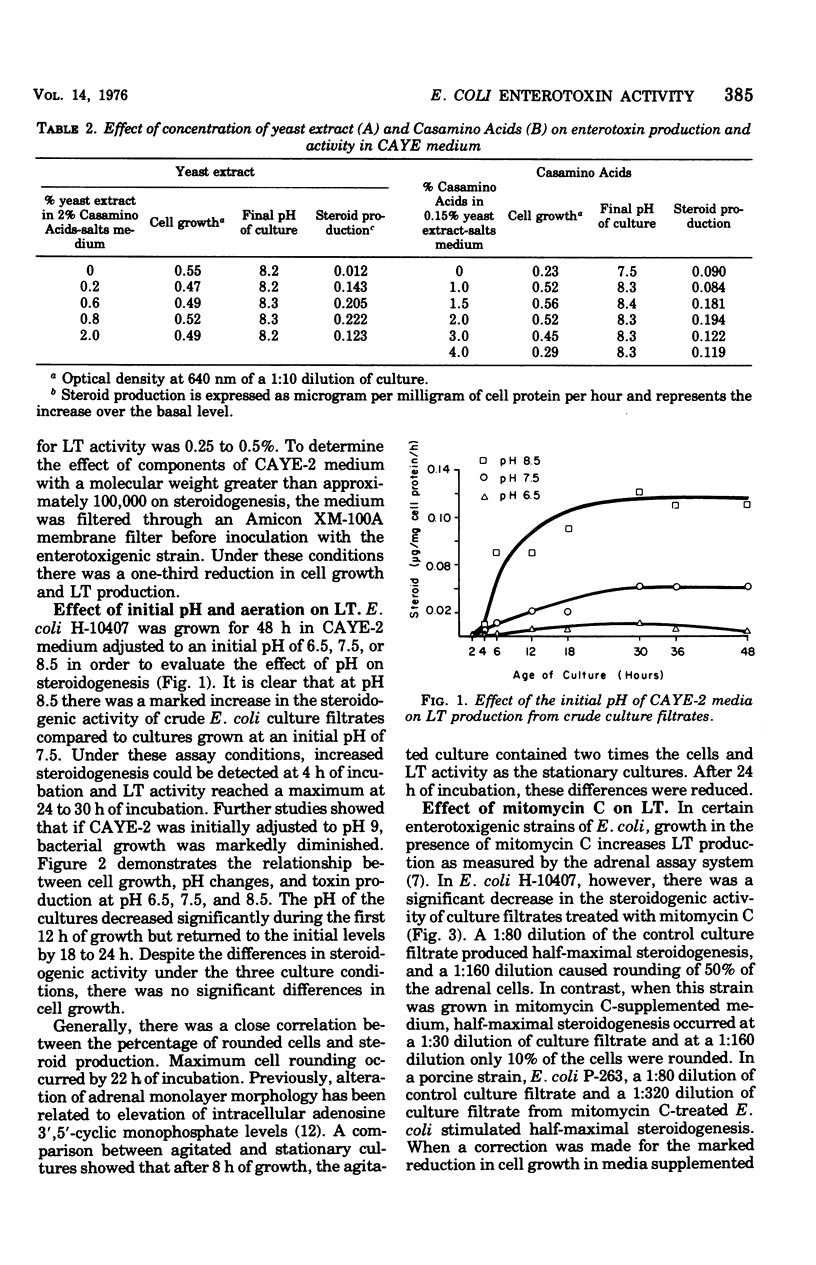
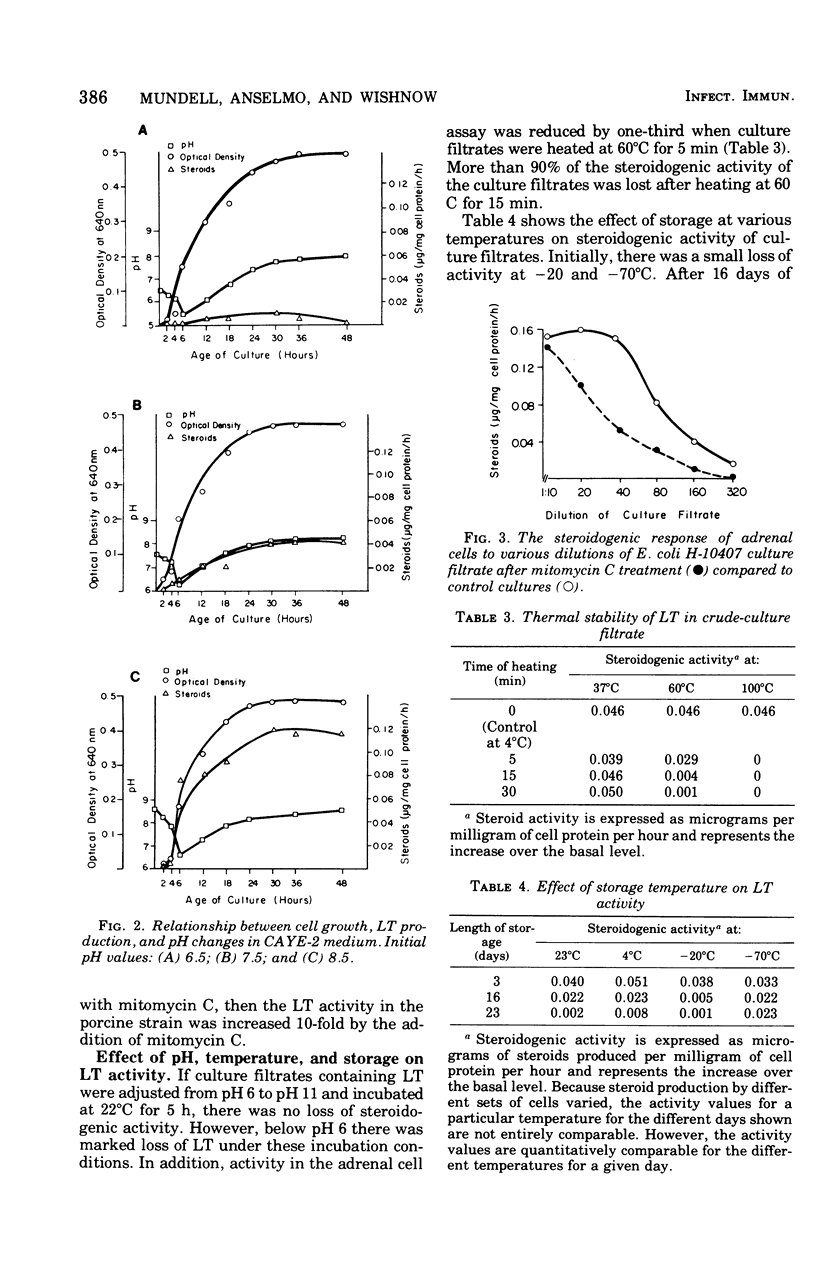
In this study, conditions for production, detection, and storage of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin (LT) in culture filtrates from E. coli H-10407 were defined by using the adrenal tumor cell assay system. An enriched medium containing 0.6% yeast extract, 2% Casamino Acids, and 0.25% glucose buffered at pH 8.5 produced the highest LT activity of the various test media. In E. coli strain H-10407, LT activity was markedly decreased if the initial pH of the culture media was reduced to pH 7.5 or less. In contrast to E. coli P-263, if strain H-10407 was grown in the presence of mitomycin C there was no increase in LT production. Crude-culture filtrates containing LT can be stored at 4 degrees C for several days without an appreciable loss of activity; however, for long-term storage lyophilization or freezing at -70 degrees C is recommended.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carpenter C. C. Cholera and other enterotoxin-related diarrheal diseases. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):551–564. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Production of vascular permeability factor by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):725–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.725-730.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G. Three characteristics associated with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):322–328. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.322-328.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Khurana C. M. Toxigenic Escherichia coli: a cause of infantile diarrhea in Chicago. N Engl J Med. 1972 Oct 19;287(16):791–795. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197210192871603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson R. E., Moon H. W. Induction of heat-labile enterotoxin synthesis in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli mitomycin C. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1271–1275. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1271-1275.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. M., Wu B. J., Braemer A. C., Bidlack D. E. Properties of the enterotoxic component in Escherichia coli enteropathogenic for swine. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):178–189. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.178-189.