Abstract
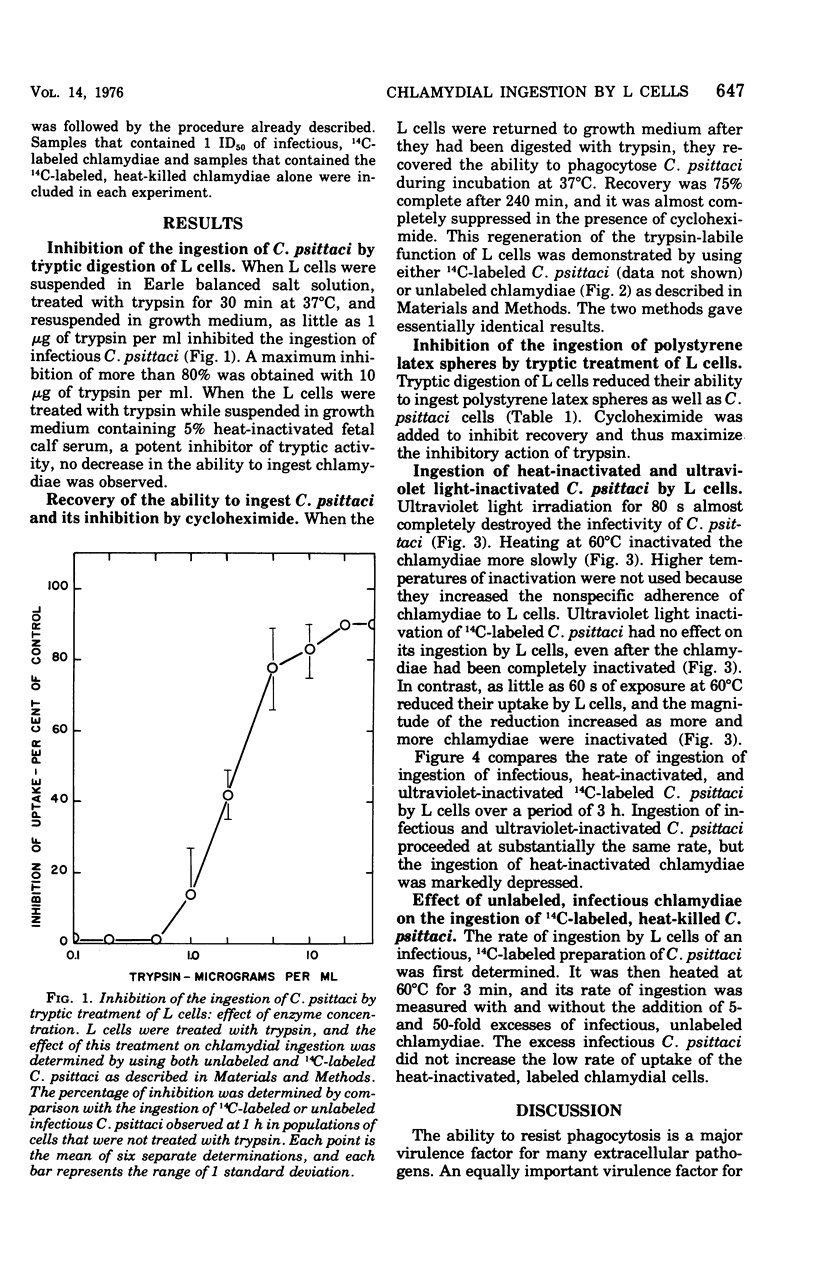
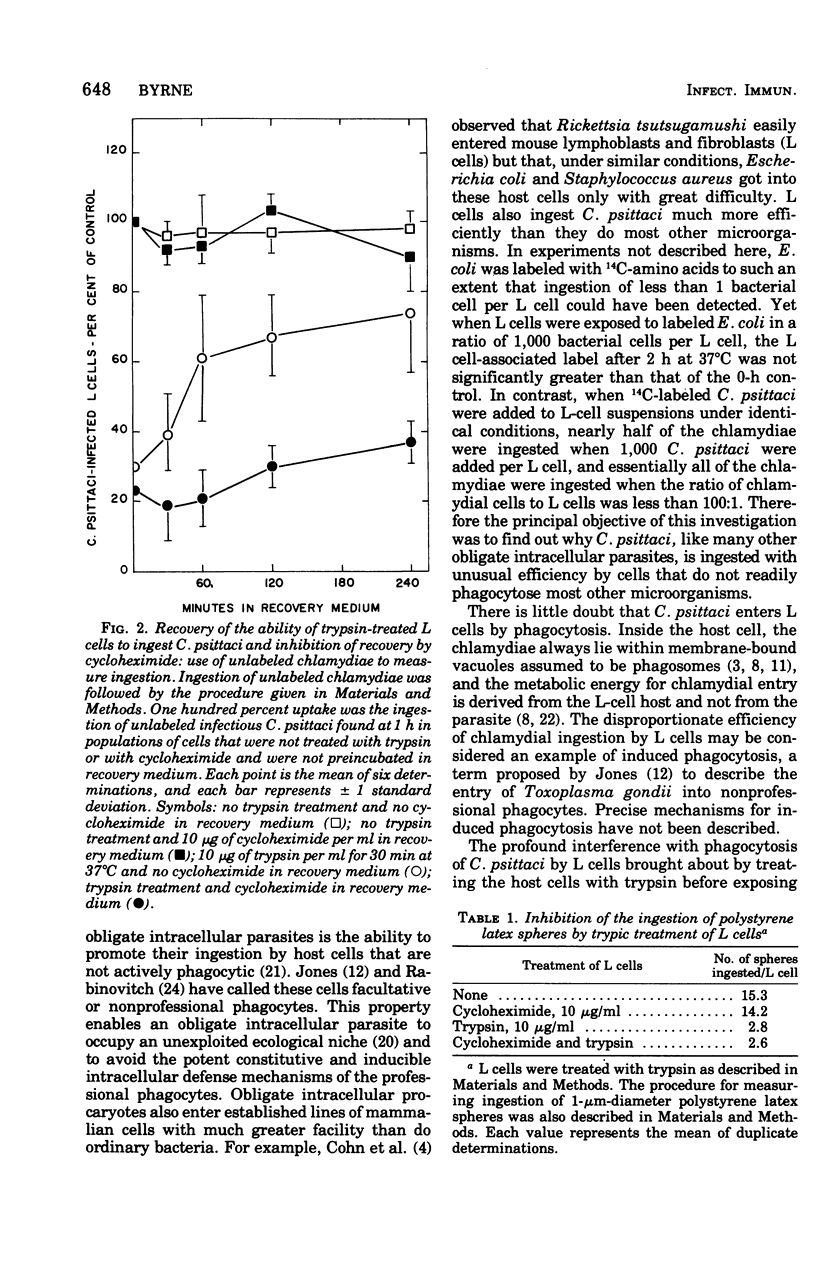
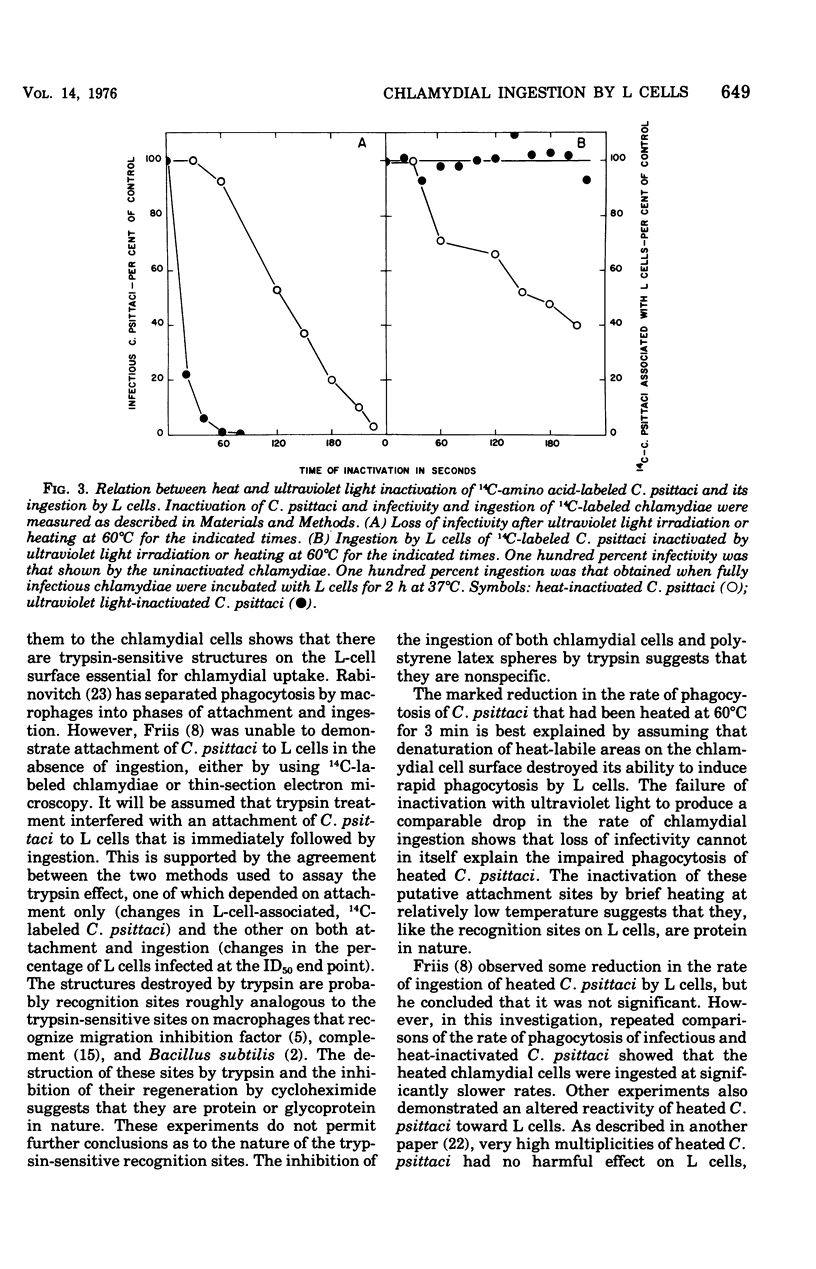
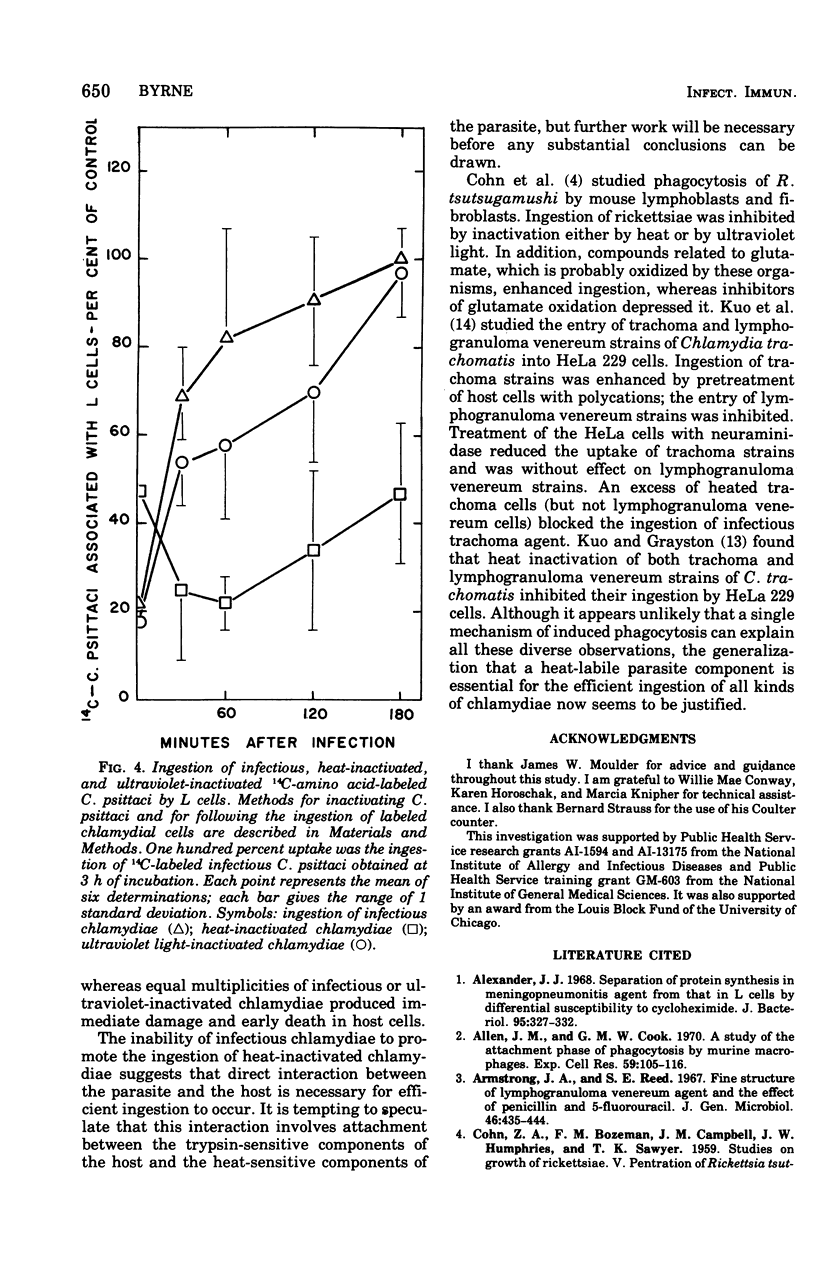
Ingestion of 14C-amino acid-labeled Chlamydia psittaci (6BC) by mouse fibroblasts (L cells) was inhibited when the host cells were incubated for 30 min at 37 degrees C in Earle salts containing 10 mug of crystalline trypsin per ml. Tryptic digestion also inhibited the ingestion of 1-mum polystrene latex beads. Trypsin-treated L cells almost completely recovered their ability to ingest chlamydiae after 4 h at 37 degrees C in medium 199 with 5% fetal calf serum. Cycloheximide (10 mug/ml) blocked this recovery. Heating 14C-amino acid-labeled C. psittaci for 3 min at 60 degrees C inhibited its ingestion by L cells, whereas inactivating it with ultraviolet light was without effect on the ingestion rate. These results show that efficient ingestion of C. psittaci by L cells involves trypsin-labile sites on the host and heat-sensitive sites on the parasite. The failure of excess unlabeled infectious C. psittaci to promote the ingestion of 14C-labeled heat-inactivated chlamydiae suggests that direct interaction between these two sites must occur for uptake to proceed normally.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. J. Separation of protein synthesis in meningopneumonitisgent from that in L cells by differential susceptibility to cycloheximide. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):327–332. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.327-332.