Abstract
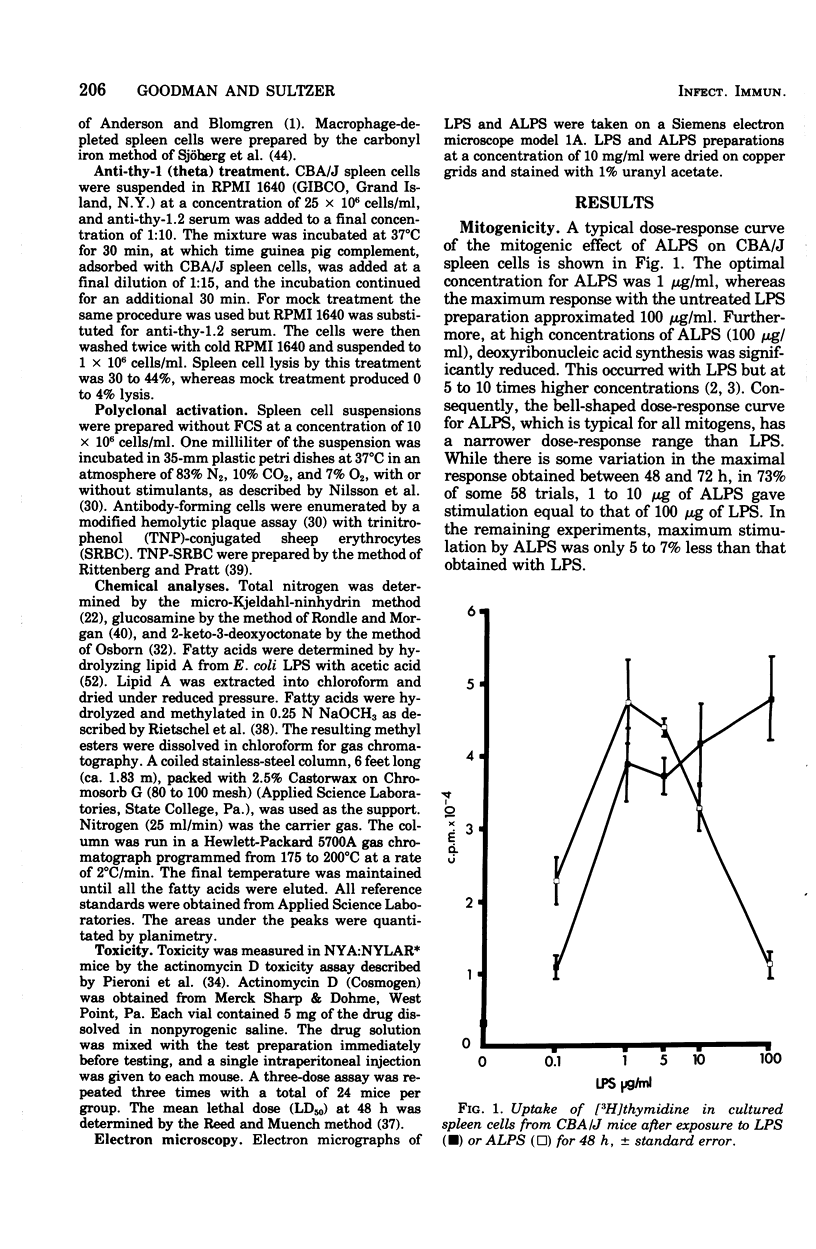
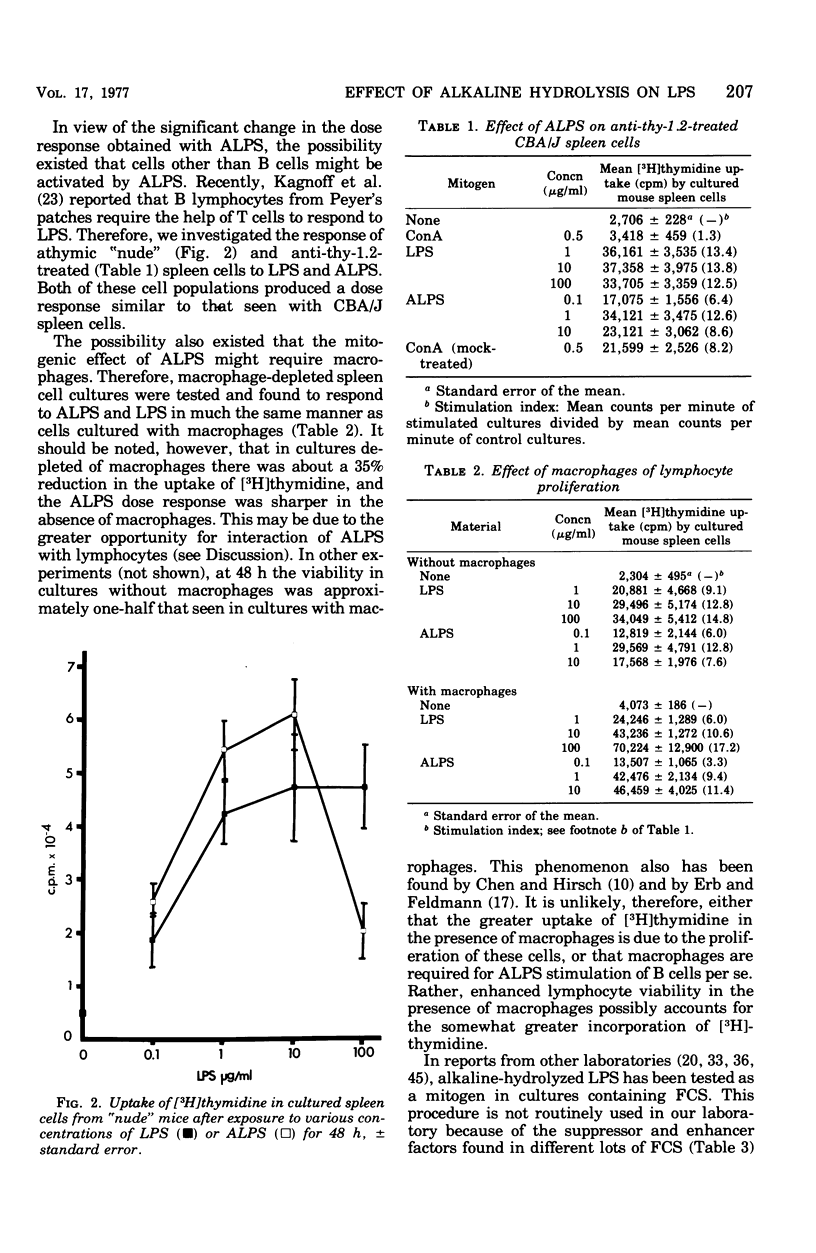
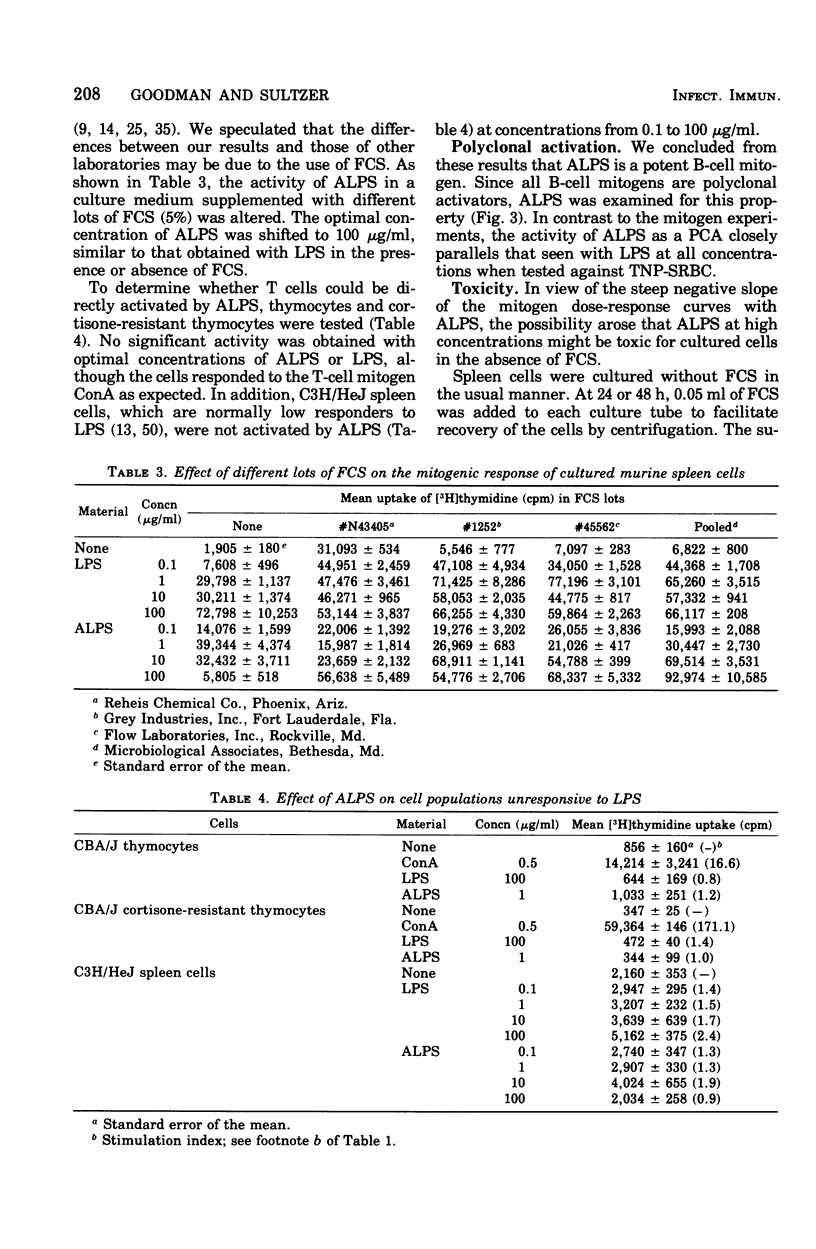
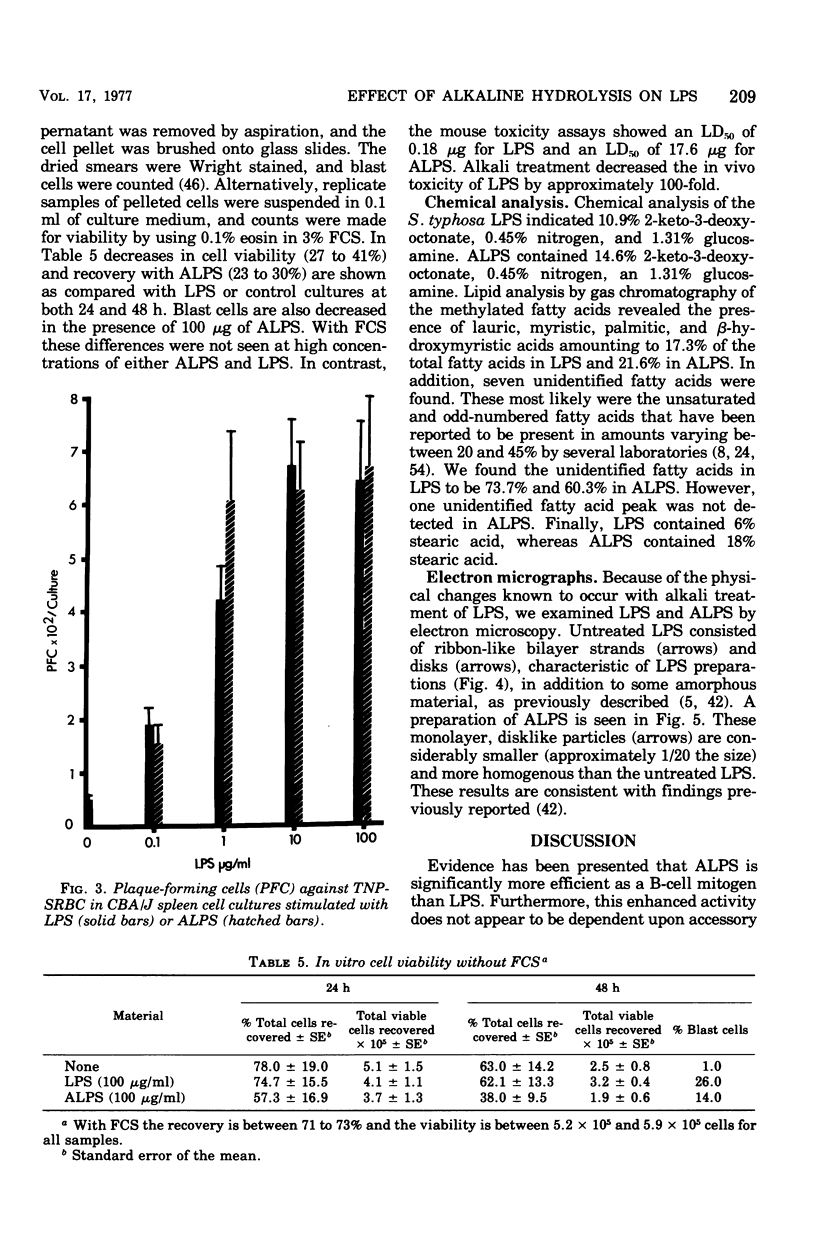
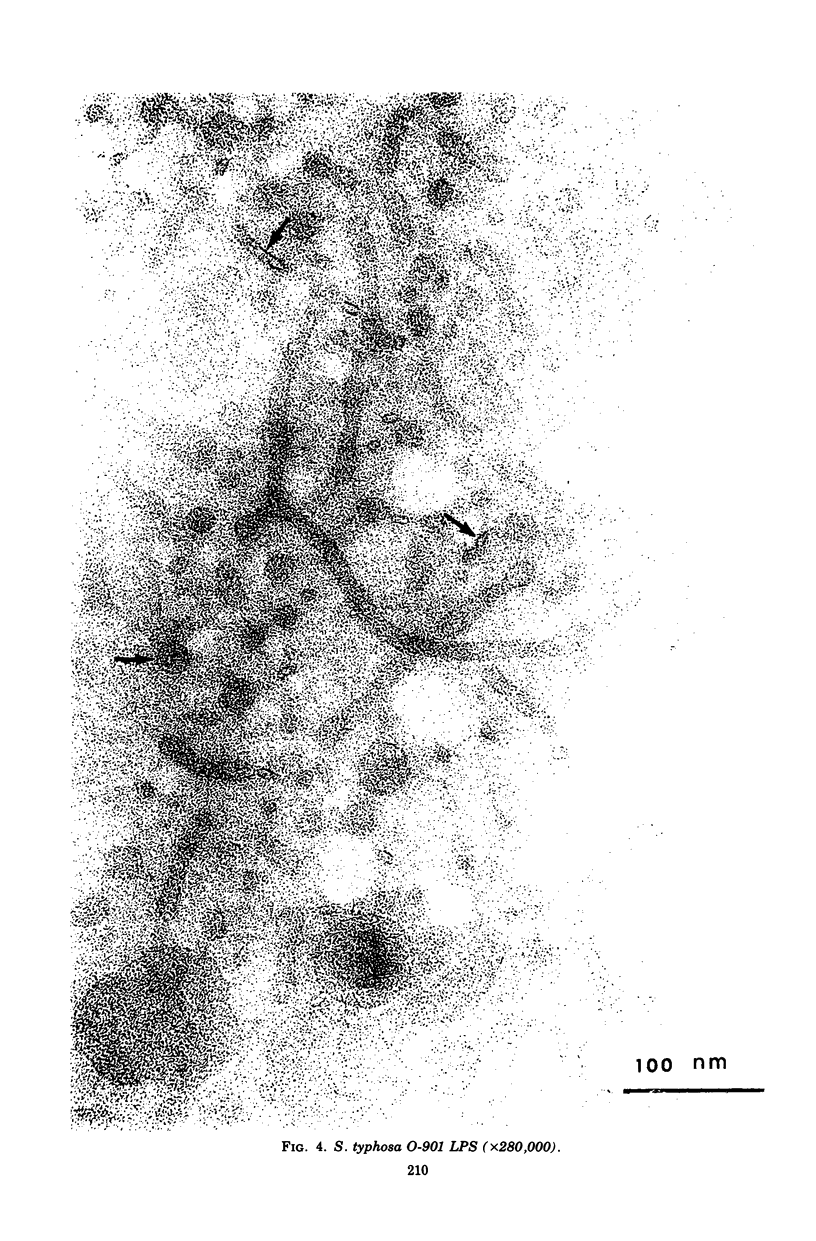
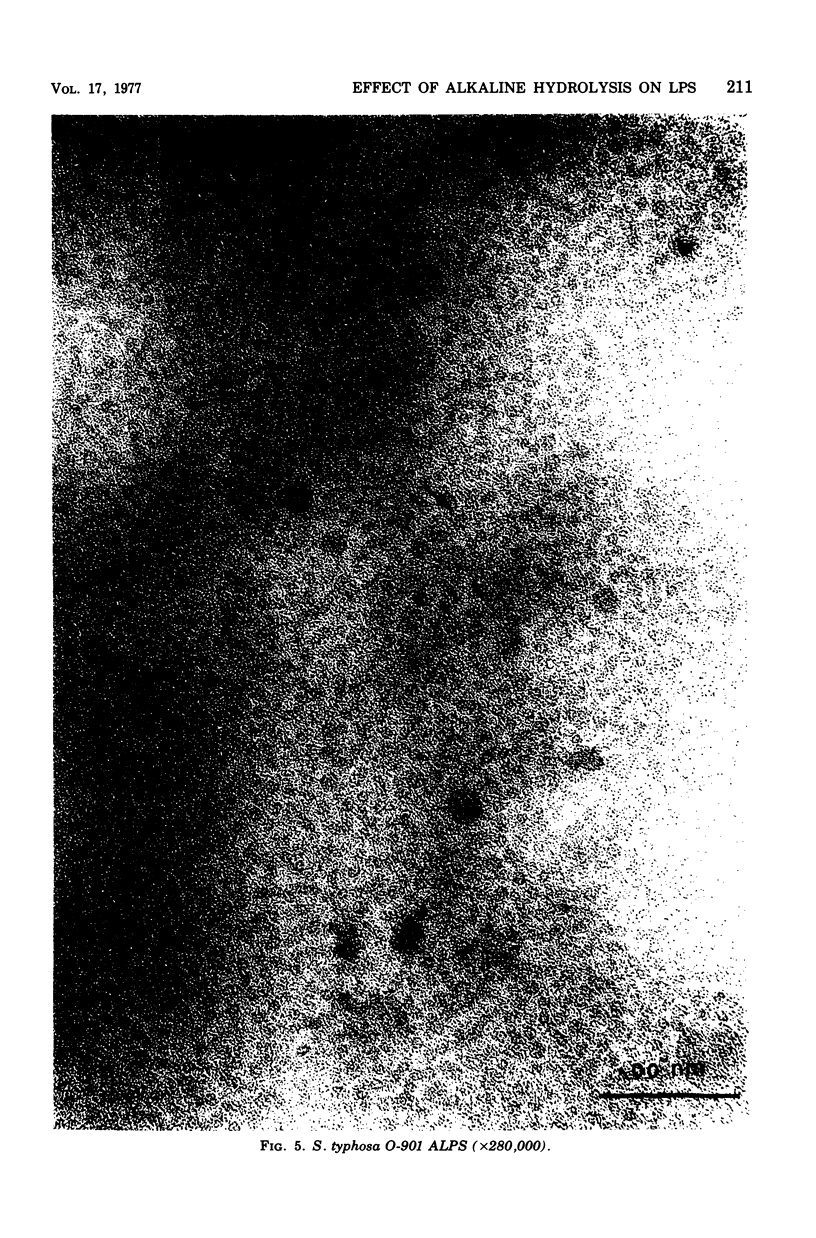
Mild alkaline hydrolysis was found to enhance the mitogenicity of lipopolysaccharide endotoxin for murine B lymphocytes. Alkaline treated lipopolysaccharide also retained its property as a polyclonal activator. Whereas this treatment reduced the lethality of endotoxin for mice, its toxicity for lymphocytes cultured in the absence of fetal calf serum was increased. Lipid analysis indicated that there were no significant changes in the fatty acids of lipid A, but particle size was significantly reduced and the material was more homogeneous and soluble than untreated lipopolysaccharide. The relationship of these effect on the structure of lipopolysaccharide endotoxin to the mechanism of B-lymphocyte activation is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson B., Blomgren H. Evidence for a small pool of immunocompetent cells in the mouse thymus. Its role in the humoral antibody response against sheep erythrocytes, bovine serum albumin, ovalbumin and the NIP determinant. Cell Immunol. 1970 Oct;1(4):362–371. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Melchers F., Galanos C., Lüderitz O. The mitogenic effect of lipopolysaccharide on bone marrow-derived mouse lymphocytes. Lipid A as the mitogenic part of the molecule. J Exp Med. 1973 Apr 1;137(4):943–953. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.4.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Möller G., Sjöberg O. Selective induction of DNA synthesis in T and B lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1972 Aug;4(4):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Sjöberg O., Möller G. Induction of immunoglobulin and antibody synthesis in vitro by lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Aug;2(4):349–353. