Abstract
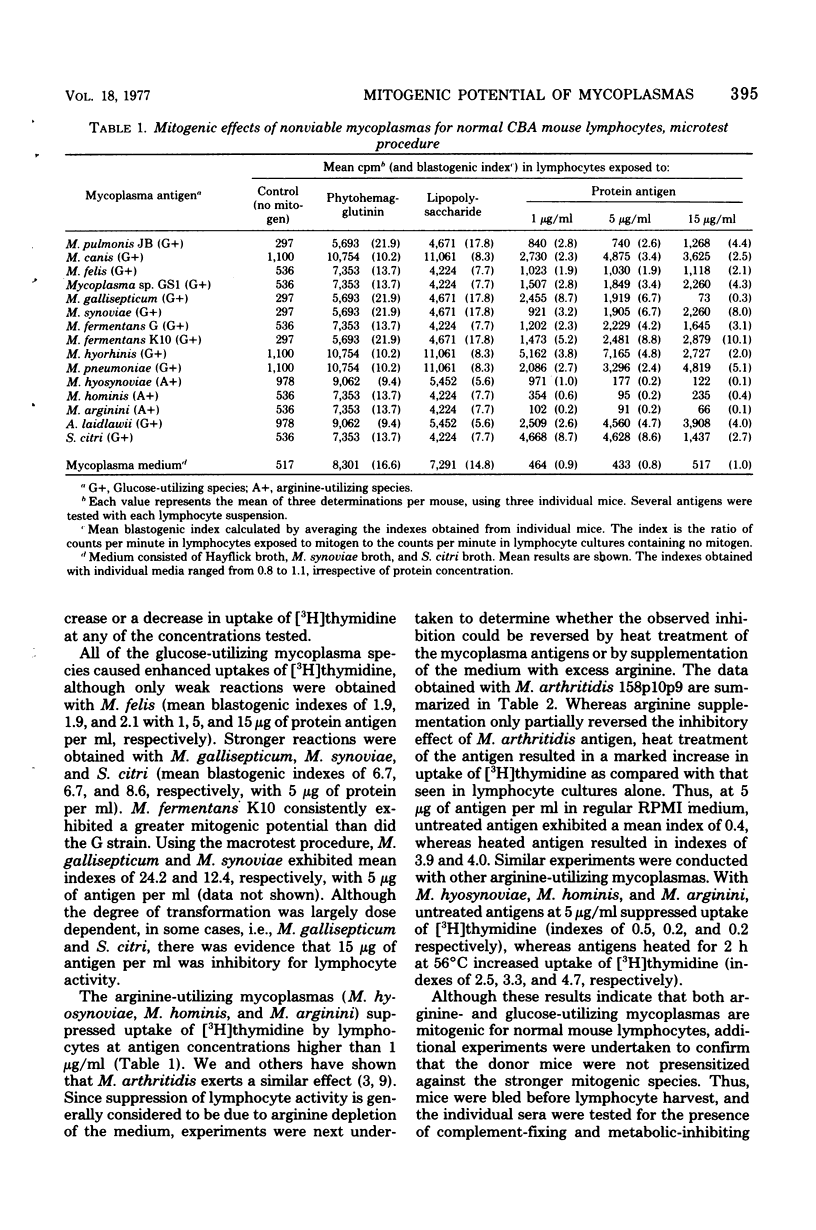
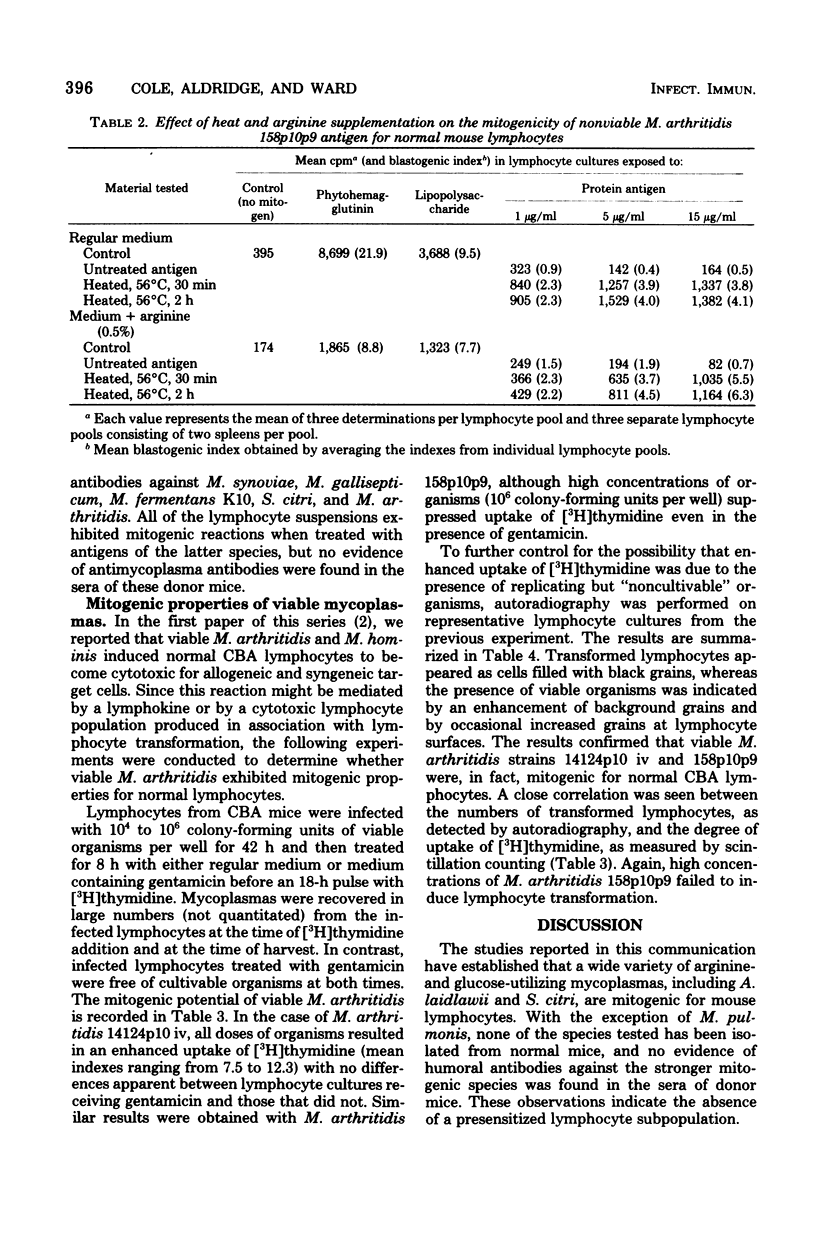
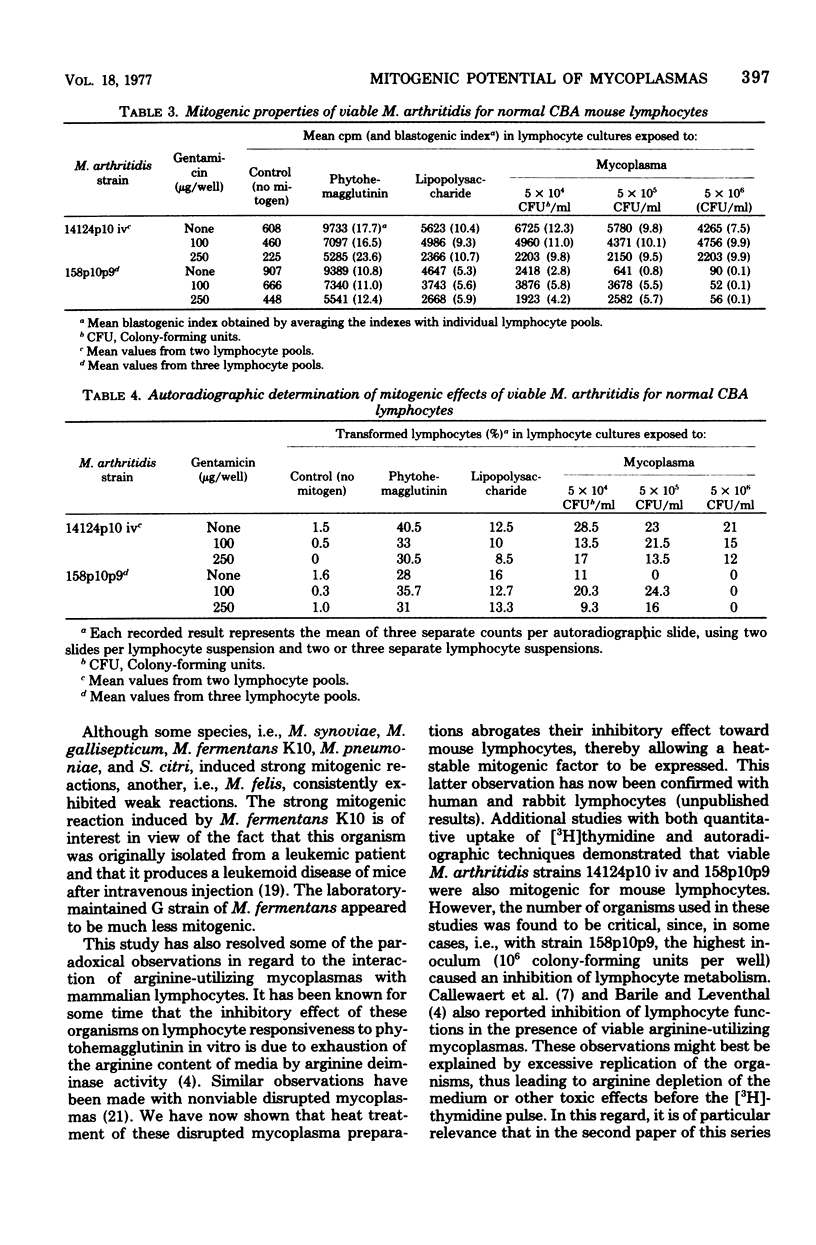
Nonviable preparations of a wide variety of glucose-utilizing mycoplasma species, including Acholeplasma laidlawii and Spiroplasma citri, were found to be mitogenic for mouse lymphocytes. Particularly strong reactions were obtained with Mycoplasma synoviae, M. gallisepticum, M. pneumoniae, S. citri, and a strain of M. fermentans that was previously isolated from a leukemic patient. Nonviable preparations of arginine-utilizing mycoplasmas inhibited the uptake of [3H]thymidine by lymphocytes, but this effect could be reversed by heat treatment or arginine supplementation, and a stimulatory effect was then observed. Viable M. arthritidis was also found to have a mitogenic effect, as detected by an increased uptake of [3H]thymidine by normal lymphocytes and by autoradiographic techniques in which an increase in the numbers of transformed cells was seen. These observations provide the potential for enhanced immunological responsiveness or lymphokine-mediated inflammation in mycoplasma-infected hosts.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge K. E., Cole B. C., Ward J. R. Mycoplasma-dependent activation of normal lymphocytes: induction of a lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity for allogeneic and syngeneic mouse target cells. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):377–385. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.377-385.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge K. E., Cole B. C., Ward J. R. Mycoplasma-dependent activation of normal lymphocytes: role of arginine and nonviable mycoplasma antigen in the induction of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity for syngeneic mouse target cells. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):386–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.386-392.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge K. E. Growth and cytopathology of Mycoplasma synoviae in chicken embryo cell cultures. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):198–204. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.198-204.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barile M. F., Leventhal B. G. Possible mechanism for Mycoplasma inhibition of lymphocyte transformation induced by phytohaemagglutinin. Nature. 