Abstract
Based on a survey of 86 isolates, approximately 5% of all naturally occurring strains of Streptococcus mutans contains a 3.6 X 10(6)-dalton (3.6-megadalton) multicopy plasmid of unknown function. The amount of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid per chromosome varies from 2 to 6% depending on the host strain. About 13% of the total covalently closed circular deoxyribonucleic acid in each of the four plasmid-containing strains consists of dimeric molecules, with interlocked circular forms predominating. Site-specific restriction endonucleases have been identified that cleave this 3.6-megadalton plasmid at single and at multiple sites. Each of the four plasmids is cleaved once by the HindIII and BamHI restriction enzymes. The HpaI, TaqI, and HhaI enzymes generate two, five, and six components, respectively, and the digestion products of each of the four plasmids are identical. Because the four plasmid-containing S. mutans strains are physiologically unique with respect to one another, we conclude this plasmid to be a disseminated extrachromosomal element in S. mutans.
Full text
PDF
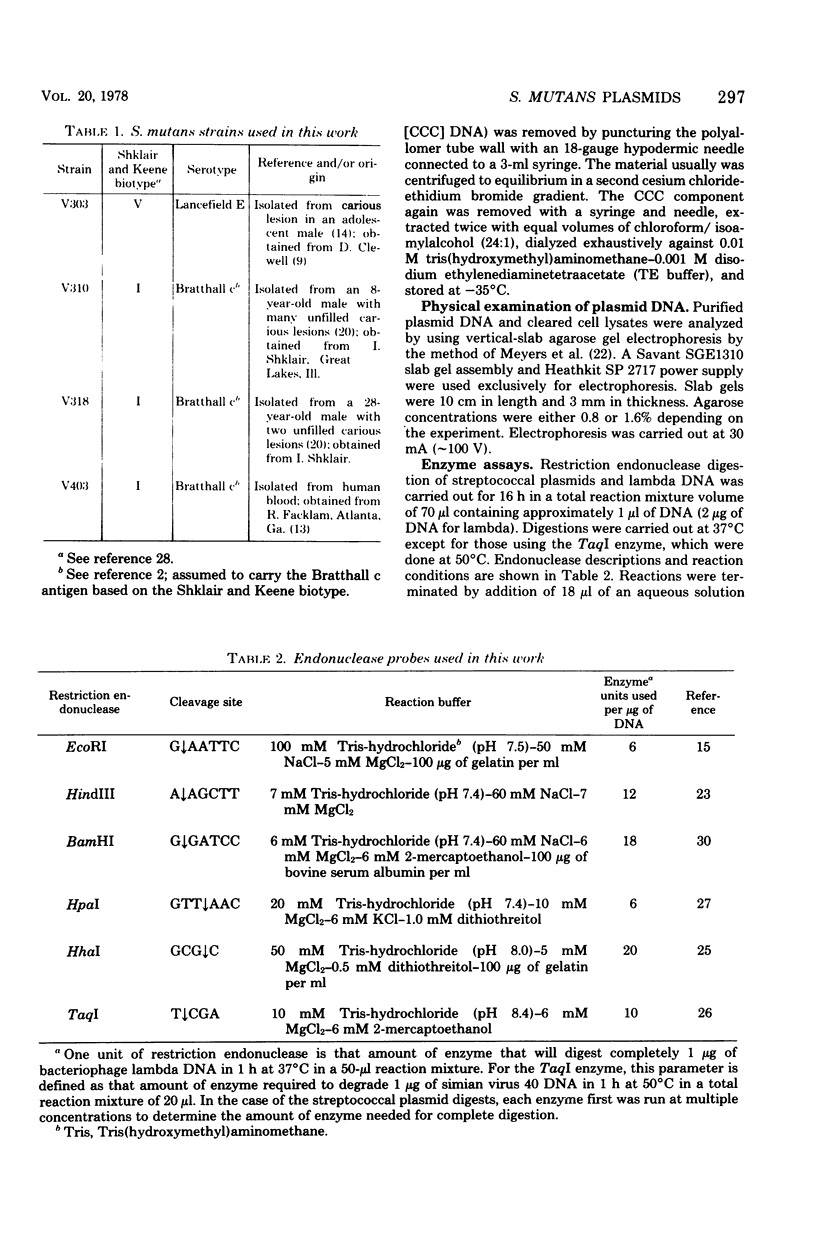

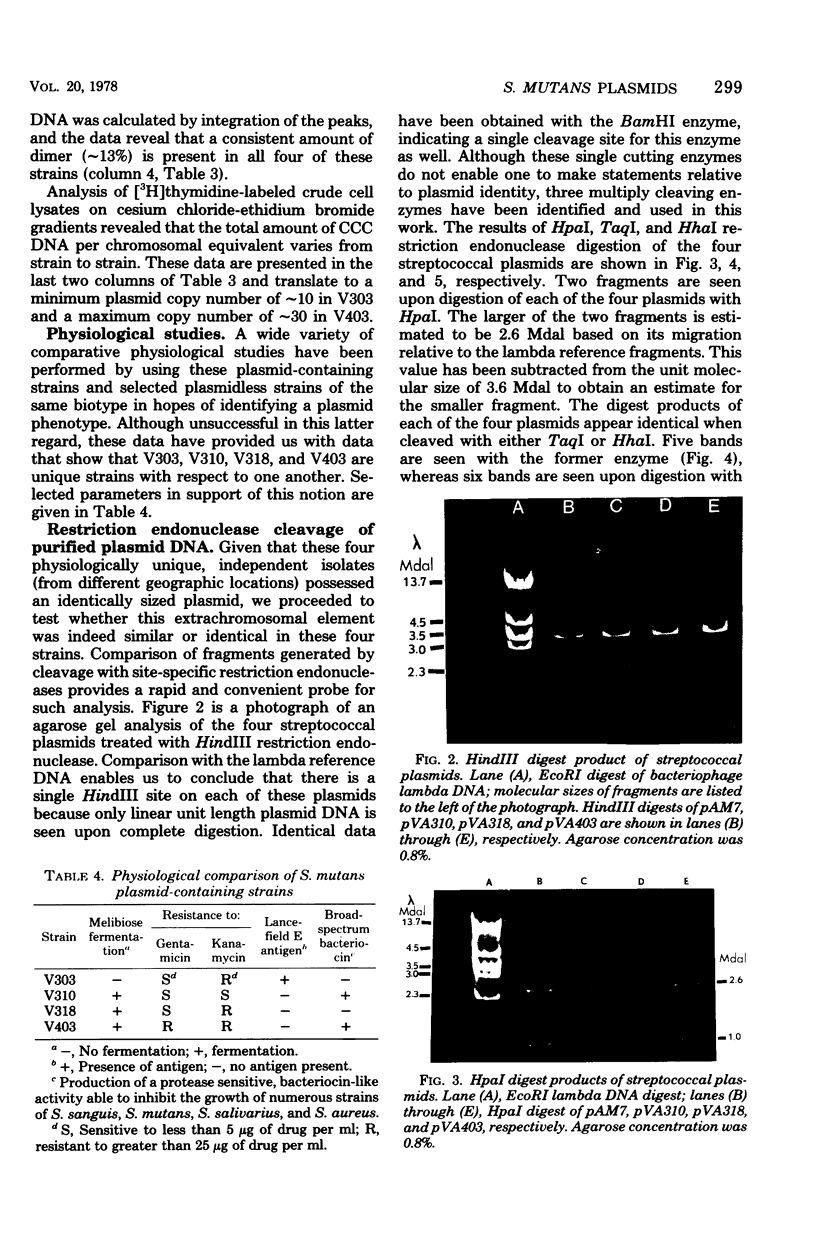



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allet B., Jeppesen P. G., Katagiri K. J., Delius H. Mapping the DNA fragments produced by cleavage by lambda DNA with endonuclease RI. Nature. 1973 Jan 12;241(5385):120–123. doi: 10.1038/241120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D. Demonstration of five serological groups of streptococcal strains resembling Streptococcus mutans. Odontol Revy. 1970;21(2):143–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Franke A. E. Characterization of a plasmid determining resistance to erythromycin, lincomycin, and vernamycin Balpha in a strain Streptococcus pyogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 May;5(5):534–537. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.5.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Yagi Y., Bauer B. Plasmid-determined tetracycline resistance in Streptococcus faecalis: evidence for gene amplification during growth in presence of tetracycline. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1720–1724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin P. M., Carlier C., Chabbert Y. A. Plasmid-linked tetracycline and erythromycin resistance in group D "streptococcus". Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Dec;123(6):755–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Birch N., Hascall G., Clewell D. B. Isolation and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid from Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1362–1364. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1362-1364.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Clewell D. B. Transmissible toxin (hemolysin) plasmid in Streptococcus faecalis and its mobilization of a noninfectious drug resistance plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):784–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.784-790.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstathiou J. D., McKay L. L. Plasmids in Streptococcus lactis: evidence that lactose metabolism and proteinase activity are plasmid linked. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.38-44.