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON A. J., CARTER H. E. PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE LIPID A COMPONENT OF THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDES FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:411–418. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beer H., Braude A. I., Brinton C. C., Jr A study of particle sizes, shapes and toxicities present in a boivin-type endotoxic preparation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):450–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetto D. A., Shands J. W., Jr, Shah D. O. The interaction of bacterial lipopolysaccharide with phospholipid bilayers and monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 16;298(2):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90346-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton S. Regulation of antibody synthesis against Escherichia coli endotoxin. II. Specificity, dose requirements and duration of paralysis induced in adult mice. Immunology. 1969 Apr;16(4):513–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd W. Restoration of the immune response to sheep erythrocytes by a serum factor. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 30;231(26):280–282. doi: 10.1038/newbio231280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Hirsch J. G. The effects of mercaptoethanol and of peritoneal macrophages on the antibody-forming capacity of nonadherent mouse spleen cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1972 Sep 1;136(3):604–617. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.3.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiller J. M., Skidmore B. J., Morrison D. C., Weigle W. O. Relationship of the structure of bacterial lipopolysaccharides to its function in mitogenesis and adjuvanticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2129–2133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciznár I., Shands J. W., Jr Effect of alkali-treated lipopolysaccharide on erythrocyte membrane stability. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):362–367. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.362-367.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho A., Gronowicz E., Sultzer B. M. Genetic control of B-cell responses. I. Selective unresponsiveness to lipopolysaccharide. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(2):139–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho A., Möller G., Anderson J., Bullock W. W. In vitro activation of mouse lymphocytes in serum-free medium: effect of T and B cell mitogens on proliferation and antibody synthesis. Eur J Immunol. 1973 May;3(5):299–306. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundy K. R., Nowotny A. Comparisons of 5 toxicity parameters of Serratia marcescens endotoxins. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Apr;127(4):999–1003. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. A., CRUMPTON M. J., MACPHERSON I. A., HUTCHISON A. M. The adsorption of bacterial polysaccharides by erythrocytes. Immunology. 1958 Apr;1(2):157–171. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erb P., Feldmann M. The role of macrophages in the generation of T-helper cells. I. The requirement for macrophages in helper cell induction and characteristics of the macrophage-T cell interaction. Cell Immunol. 1975 Oct;19(2):356–367. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90217-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A. Heterogeneity of B cells: direct evidence of selective triggering of distinct subpopulations by polyclonal activators. