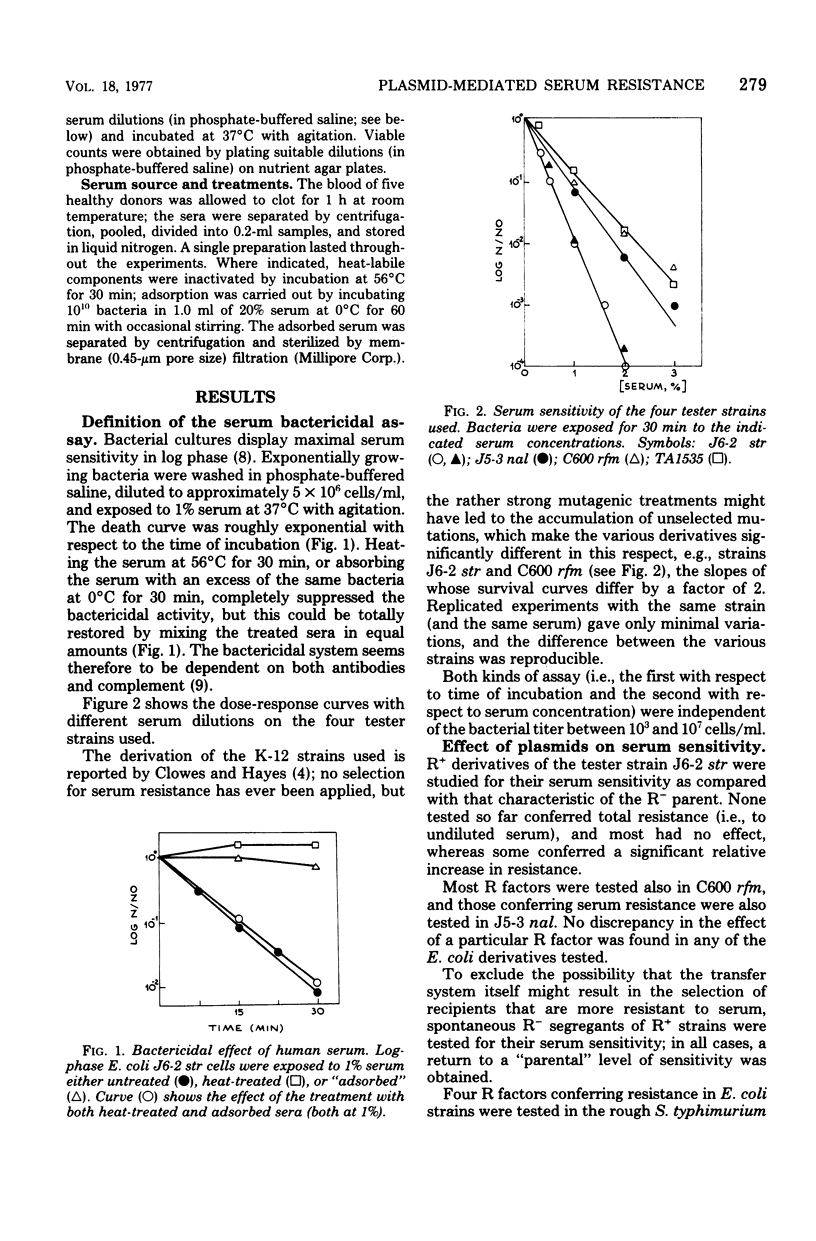
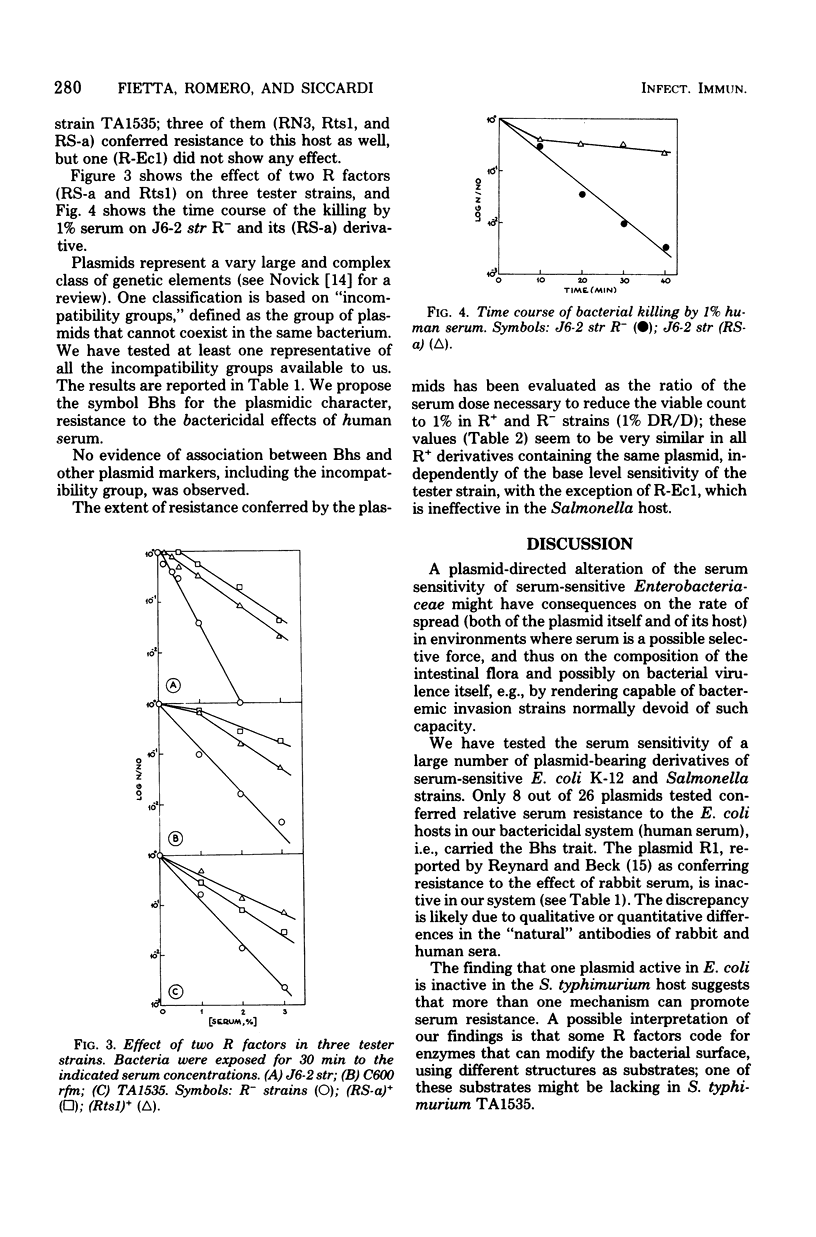
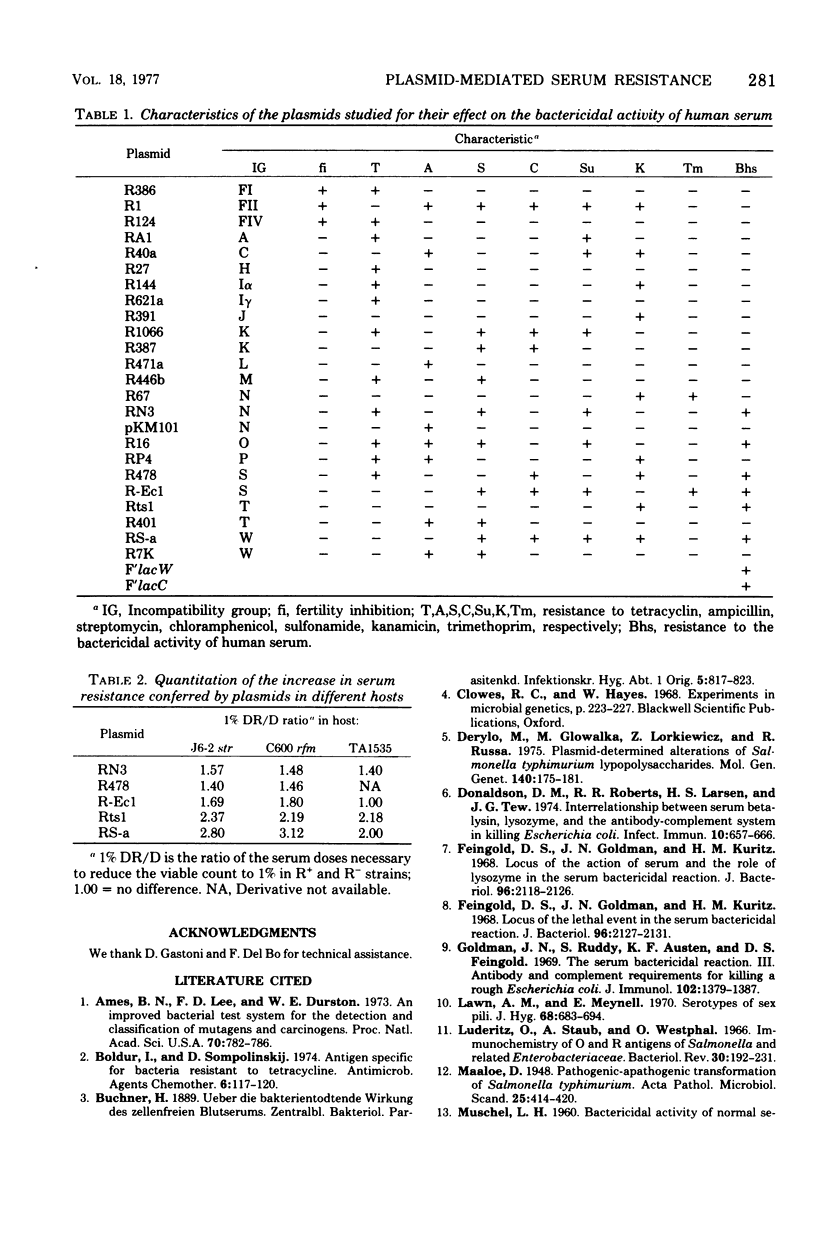
Abstract
Eight plasmids out of 26 tested confer partial serum resistance to Escherichia coli K-12 strains (Bhs character). Four Bhs+ plasmids were tested in a rough Salmonella typhimurium host, and three conferred partial serum resistance to this host as well. Plasmids representative of 19 different incompatibility groups were examined; the Bhs+ property was found in some (but not all) representatives of groups N, O, S, T, W, and F'lac (FI), and there was no apparent association between other plasmid markers and Bhs. It is likely that more than one mechanism can promote the Bhs+ phenotype and that Bhs genes are responsible for modifications of the surface structures involved in serum sensitivity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Lee F. D., Durston W. E. An improved bacterial test system for the detection and classification of mutagens and carcinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):782–786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldur I., Sompolinsky D. Antigen specific for bacteria resistant to tetracycline. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):117–120. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derylo M., Glowacka M., Lorkiewicz Z., Russa R. Plasmid-determined alterations of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Sep 29;140(2):175–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00329785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson D. M., Roberts R. R., Larsen H. S., Tew J. G. Interrelationship between serum beta-lysin, lysozyme, and the antibody-complement system in killing Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):657–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.657-666.