Abstract
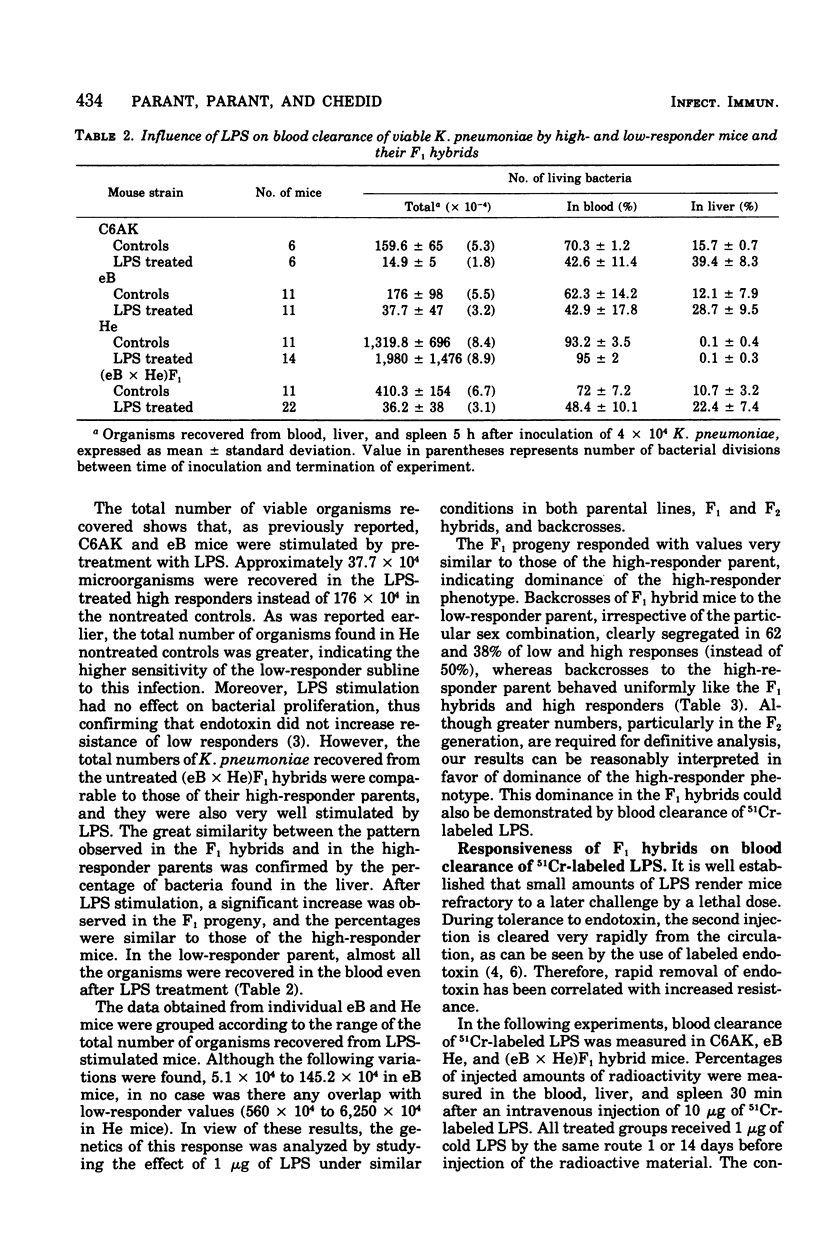
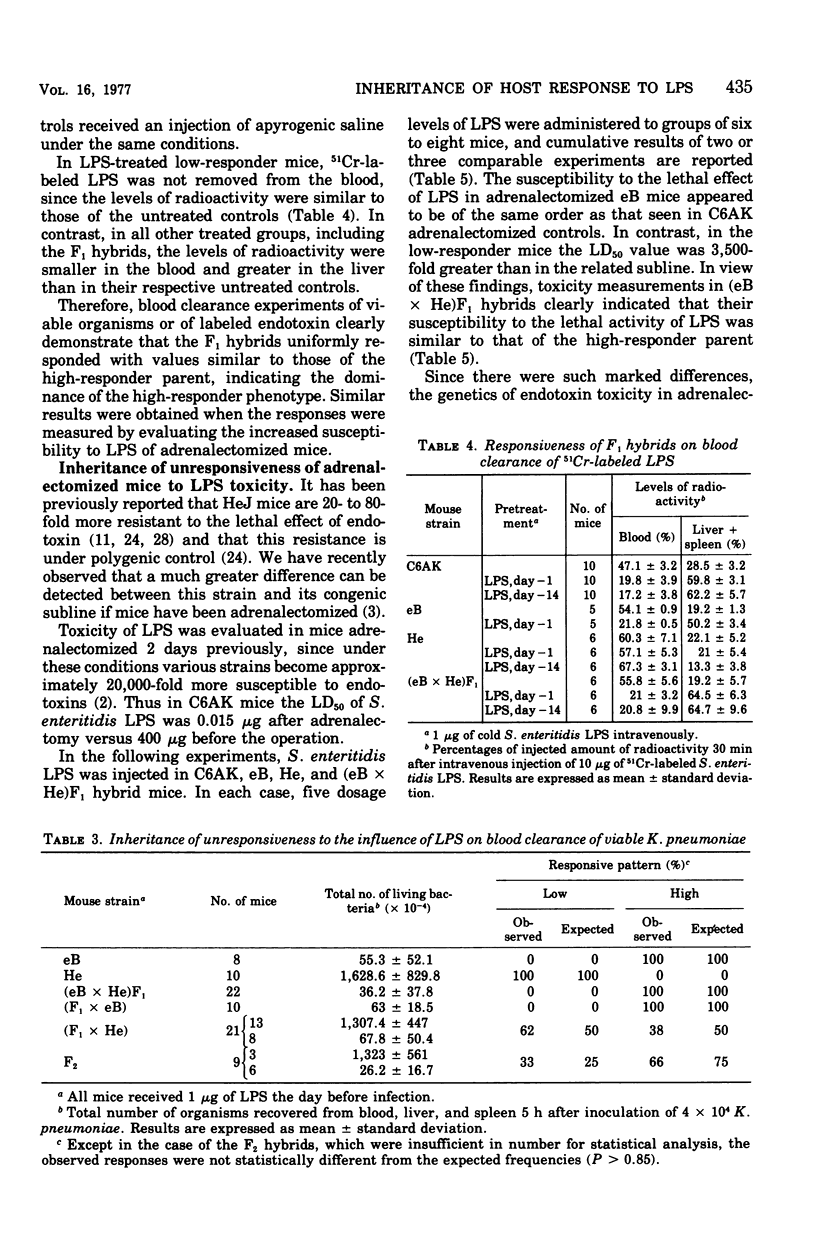
In a previous study, we demonstrated that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and other bacterial immunostimulants, in contrast to their activity in a closely related high-responder subline, failed to elicit nonspecific resistance in LPS low-responder mice against Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. To investigate the type of inheritance controlling the LPS-induced nonspecific resistance to infection, the present study was performed in low- and high-responder C3H sublines and in F1 and F2 hybrids. In addition, F1 mice were backcrossed to each parental type. Inheritance of susceptibility to endotoxin was also tested in both sublines and their hybrids and backcross progeny. For these latter assays, mice were previously adrenalectomized because removal of this gland considerably enhances their sensitivity. Our present findings are consistent with the hypothesis that LPS enhances nonspecific resistance to infection and that susceptibility to endotoxin shock in the absence of corticoids may be determined by a single autosomal dominant gene.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Möller G., Sjöberg O. Selective induction of DNA synthesis in T and B lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1972 Aug;4(4):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEDID L., PARANT M. [Study of the tolerance of adrenalectomized mice using an endotoxin labeled with Cr-51]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1961 Aug;101:170–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEDID L., SKARNES R. C., PARANT M. Characterization of a Cr51-labeled endotoxin and its identification in plasma and urine after parenteral administration. J Exp Med. 1963 Apr 1;117:561–571. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.4.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant F., Parant M., Boyer F. Localization and fate of 51-Cr-labeled somatic antigens of smooth and rough Salmonellae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):712–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Damais C., Parant F., Juy D., Galelli A. Failure of endotoxin to increase nonspecific resistance to infection of lipopolysaccharide low-responder mice. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):722–727. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.722-727.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Parant F., Boyer F. A proposed mechanism for natural immunity to enterobacterial pathogens. J Immunol. 