1968 Aug 17;219(5155):750–752. doi: 10.1038/219751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergquist L. M., Lau B. H., Winter C. E. Mycoplasma-associated immunosuppression: effect on hemagglutinin response to common antigens in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):410–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.410-415.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld G., Gronowicz E. Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a polyclonal B-cell activator. Nature. 1976 May 20;261(5557):238–239. doi: 10.1038/261238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callewaert D. M., Kaplan J., Peterson W. D., Jr, Lightbody J. J. Suppression of lymphocyte activation by a factor produced by Mycoplasma arginini. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1662–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Golightly-Rowland L., Ward J. R. Arthritis of mice induced by Mycoplasma pulmonis: humoral antibody and lymphocyte responses of CBA mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1083–1092. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1083-1092.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Golightly-Rowland L., Ward J. R. Chronic proliferative arthritis of mice induced by Mycoplasma arthritidis: demonstration of a cell-mediated immune response to mycoplasma antigens in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1159–1161. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1159-1161.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Overall J. C., Jr, Lombardi P. S., Glasgow L. A. Induction of interferon in ovine and human lymphocyte cultures by mycoplasmas. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):88–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.88-94.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Ward J. R., Jones R. S., Cahill J. F. Chronic proliferative arthritis of mice induced by Mycoplasma arthritidis. I. Induction of disease and histopathological characteristics. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):344–355. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.344-355.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copperman R., Morton H. E. Reversible inhibition of mitosis in lymphocyte cultures by non-viable Mycoplasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Dec;123(3):790–795. