Abstract
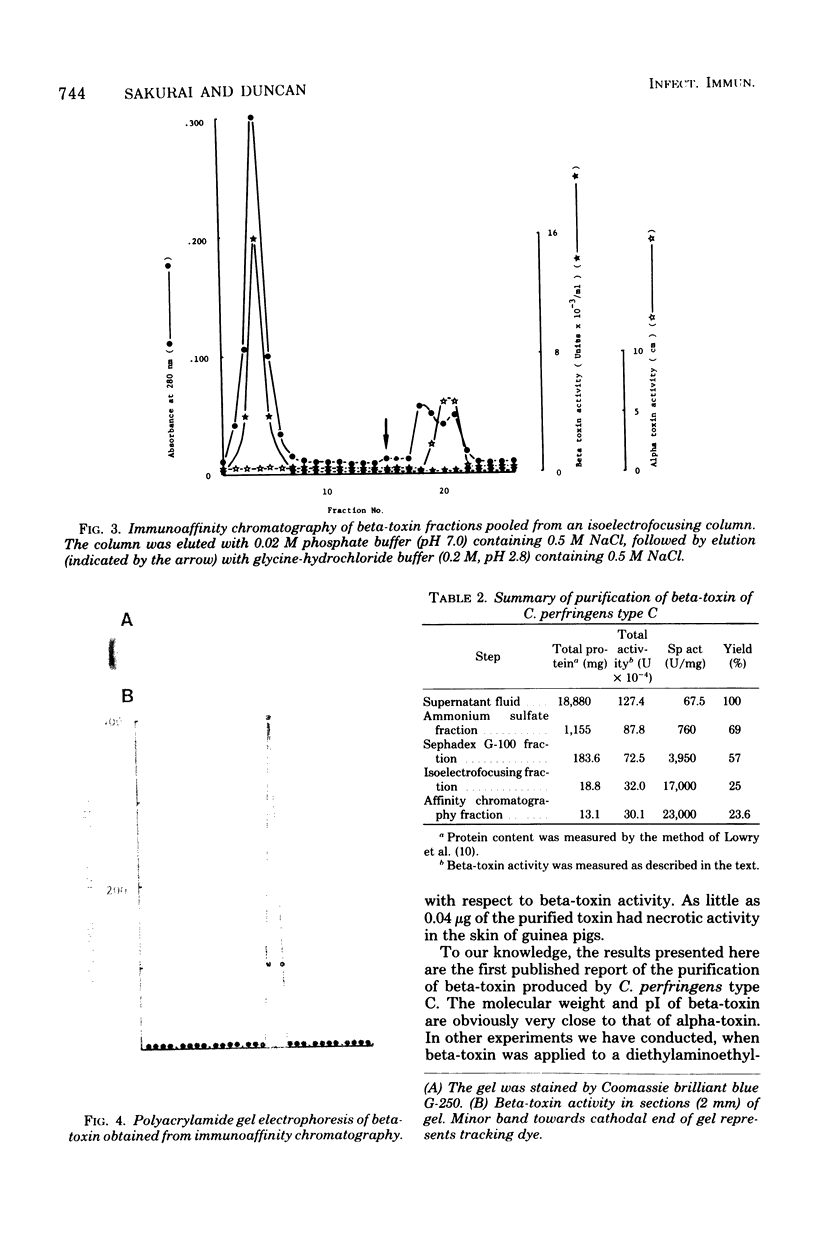
Beta-toxin was purified about 340-fold from culture supernatant fluid of Clostridium perfringens type C with a yield of about 24% in terms of biologically active beta-toxin. The purification involved ammonium sulfate fractionation, gel filtration through Sephadex G-100, isoelectrofocusing in a pH 3 to 6 gradient, and immunoaffinity chromatography. The purified beta-toxin gave a single band on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernheimer A. W., Grushoff P. Cereolysin: production, purification and partial characterization. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Jan;46(1):143–150. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-1-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGERTON J. R., WALKER P. D. THE ISOLATION OF CLOSTRIDIUM PERFRINGENS TYPE C FROM NECROTIC ENTERITIS OF MAN IN PAPUA-NEW GUINEA. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:275–278. doi: 10.1002/path.1700880134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRINER L. A., BRACKEN F. K. Clostridium perfringens (type C) in acute hemorrhagic enteritis of calves. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1953 Feb;122(911):99–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRINER L. A., JOHNSON H. W. Clostridium perfringens type C in hemorrhagic enterotoxemia of lambs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1954 Aug;125(929):125–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert G. A., Pelham P. L., Pittman B. Determination of the optimal ammonium sulfate concentration for the fractionation of rabbit, sheep, horse, and goat antisera. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jan;25(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/am.25.1.26-36.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe R. G., Duncan C. L. Sporulation and enterotoxin production by Clostridium perfringens type A under conditions of controlled pH and temperature. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Nov;20(11):1493–1501. doi: 10.1139/m74-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Arbuthnott J. P. Properties of Clostridium perfringens (welchii) type-A alpha-toxin (phospholipase C) purified by electrofocusing. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Feb;7(1):41–66. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-1-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]