Abstract
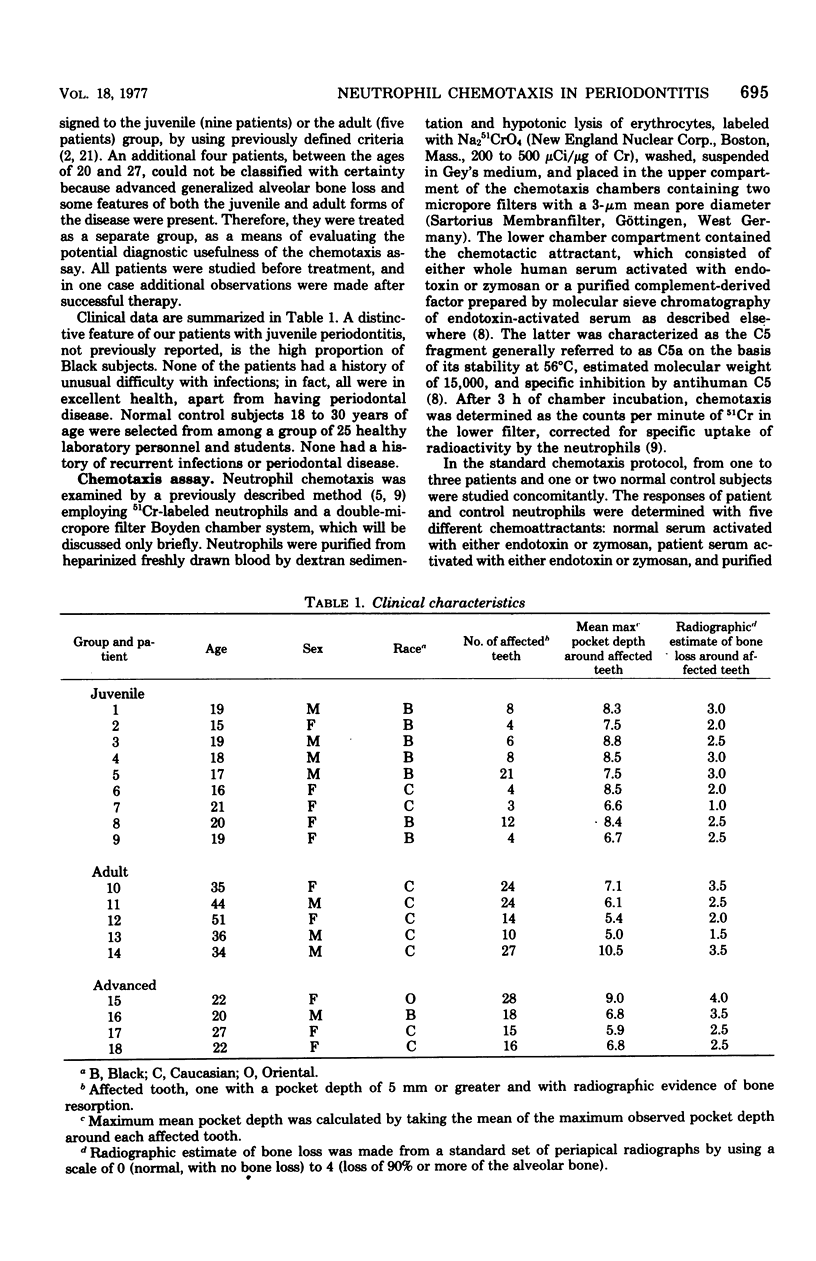
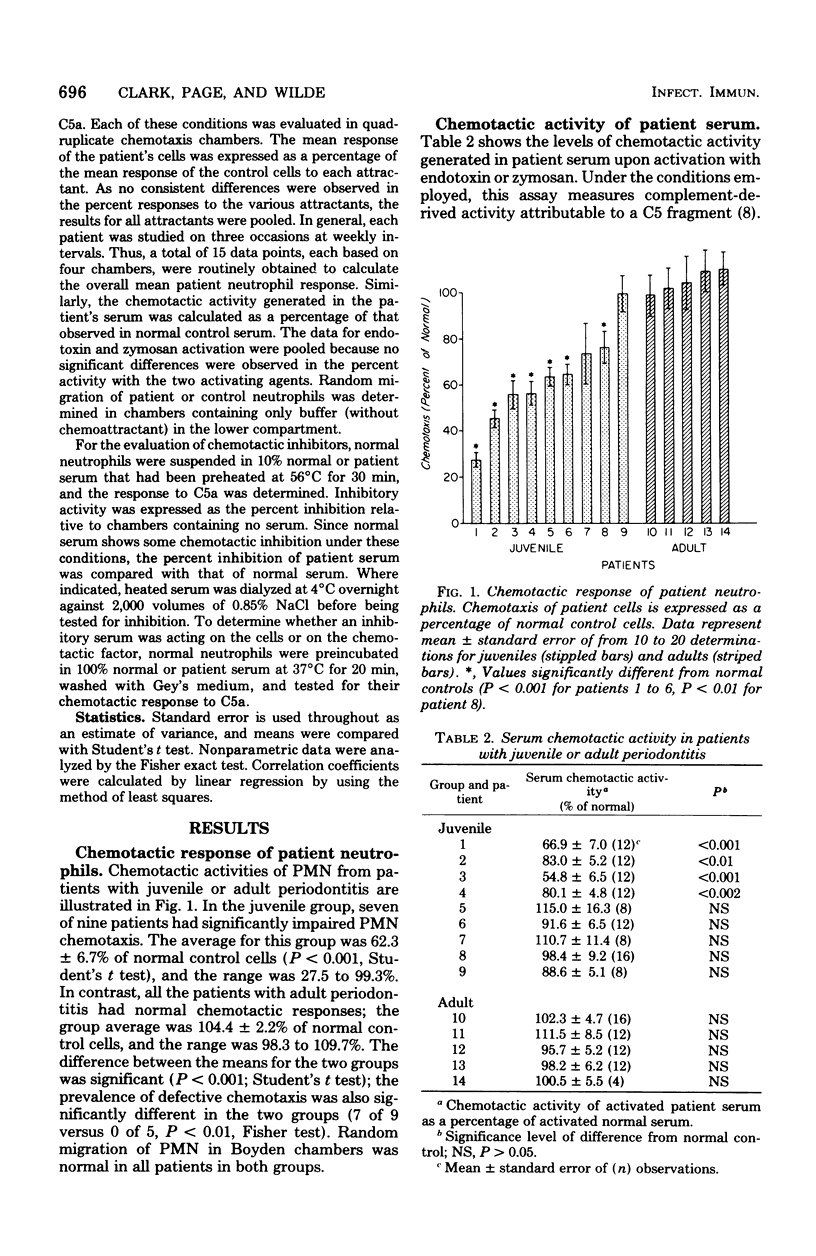
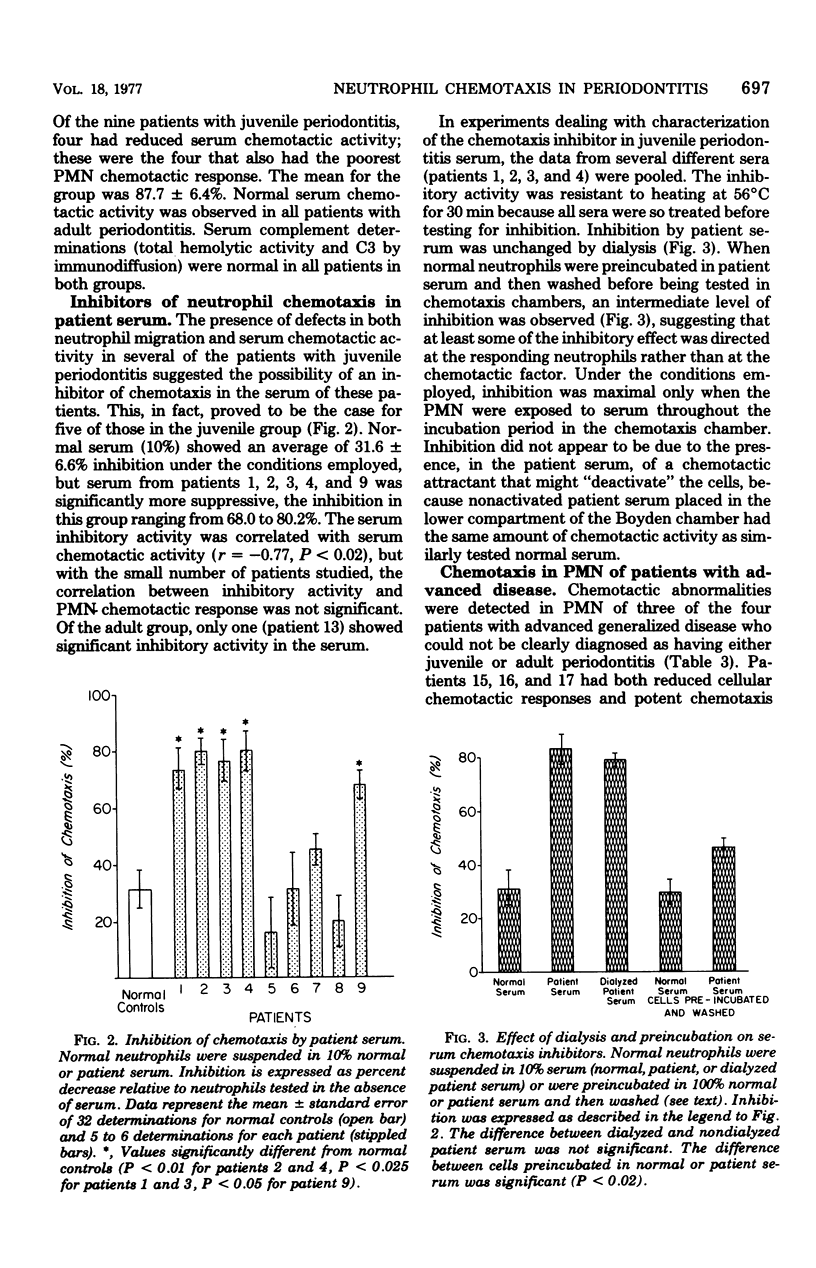
Neutrophil chemotaxis was evaluated in nine patients with juvenile periodontitis, with normal subjects and patients with the adult form of periodontitis as controls. Defective chemotactic responses were observed in neutrophils from seven of nine juvenile patients, and a reduced level of complement-derived chemotactic activity was demonstrated in serum from four patients. These determinations were normal in all the patients with adult periodontitis. Serum from five of the juvenile patients contained a heat-stable, non-dialyzable factor that markedly inhibited the chemotaxis of normal neutrophils. Thus the characteristic tissue destruction seen in juvenile periodontitis may be, at least in part, a consequence of a failure of host defense mechanisms.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attström R. Studies on neutrophil polymorphonuclear leukocytes at the dento-gingival junction in gingival health and disease. J Periodontal Res Suppl. 1971;8:1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer P. N. The case for periodontosis as a clinical entity. J Periodontol. 1971 Aug;42(8):516–520. doi: 10.1902/jop.1971.42.8.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cainciola L. J., Genco R. J., Patters M. R., McKenna J., van Oss C. J. Defective polymorphonuclear leukocyte function in a human periodontal disease. Nature. 1977 Feb 3;265(5593):445–447. doi: 10.1038/265445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Johnson F. L., Klebanoff S. J., Thomas E. D. Defective neutrophil chemotaxis in bone marrow transplant patients. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):22–31. doi: 10.1172/JCI108452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Kimball H. R. Defective granulocyte chemotaxis in the Chediak-Higashi syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2645–2652. doi: 10.1172/JCI106765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epps D. E., Williams R. C., Jr Serum chemotactic inhibitory activity: heat activation of chemotactic inhibition. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):741–749. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.741-749.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Clark R. A., Frank M. M. Kinetic analysis of chemotactic factor generation in human serum via activation of the classical and alternate complement pathways. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Jan;3(3):334–346. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Clark R. A., Kimball H. R. Granulocyte chemotaxis: an improved in vitro assay employing 51 Cr-labeled granulocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):233–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. On the formation of dental plaques. J Periodontol. 1973 Jun;44(6):347–360. doi: 10.1902/jop.1973.44.6.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gothier D. E., Gaumer H. R., Pihlstrom B. L., Folke L. E. Elevation of a serum component in periodontal disease capable of modulating chemotactic infiltration. J Periodontal Res. 1975 May;10(2):65–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1975.tb00009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. E., Jr, Giansanti J. S. The Chediak-Higashi syndrome. Report of a case and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1974 May;37(5):754–761. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(74)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamp S. E., Folke L. E. The lysosomes and their possible role in periodontal disease. Odontol Tidskr. 1968 Dec 31;76(6):353–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heijl L., Rifkin B. R., Zander H. A. Conversion of chronic gingivitis to periodontitis in squirrel monkeys. J Periodontol. 1976 Dec;47(12):710–716. doi: 10.1902/jop.1976.47.12.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavine W. S., Page R. C., Padgett G. A. Host response in chronic periodontal disease. V. The dental and periodontal status of mink and mice affected by Chediak-Higashi syndrome. J Periodontol. 