Abstract
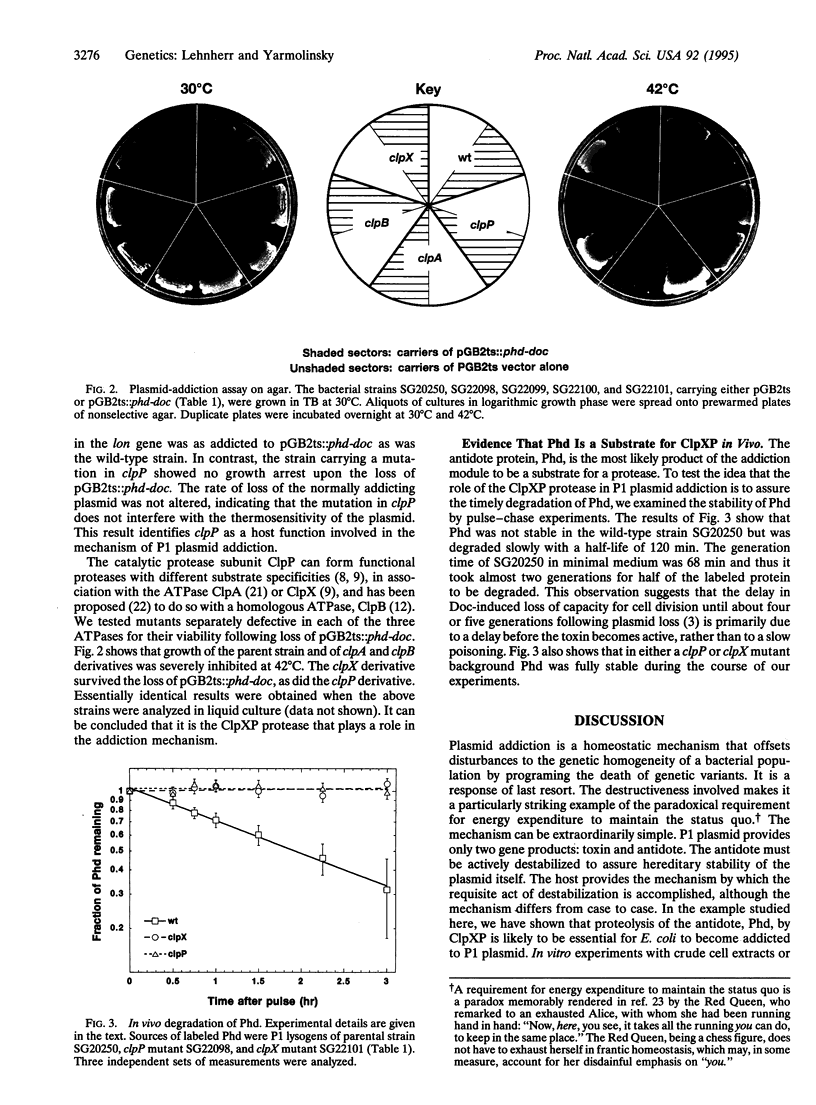
Plasmid-encoded addiction genes augment the apparent stability of various low copy number bacterial plasmids by selectively killing plasmid-free (cured) segregants or their progeny. The addiction module of plasmid prophage P1 consists of a pair of genes called phd and doc. Phd serves to prevent host death when the prophage is retained and, should retention mechanisms fail, Doc causes death on curing. Doc acts as a cell toxin to which Phd is an antidote. In this study we show that host mutants with defects in either subunit of the ClpXP protease survive the loss of a plasmid that contains a P1 addiction module. The small antidote protein Phd is fully stable in these two mutant hosts, whereas it is labile in a wild-type host. We conclude that the role of ClpXP in the addiction mechanism of P1 is to degrade the Phd protein. This conclusion situates P1 among plasmids that elicit severe withdrawal symptoms and are able to do so because they encode both a cell toxin and an actively degraded macromolecule that blocks the synthesis or function of the toxin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bejarano I., Klemes Y., Schoulaker-Schwarz R., Engelberg-Kulka H. Energy-dependent degradation of lambda O protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Dec;175(23):7720–7723. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.23.7720-7723.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo A., de Torrontegui G., Díaz R. Identification of components of a new stability system of plasmid R1, ParD, that is close to the origin of replication of this plasmid. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Nov;210(1):101–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00337764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerget M. Site-specific recombination promoted by a short DNA segment of plasmid R1 and by a homologous segment in the terminus region of the Escherichia coli chromosome. New Biol. 1991 Aug;3(8):780–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortson M. R., Scott J. R., Yun T., Vapnek D. Map location of the kanamycin resistance determinant in P1Km0. Virology. 1979 Jul 15;96(1):332–334. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90206-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes K., Nielsen A., Thorsted P., Wagner E. G. Mechanism of killer gene activation. Antisense RNA-dependent RNase III cleavage ensures rapid turn-over of the stable hok, srnB and pndA effector messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 5;226(3):637–649. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90621-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes K., Poulsen L. K., Thisted T., Nielsen A. K., Martinussen J., Andreasen P. H. The hok killer gene family in gram-negative bacteria. New Biol. 1990 Nov;2(11):946–956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuskens V., Mhammedi-Alaoui A., Desmet L., Toussaint A. Virulence in bacteriophage Mu: a case of trans-dominant proteolysis by the Escherichia coli Clp serine protease. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5121–5127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05619.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Clark W. P., Maurizi M. R. The ATP-dependent Clp protease of Escherichia coli. Sequence of clpA and identification of a Clp-specific substrate. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7886–7893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Clark W. P., de Crecy-Lagard V., Maurizi M. R. ClpX, an alternative subunit for the ATP-dependent Clp protease of Escherichia coli. Sequence and in vivo activities. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22618–22626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Maurizi M. R. Regulation by proteolysis: energy-dependent proteases and their targets. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):592–621. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.592-621.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Squires C., Pichersky E., Carrington M., Hobbs M., Mattick J. S., Dalrymple B., Kuramitsu H., Shiroza T., Foster T. Conservation of the regulatory subunit for the Clp ATP-dependent protease in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3513–3517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Arber W. On the role of IS1 in the formation of hybrids between the bacteriophage P1 and the R plasmid NR1. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Jan;177(2):261–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00267437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston T. C., Thompson R. B., Baldwin T. O. Nucleotide sequence of the luxB gene of Vibrio harveyi and the complete amino acid sequence of the beta subunit of bacterial luciferase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4805–4811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa M., Wada C., Yoshioka S., Yura T. Expression of ClpB, an analog of the ATP-dependent protease regulatory subunit in Escherichia coli, is controlled by a heat shock sigma factor (sigma 32). J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4247–4253. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4247-4253.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehnherr H., Maguin E., Jafri S., Yarmolinsky M. B. Plasmid addiction genes of bacteriophage P1: doc, which causes cell death on curing of prophage, and phd, which prevents host death when prophage is retained. J Mol Biol. 1993 Oct 5;233(3):414–428. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda Y., Miyakawa K., Nishimura Y., Ohtsubo E. chpA and chpB, Escherichia coli chromosomal homologs of the pem locus responsible for stable maintenance of plasmid R100. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):6850–6856. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.6850-6856.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström K., Austin S. J. Mechanisms that contribute to the stable segregation of plasmids. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:37–69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen L. K., Larsen N. W., Molin S., Andersson P. A family of genes encoding a cell-killing function may be conserved in all gram-negative bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1463–1472. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner J. L. Formation, induction, and curing of bacteriophage P1 lysogens. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):679–689. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires C., Squires C. L. The Clp proteins: proteolysis regulators or molecular chaperones? J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1081–1085. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1081-1085.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout V., Torres-Cabassa A., Maurizi M. R., Gutnick D., Gottesman S. RcsA, an unstable positive regulator of capsular polysaccharide synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1738–1747. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1738-1747.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisted T., Gerdes K. Mechanism of post-segregational killing by the hok/sok system of plasmid R1. Sok antisense RNA regulates hok gene expression indirectly through the overlapping mok gene. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 5;223(1):41–54. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90714-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisted T., Nielsen A. K., Gerdes K. Mechanism of post-segregational killing: translation of Hok, SrnB and Pnd mRNAs of plasmids R1, F and R483 is activated by 3'-end processing. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 15;13(8):1950–1959. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisted T., Sørensen N. S., Wagner E. G., Gerdes K. Mechanism of post-segregational killing: Sok antisense RNA interacts with Hok mRNA via its 5'-end single-stranded leader and competes with the 3'-end of Hok mRNA for binding to the mok translational initiation region. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 15;13(8):1960–1968. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06465.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchimoto S., Nishimura Y., Ohtsubo E. The stable maintenance system pem of plasmid R100: degradation of PemI protein may allow PemK protein to inhibit cell growth. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4205–4211. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4205-4211.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Melderen L., Bernard P., Couturier M. Lon-dependent proteolysis of CcdA is the key control for activation of CcdB in plasmid-free segregant bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Mar;11(6):1151–1157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojtkowiak D., Georgopoulos C., Zylicz M. Isolation and characterization of ClpX, a new ATP-dependent specificity component of the Clp protease of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22609–22617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H. A., Comstock L. J., Vasser M. The tac promoter: a functional hybrid derived from the trp and lac promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Guan C., Li P., Riggs P. D., Inouye H. Vectors that facilitate the expression and purification of foreign peptides in Escherichia coli by fusion to maltose-binding protein. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