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Cook G. M. A study of the attachment phase of phagocytosis by murine macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Jan;59(1):105–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90629-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BOZEMAN F. M., CAMPBELL J. M., HUMPHRIES J. W., SAWYER T. K. Study on growth of Rickettsia. V. Penetration of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi into mammalian cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1959 Mar 1;109(3):271–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVID J. R., LAWRENCE H. S., THOMAS L. THE IN VITRO DESENSITIZATION OF SENSITIVE CELLS BY TRYPSIN. J Exp Med. 1964 Dec 1;120:1189–1200. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.6.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis R. R. Interaction of L cells and Chlamydia psittaci: entry of the parasite and host responses to its development. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):706–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.706-721.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayston J. T., Wang S. New knowledge of chlamydiae and the diseases they cause. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):87–105. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGASHI N. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON THE MODE OF REPRODUCTION OF TRACHOMA VIRUS AND PSITTACOSIS VIRUS IN CELL CULTURES. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Feb;76:24–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P. Competition between Chlamydia psittaci and L cells for host isoleucine pools: a limiting factor in chlamydial multiplication. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):211–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.211-220.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Grayston T. Interaction of Chlamydia trachomatis organisms and HeLa 229 cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1103–1109. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1103-1109.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Effect of polycations, polyanions and neuraminidase on the infectivity of trachoma-inclusin conjunctivitis and lymphogranuloma venereum organisms HeLa cells: sialic acid residues as possible receptors for trachoma-inclusion conjunction. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):74–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.74-79.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Nussenzweig V. Receptors for complement of leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):991–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANIRE G. P., GALASSO G. J. Persistent infection of HeLa cells with meningopneumonitis virus. J Immunol. 1959 Nov;83:529–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLIMANS W. F., DAVIS E. V., GLOVER F. L., RAKE G. W. The submerged culture of mammalian cells; the spinner culture. J Immunol. 1957 Nov;79(5):428–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W., Hatch T. P., Byrne G. I., Kellogg K. R. Immediate toxicity of high multiplicities of Chlamydia psittaci for mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):277–289. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.277-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Intracellular parasitism: life in an extreme environment. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):300–306. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. The contribution of model systems to the understanding of infectious diseases. Perspect Biol Med. 1971 Spring;14(3):486–502. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1971.0024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. The dissociation of the attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis by macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Apr;46(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90405-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. Uptake of aldehyde-treated erythrocytes by L2 cells: inhibition by anti-red cell antibody or by coating the erythrocytes with purified proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Feb;54(2):210–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90235-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter E. M. Synthesis of nucleic acid and protein in L cells infected with the agent of meningopneumonitis. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2069–2080. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2069-2080.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