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Saunders J. R., Richmond M. H., Falkow S. Relationships among some R plasmids found in Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):356–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.356-362.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Berman K. S., Knoettner P., Kapsimalis B. Dental caries and alveolar bone loss in gnotobiotic rats infected with capsule forming streptococci of human origin. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Jun;11(6):549–560. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Araya S., Higuchi M. Plasmid DNA satellite bands seen in lysates of Streptococcus mutans that form insoluble extracellular polysaccharides. J Dent Res. 1976 Mar-Apr;55(2):266–271. doi: 10.1177/00220345760550021801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horodniceanu T., Bouanchaud D. H., Bieth G., Chabbert Y. A. R plasmids in Streptococcus agalactiae (group B). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):795–801. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupersztoch Y. M., Helinski D. R. A catenated DNA molecule as an intermediate in the replication of the resistance transfer factor R6K in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 15;54(4):1451–1459. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Hassell F. P. Transformation of Streptococcus sanguis Challis by plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid from Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):347–355. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.347-355.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Reider J. L., Virgili S. S., Kopecko D. J. Survey of the extrachromosomal gene pool of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):215–226. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.215-226.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Weatherly G. G., Curtiss R., 3rd R6K plasmid replication: influence of chromosomal genotype in minicell-producing strains of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1387–1400. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1387-1400.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old R., Murray K., Boizes G. Recognition sequence of restriction endonuclease III from Hemophilus influenzae. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 25;92(2):331–339. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J., Myers P. A., Morrison A., Murray K. A specific endonuclease from Haemophilus haemolyticus. J Mol Biol. 1976 May 5;103(1):199–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Hutchinson C. A., 3rd, Harris J. I. A thermostable sequence-specific endonuclease from Thermus aquaticus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):542–546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shklair I. L., Keene H. J. A biochemical scheme for the separation of the five varieties of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Nov;19(11):1079–1081. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. A., Young F. E. Isolation of a sequence-specific endonuclease (BamI) from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens H. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 5;97(1):123–125. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]