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., Goldman J. N., Kuritz H. M. Locus of the action of serum and the role of lysozyme in the serum bactericidal reaction. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2118–2126. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2118-2126.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., Goldman J. N., Kuritz H. M. Locus of the lethal event in the serum bactericidal reaction. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2127–2131. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2127-2131.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. N., Ruddy S., Austen K. F., Feingold D. S. The serum bactericidal reaction. 3. Antibody and complement requirements for killing a rough Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1969 Jun;102(6):1379–1387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn A. M., Meynell E. Serotypes of sex pili. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Dec;68(4):683–694. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Staub A. M., Westphal O. Immunochemistry of O and R antigens of Salmonella and related Enterobacteriaceae. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):192–255. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.192-255.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHER K., ROTHER U., PETERSEN K. F., GEMSA D., MITZE F. IMMUNE BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY OF COMPLEMENT. SEPARATION AND DESCRIPTION OF INTERMEDIATE STEPS. J Immunol. 1964 Aug;93:319–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D. The virulence of strains of Bacterium coli for mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Dec;35(6):528–538. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynard A. M., Beck M. E. Plasmid-mediated resistance to the bactericidal effects of normal rabbit serum. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):848–850. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.848-850.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J., Rantz L. A. A STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP OF THE NORMAL BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY OF HUMAN SERUM TO BACTERIAL INFECTION. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39(1):72–81. doi: 10.1172/JCI104029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K. Normal serum cytotoxicity for P32-labeled smooth Enterobacteriaceae. 3. Isolation of a gammag normal antibody and characterization of other serum factors causing P32 loss. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):401–408. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.401-408.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirm S., Orskov F., Orskov I., Mansa B. Episome-carried surface antigen K88 of Escherichia coli. II. Isolation and chemical analysis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):731–739. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.731-739.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. M., Glynn A. A. Release of 14C label and complement killing of Escherichia coli. Immunology. 1975 Mar;28(3):391–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. A., Spitznagel J. K. Molecular and structural damage to Escherichia coli produced by antibody, complement, and lysozyme systems. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1339–1348. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1339-1348.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