1976 Nov;47(11):621–635. doi: 10.1902/jop.1976.47.11.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T. Immunological aspects of dental caries and periodontal disease. Br Med Bull. 1975 May;31(2):125–130. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Wilton J. M., Ivanyi L., Manson J. D. Immunological aspects of juvenile periodontitis (periodontosis). J Periodontal Res. 1974;9(5):261–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1974.tb00681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maderazo E. C., Ward P. A., Quintiliani R. Defective regulation of chemotaxis in cirrhosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Apr;85(4):621–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson J. D., Lehner T. Clinical features of juvenile periodontitis (periodontosis). J Periodontol. 1974 Aug;45(8):636–640. doi: 10.1902/jop.1974.45.8.2.636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. E., Oski F. A., Harris M. B. Lazy-leucocyte syndrome. A new disorder of neutrophil function. Lancet. 1971 Apr 3;1(7701):665–669. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92679-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G., Socransky S. S., Savitt E. D., Propas D. A., Crawford A. Studies of the microbiology of periodontosis. J Periodontol. 1976 Jul;47(7):373–379. doi: 10.1902/jop.1976.47.7.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page R. C., Schroeder H. E. Pathogenesis of inflammatory periodontal disease. A summary of current work. Lab Invest. 1976 Mar;34(3):235–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. A., Page R. C., Ogilvie A. L., Hall W. B. Histopathologic features of the initial and early stages of experimental gingivitis in man. J Periodontal Res. 1975 May;10(2):51–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1975.tb00008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Thomas I. T., Clark R. A., Ochs H. D. Defective neutrophil chemotaxis with variant ichthyosis, hyperimmunoglobulinemia E, and recurrent infections. J Pediatr. 