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Nicolet J. Extensive transformation of lymphocytes by a mycoplasma organism. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 5;246(153):143–146. doi: 10.1038/newbio246143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaklamanis E., Pavlatos M. The immunosuppressive effect of mycoplasma infection. I. Effect on the humoral and cellular response. Immunology. 1972 Apr;22(4):695–702. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauel J., Rudolf H., Chapuis B., Brunner K. T. Studies of allograft immunity in mice. II. Mechanism of target cell inactivation in vitro by sensitized lymphocytes. Immunology. 1970 Apr;18(4):517–535. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Holm G. Cytotoxic effects of lymphoid cells in vitro. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:117–193. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60479-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plata E. J., Abell M. R., Murphy W. H. Induction of leukemoid disease in mice by Mycoplasma fermentans. J Infect Dis. 1973 Nov;128(5):588–597. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.5.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simberkoff M. S., Thorbecke G. J., Thomas L. Studies of PPLO infection. V. Inhibition of lymphocyte mitosis and antibody formation by mycoplasmal extracts. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1163–1181. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F., Langworthy T. A., Mayberry W. R. Distribution and composition of lipopolysaccharides from mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):916–922. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.916-922.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerson N. L., James W. D., Walls B. E., Chanock R. M. Growth of Mycoplasma pneumoniae on a glass surface. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):384–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soulillou J. P., Carpenter C. B., Lundin A. P., Strom T. B. Augmentation of proliferation and in vitro production of cytotoxic cells by 2-ME in the rat. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1566–1571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P., Rosenthal M., Andreis M., Cooke D., Ziff M. Lymphokines in rheumatoid synovitis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:117–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