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor H. S. Enterotoxins of Escherichia coli and vibriocholerae: tools for the molecular biologist. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131 (Suppl):S22–S32. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.supplement.s22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor H. S., Tao P., Wisdom C. Action of Escherichia coli enterotoxin: adenylate cyclase behavior of intestinal epithelial cells in culture. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1003–1010. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1003-1010.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan C. N., Wishnow R. M. Adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate and adrenal tumor cell morphology. In Vitro. 1974 Nov-Dec;10(5-6):268–273. doi: 10.1007/BF02615307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan C. N., Wishnow R. M. Escherichia coli enterotoxin-induced steroidogenesis in cultured adrenal tumor cells. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):146–151. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.146-151.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell I. D., Tame M. J., Kenworthy R. Separation and purification of enterotoxins from a strain Escherichia coli pathogenic for pigs. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Nov;7(4):439–450. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-4-439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundell D. H., Anselmo C. R., Thrupp L. D., Wishnow R. M. Toxigenic Escherichia coli and childhood diarrhea. West J Med. 1976 May;124(5):357–360. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport R. S., Grant N. H. Growth hormone releasing factor of microbial origin. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):73–75. doi: 10.1038/248073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishnow R. M., Feist P. The effect of cholera enterotoxin on steroidogenesis in cultured adrenal tumor cells. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(6):690–695. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.6.690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishnow R. M., Lifrak E., Chen C. C. Mode of action of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin in cultured adrenal tumor cells. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133 (Suppl):108–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