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(1-2):55–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb02992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs D. M., Morrison D. C. Stimulation of a T-independent primary anti-hapten response in vitro by TNP-lipopolysaccharide (TNP-LPS). J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):360–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. D., Morrison D. C. Dissociation between mitogenicity and immunogenicity of TNP-lipopolysaccharide, a T-independent antigen. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1453–1458. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KABAT E. A., SCHIFFMAN G. Immunochemical studies on blood groups. 28. Further studies on the oligosaccharide determinats of blood group B and BP1 specificity. J Immunol. 1962 Jun;88:782–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Billings P., Cohn M. Functional characteristics of Peyer's patch lymphoid cells. II. Lipopolysaccharide is thymus dependent. J Exp Med. 1974 Feb 1;139(2):407–413. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai N. Chemical studies on the lipid component of endotoxin, with special emphasis on its relation to biological activities. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):486–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner H., Oppenheim J. J. Stimulation of chicken lymphocytes in a serum-free medium. Cell Immunol. 1972 Apr;3(4):695–699. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy M., Baker P. J. Cytodynamics of the distinctive immune response produced in regional lymph nodes by Salmonella somatic polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1966 Nov;97(5):670–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx A., Musetescu M., Sendrea M., Mihalca M. Relationship between particle size and biological activity of Salmonella typhimurium endotoxin. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1968;207(3):313–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., WESTPHAL O., LUDERITZ O. Effects of lecithin, cholesterol, and serum on erythrocyte modification and antibody neutralization by enterobacterial lipopolysaccharides. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Mar;88(3):339–341. doi: 10.3181/00379727-88-21582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., WESTPHAL O., LUDERITZ O., GORZYNSKI E. A., EICHENBERGER E. Studies of enterobacterial lipopolysaccharides; effects of heat and chemicals on erythrocyte-modifying, antigenic, toxic and pyrogenic properties. J Immunol. 1956 May;76(5):377–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B. S., Sultzer B. M., Bullock W. W. Purified protein derivative of tuberculin induces immunoglobulin production in normal mouse spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):127–139. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa M., Milner K. C., Ribi E., Rudbach J. A. Alteration of physical, chemical, and biological properties of endotoxin by treatment with mild alkali. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1069–1077. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1069-1077.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Shands J. W., Jr, Adler W. H., Smith R. T. Mitogenicity of bacterial endotoxins: characterization of the mitogenic principle. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):352–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieroni R. E., Broderick E. J., Bundeally A., Levine L. A simple method for the quantitation of submicrogram amounts of bacterial endotoxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Mar;133(3):790–794. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poe W. J., Michael J. G. Separation of the mitogenic and antigenic responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Immunology. 1976 Feb;30(2):241–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poe W. J., Michael J. G. The effect of serum inhibitor on the antigenic and mitogenic responses to E. coli bacteria. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):1129–1133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RONDLE C. J., MORGAN W. T. The determination of glucosamine and galactosamine. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):586–589. doi: 10.1042/bj0610586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Gottert H., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Nature and linkages of the fatty acids present in the lipid-A component of Salmonella lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):166–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg M. B., Pratt K. L. Antitrinitrophenyl (TNP) plaque assay. Primary response of Balb/c mice to soluble and particulate immunogen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):575–581. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudbach J. A. Molecular immunogenicity of bacterial lipopolysaccharide antigens: establishing a quantitative system. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):993–1001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr Evidence for a bilayer structure in gram-negative lipopolysaccharide: relationship to toxicity. Infect Immun. 1971 Aug;4(2):167–172. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.2.167-172.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöberg O., Andersson J., Möller G. Requirement for adherent cells in the primary and secondary immune response in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Apr;2(2):123–126. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore B. J., Chiller J. M., Morrison D. C., Weigle W. O. Immunologic properties of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS): correlation between the mitogenic, adjuvant, and immunogenic activities. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):770–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M. Genetic analysis of lymphocyte activation by lipopolysaccharide Endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1579–1584. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1579-1584.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M. Genetic control of host responses to endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1972 Jan;5(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.1.107-113.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M. Genetic factors in leucocyte responses to endotoxin: further studies in mice. J Immunol. 1969 Jul;103(1):32–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M., Nilsson B. S. PPD tuberculin--a B-cell mitogen. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 13;240(102):198–200. doi: 10.1038/newbio240198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripodi D., Nowotny A. Relation of structure to function in bacterial O-antigens. V. Nature of active sites in endotoxic lipopolysaccharides of Serratia marcescens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):604–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wober W., Alaupović P. Studies on the protein moiety of endotoxin from gram-negative bacteria. Characterization of the protein moiety isolated by phenol treatment of endotoxin from Serratia marcescens 08 and Escherichia coli 0 141:K85(B). Eur J Biochem. 1971 Apr;19(3):340–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]