1975 Dec;87(6 Pt 1):908–911. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80903-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. E., Graf-de Beer M., Attström R. Initial gingivitis in dogs. J Periodontal Res. 1975 Jul;10(3):128–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1975.tb00017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S. Relationship of bacteria to the etiology of periodontal disease. J Dent Res. 1970 Mar-Apr;49(2):203–222. doi: 10.1177/00220345700490020401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taichman N. S., Freedman H. L., Uriuhara T. Inflammation and tissue injury. I. The response to intradermal injections of human dentogingival plaque in normal and leukopenic rabbits. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Dec;11(12):1385–1392. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempel T. R., Snyderman R., Jordan H. V., Mergenhagen S. E. Factors from saliva and oral bacteria, chemotactic for polymorphonuclear leukocytes: their possible role in gingival inflammation. J Periodontol. 1970 Feb;41(2):71–80. doi: 10.1902/jop.1970.41.2.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Strickland R. G., Williams R. C., Jr Inhibitors of leukocyte chemotaxis in alcoholic liver disease. Am J Med. 1975 Aug;59(2):200–207. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90354-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Berenberg J. L. Defective regulation of inflammatory mediators in Hodgkin's disease. Supernormal levels of chemotactic-factor inactivator. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 10;290(2):76–80. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197401102900203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Schlegel R. J. Impaired leucotactic responsiveness in a child with recurrent infections. Lancet. 1969 Aug 16;2(7616):344–347. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92699-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