1968 Feb;100(2):292–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho A., Gronowicz E., Sultzer B. M. Genetic control of B-cell responses. I. Selective unresponsiveness to lipopolysaccharide. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(2):139–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho A., Moller G., Gronowicz E. Genetical control of B-cell responses. IV. Inheritance of the unresponsiveness to lipopolysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):253–258. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOS R. J., SCHAEDLER R. W. Reversible changes in the susceptibility of mice to bacterial infections. I. Changes brought about by injection of pertussis vaccine or of bacterial endotoxins. J Exp Med. 1956 Jul 1;104(1):53–65. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzl R. E., McMaster P. D. The primary immune response in mice. I. The enhancement and suppression of hemolysin production by a bacterial endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1968 Jun 1;127(6):1087–1107. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.6.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppner G., Weiss D. W. High Susceptibility of Strain A Mice to Endotoxin and Endotoxin-Red Blood Cell Mixtures. J Bacteriol. 1965 Sep;90(3):696–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.3.696-703.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON A. G., GAINES S., LANDY M. Studies on the O antigen of Salmonella typhosa. V. Enhancement of antibody response to protein antigens by the purified lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1956 Feb 1;103(2):225–246. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamensans A., Chedid L., Lederer E., Rosselet J. P., Gustafson R. H., Spencer H. J., Ludwig B., Berger F. M. Enhancement of immunity against murine syngeneic tumors by a fraction extracted from non-pathogenic mycobacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3656–3660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer S. B., Vaughan J. H., Tan E. M. Adjuvant activity of the histamine-sensitizing factor of Bordetella pertussis in different strains of mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;49(6):796–813. doi: 10.1159/000231464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARANT M., BOYER F., CHEDID L. AUGMENTATION DE LA R'ESISTANCE AUX INFECTIONS CONS'ECUTIVE 'A UNE INJECTION D'ENDOTOXINE. MISE EN 'EVIDENCE DU M'ECANISME PAR L'ASSOCIATION DE SULFAMIDE. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 1;260:2630–2633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parant M. Recherche d'opsonines chez la souris après stimulation par l'endotoxine de sa résistance à l'infection. