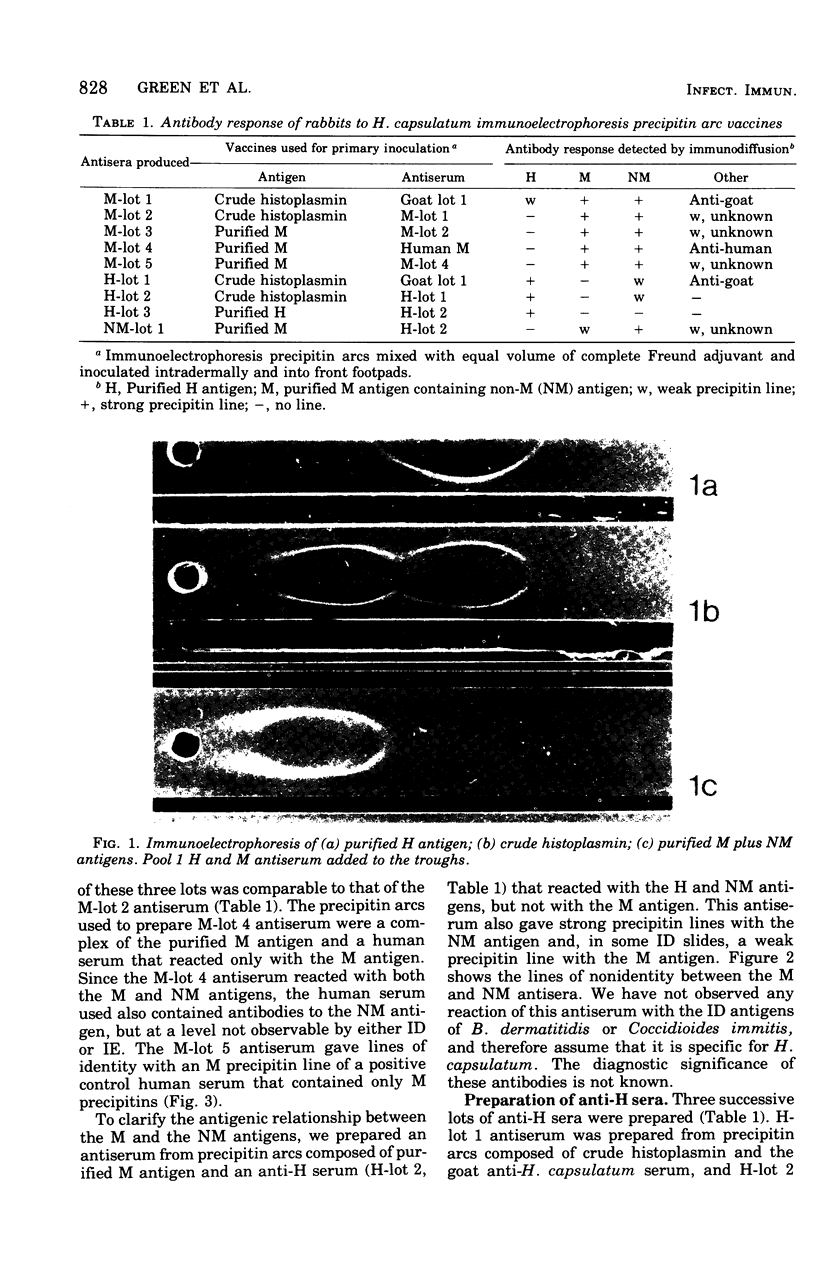
Abstract
Antiserum has been prepared in rabbits against the H and M antigens of H. capsulatum with immunoelectrophoretic precipitin arcs used as vaccines. The antiserum is specific for H. capsulatum in the immunodiffusion test and can be used as reference serum for identifying antibodies to these antigens in sera from suspected cases histoplasmosis. We found that (1) hand m antigens are not located on the surface of yeast-phase cells and (ii) complement fixation releases the antigens reactive in the complement fixation test from yeast-phase cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aufman L. Serology of systemic fungus diseases. Public Health Rep. 1966 Feb;81(2):177–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauman D. S., Smith C. D. Comparison of immunodiffusion and complement fixation tests in the diagnosis of histoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;2(2):77–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley G., Pine L., Reeves M. W., Moss C. W. Purification, composition, and serological characterization of histoplasmin-H and M antigens. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):870–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.870-880.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busey J. F., Hinton P. F. Precipitins in histoplasmosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Oct;92(4):637–639. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.92.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhard H. B., Pine L. Factors influencing the production of H and M antigens by Histoplasma capsulatum: development and evaluation of a shake culture. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):236–249. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.236-249.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhard H. B., Pine L. Factors influencing the production of H and M antigens by Histoplasma capsulatum: effect of physical factors and composition of medium. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):250–261. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.250-261.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross H., Bradley G., Pine L., Gray S., Green J. H., Harrell W. K. Evaluation of histoplasmin for the presence of H and M antigens: some difficulties encountered in the production and evaluation of a product suitable for the immunodiffusion test. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):330–334. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.330-334.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINER D. C. Diagnosis of histoplasmosis using precipitin reactions in agargel. Pediatrics. 1958 Oct;22(4 Pt 1):616–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN L., KAPLAN W. Preparation of a fluorescent antibody specific for the yeast phase of Histoplasma capsulatum. J Bacteriol. 1961 Nov;82:729–735. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.5.729-735.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan W., Kaufman L., McClure H. M. Pathogenesis and immunological aspects of experimental histoplasmosis in cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):847–853. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.847-853.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L., Blumer S. Development and use of a polyvalent conjugate to differentiate Histoplasma capsulatum and Histoplasma duboisii from other pathogens. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1243–1246. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1243-1246.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Pine L., Bradley G. Characterization and evaluation of a soluble antigen complex prepared from the yeast phase of Histoplasma capsulatum. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1033–1044. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1033-1044.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Pine L., Kaufman L., McLaughlin D. Isolation of a new soluble antigen from the yeast phase of Histoplasma capsulatum. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):841–843. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.841-843.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUBERT J. H., LYNCH H. J., Jr, AJELLO L. Evaluation of the agar-plate precipitin test for histoplasmosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Dec;84:845–849. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.84.6.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H., GALLOP R. C., TOZER B. T. THE PRODUCTION OF SPECIFIC RABBIT ANTIBODIES BY INJECTING INDIVIDUAL ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEXES SEPARATED FROM MIXED ANTIGENS. Immunology. 1964 Mar;7:111–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharbaugh R. J., DiSalvo A. F., Goodman N. L., Reddick R. A. Serologic aspects of experimental histoplasmosis in cattle. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):186–189. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivers C. A., James J. M. Specific antibodies produced against antigens of agar-gel precipitates. Immunology. 1967 Dec;13(6):547–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]