Abstract
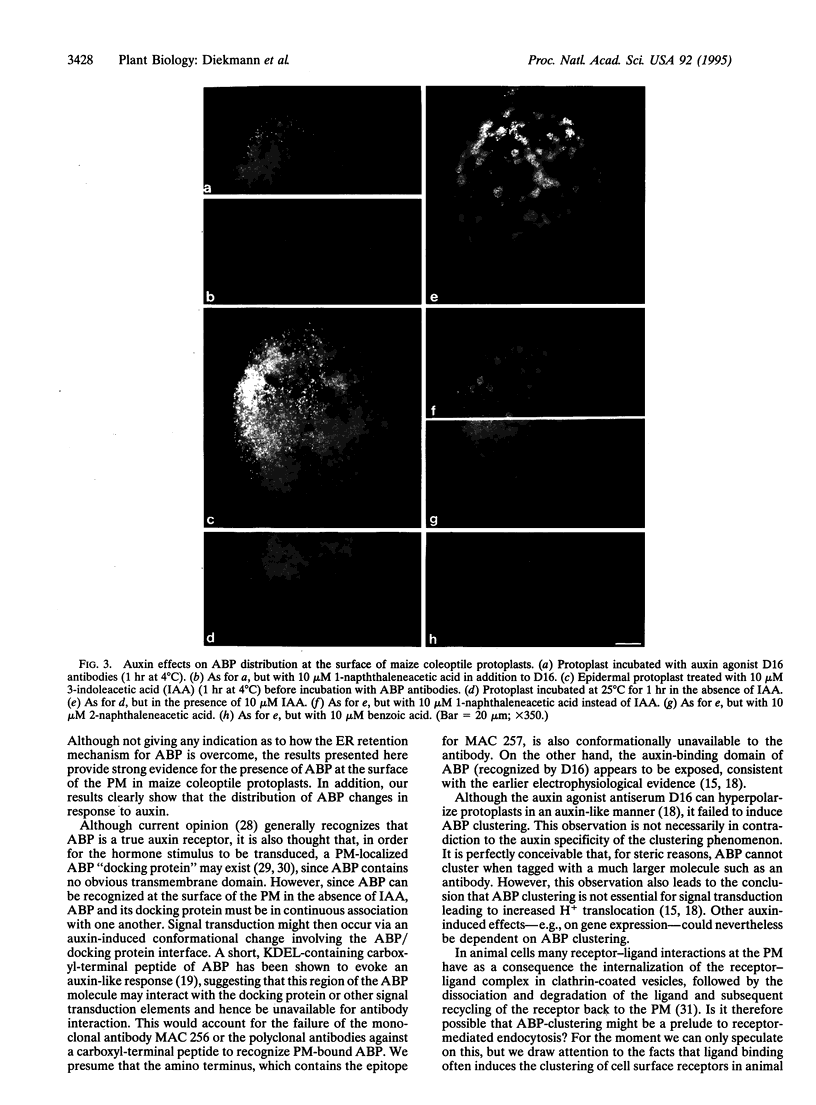
The predominant localization of the major auxin-binding protein (ABP1) of maize is within the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. Nevertheless, all the electrophysiological evidence supporting a receptor role for ABP1 implies that a functionally important fraction of the protein must reside at the outer face of the plasma membrane. Using methods of protoplast preparation designed to minimize proteolysis, we report the detection of ABP at the surface of maize coleoptile protoplasts by the technique of silver-enhanced immunogold viewed by epipolarization microscopy. We also show that ABP clusters following auxin treatment and that this response is temperature-dependent and auxin-specific.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aducci P., Ballio A., Fogliano V., Fullone M. R., Marra M., Proietti N. Purification and photoaffinity labeling of fusicoccin receptors from maize. Eur J Biochem. 1993 May 15;214(1):339–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbier-Brygoo H., Ephritikhine G., Klämbt D., Ghislain M., Guern J. Functional evidence for an auxin receptor at the plasmalemma of tobacco mesophyll protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):891–895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith M. H. Cellular signaling: new insights into the action of the plant growth hormone auxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11442–11445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Anderson R. G., Russell D. W., Schneider W. J. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: concepts emerging from the LDL receptor system. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffetz D., Zick Y. Receptor aggregation is necessary for activation of the soluble insulin receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):889–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse T., Feldwisch J., Balshüsemann D., Bauw G., Puype M., Vandekerckhove J., Löbler M., Klämbt D., Schell J., Palme K. Molecular cloning and structural analysis of a gene from Zea mays (L.) coding for a putative receptor for the plant hormone auxin. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2453–2461. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08380.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn M. A., Heinstein P. F., Low P. S. Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis in Plant Cells. Plant Cell. 1989 Oct;1(10):1003–1009. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.10.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inohara N., Shimomura S., Fukui T., Futai M. Auxin-binding protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum of maize shoots: molecular cloning and complete primary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3564–3568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. M., Herman E. M. KDEL-Containing Auxin-Binding Protein Is Secreted to the Plasma Membrane and Cell Wall. Plant Physiol. 1993 Feb;101(2):595–606. doi: 10.1104/pp.101.2.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klämbt D. A view about the function of auxin-binding proteins at plasma membranes. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Jun;14(6):1045–1050. doi: 10.1007/BF00019401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löbler M., Klämbt D. Auxin-binding protein from coleoptile membranes of corn (Zea mays L.). I. Purification by immunological methods and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9848–9853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H. Transmembrane signaling: the joy of aggregation. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 1;149(5):1477–1487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napier R. M., Fowke L. C., Hawes C., Lewis M., Pelham H. R. Immunological evidence that plants use both HDEL and KDEL for targeting proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jun;102(Pt 2):261–271. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napier R. M., Venis M. A. Epitope mapping reveals conserved regions of an auxin-binding protein. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 15;284(Pt 3):841–845. doi: 10.1042/bj2840841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palme K., Hesse T., Moore I., Campos N., Feldwisch J., Garbers C., Hesse F., Schell J. Hormonal modulation of plant growth: the role of auxin perception. Mech Dev. 1991 Feb;33(2):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90076-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Control of protein exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:1–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Direct visualization of binding, aggregation, and internalization of insulin and epidermal growth factor on living fibroblastic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2659–2663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura S., Sotobayashi T., Futai M., Fukui T. Purification and properties of an auxin-binding protein from maize shoot membranes. J Biochem. 1986 May;99(5):1513–1524. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel G., Blatt M. R., Fricker M. D., White I. R., Millner P. Modulation of K+ channels in Vicia stomatal guard cells by peptide homologs to the auxin-binding protein C terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11493–11497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillmann U., Viola G., Kayser B., Siemeister G., Hesse T., Palme K., Löbler M., Klämbt D. cDNA clones of the auxin-binding protein from corn coleoptiles (Zea mays L.): isolation and characterization by immunological methods. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2463–2467. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venis M. A., Napier R. M., Barbier-Brygoo H., Maurel C., Perrot-Rechenmann C., Guern J. Antibodies to a peptide from the maize auxin-binding protein have auxin agonist activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7208–7212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Maxfield F. R., Pastan I. H. alpha 2 Macroglobulin binding to the plasma membrane of cultured fibroblasts. Diffuse binding followed by clustering in coated regions. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):614–625. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]