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1968 Aug;115(2):264–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Adler W. H., Smith R. T. The mitogenic effects of endotoxin and staphylococcal enterotoxin B on mouse spleen cells and human peripheral lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1453–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D. Stimulation of natural immunity to Escherichia coli infection: observations on mice. Lancet. 1955 Jan 29;268(6857):232–234. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(55)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard C. Etude antigénique et biochimique de 500 souches de Klebsiella. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1973;31(4):295–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore B. J., Chiller J. M., Weigle W. O., Riblet R., Watson J. Immunologic properties of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). III. Genetic linkage between the in vitro mitogenic and in vivo adjuvant properties of LPS. J Exp Med. 1976 Jan 1;143(1):143–150. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M. Genetic analysis of lymphocyte activation by lipopolysaccharide Endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1579–1584. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1579-1584.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M. Genetic control of host responses to endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1972 Jan;5(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.1.107-113.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M., Nilsson B. S. PPD tuberculin--a B-cell mitogen. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 13;240(102):198–200. doi: 10.1038/newbio240198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vas S. I., Roy R. S., Robson H. G. Endotoxin sensitivity of inbred mouse strains. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jul;19(7):767–769. doi: 10.1139/m73-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw A. C. Inheritance of responsiveness to pertussis HSF in mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;38(6):573–589. doi: 10.1159/000230313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Riblet R. Genetic control of responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharides in mice. I. Evidence for a single gene that influences mitogenic and immunogenic respones to lipopolysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1147–1161. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


