Abstract
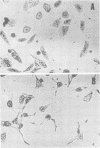
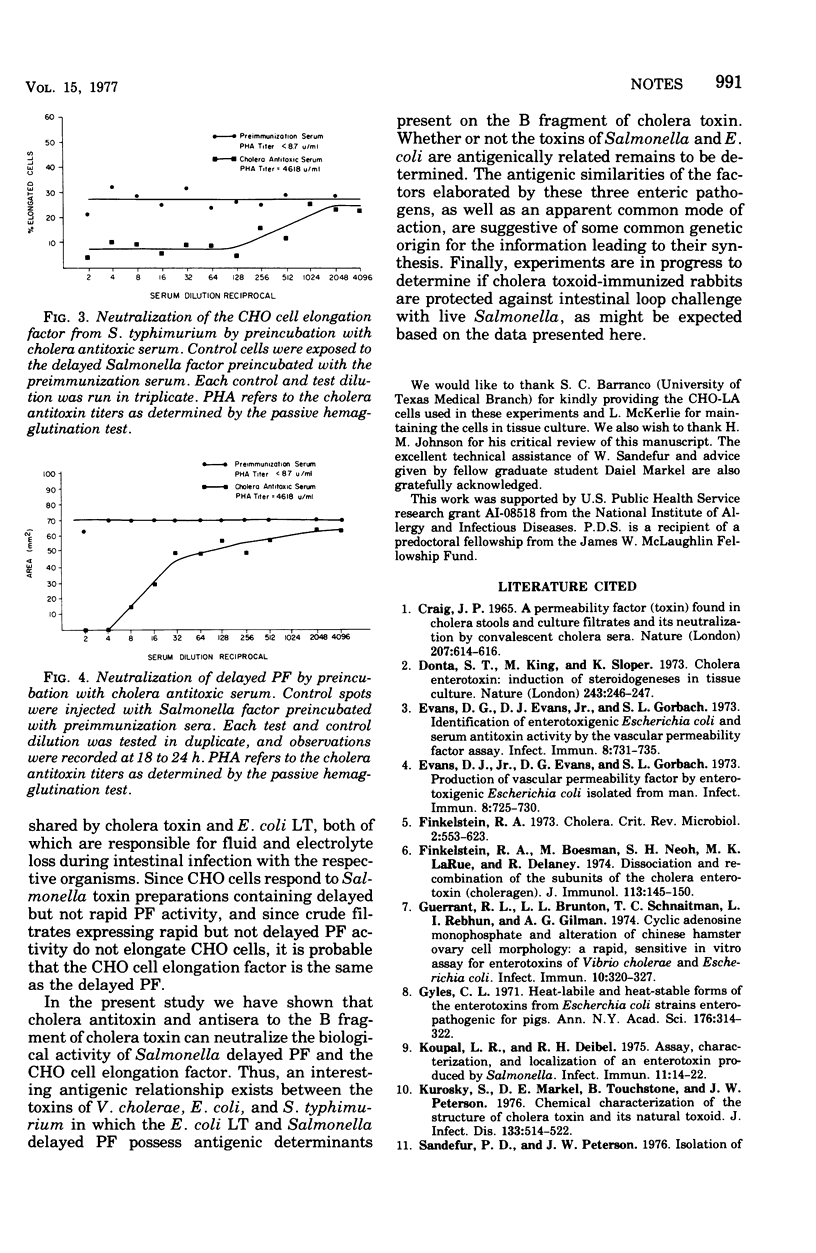
A partially purified preparation of the delayed skin permeability factor from Salmonella typhimurium caused Chinese hamster ovary cells to elongate. The elongation effect and the skin test activity were blocked by monospecific rabbit antisera against cholera toxin and against the B fragment of cholera toxin,
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Craig J. P. A permeability factor (toxin) found in cholera stools and culture filtrates and its neutralization by convalescent cholera sera. Nature. 1965 Aug 7;207(997):614–616. doi: 10.1038/207614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., King M., Sloper K. Induction of steroidogenesis in tissue culture by cholera enterotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 20;243(129):246–247. doi: 10.1038/newbio243246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Gorbach S. L. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and serum antitoxin activity by the vascular permeability factor assay. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):731–735. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.731-735.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Production of vascular permeability factor by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):725–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.725-730.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Boesman M., Neoh S. H., LaRue M. K., Delaney R. Dissociation and recombination of the subunits of the cholera enterotoxin (choleragen). J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koupal L. R., Deibel R. H. Assay, characterization, and localization of an enterotoxin produced by Salmonella. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):14–22. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.14-22.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandefur P. D., Peterson J. W. Isolation of skin permeability factors from culture filtrates of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):671–679. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.671-679.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer D. E., Lust W. D., Sircar B., Goldberg N. D. Elevated concentration of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in intestinal mucosa after treatment with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):851–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by cholera toxin. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):266–269. doi: 10.1038/229266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The effect of cell-free fluids prepared from cultures of human and animal enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli on ligated intestinal segments of rabbits and pigs. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):403–409. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. W., Sack R. B. Immunologic cross-reactions of enterotoxins from Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):164–170. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]