Abstract
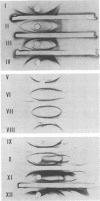
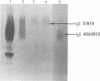
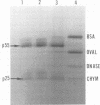
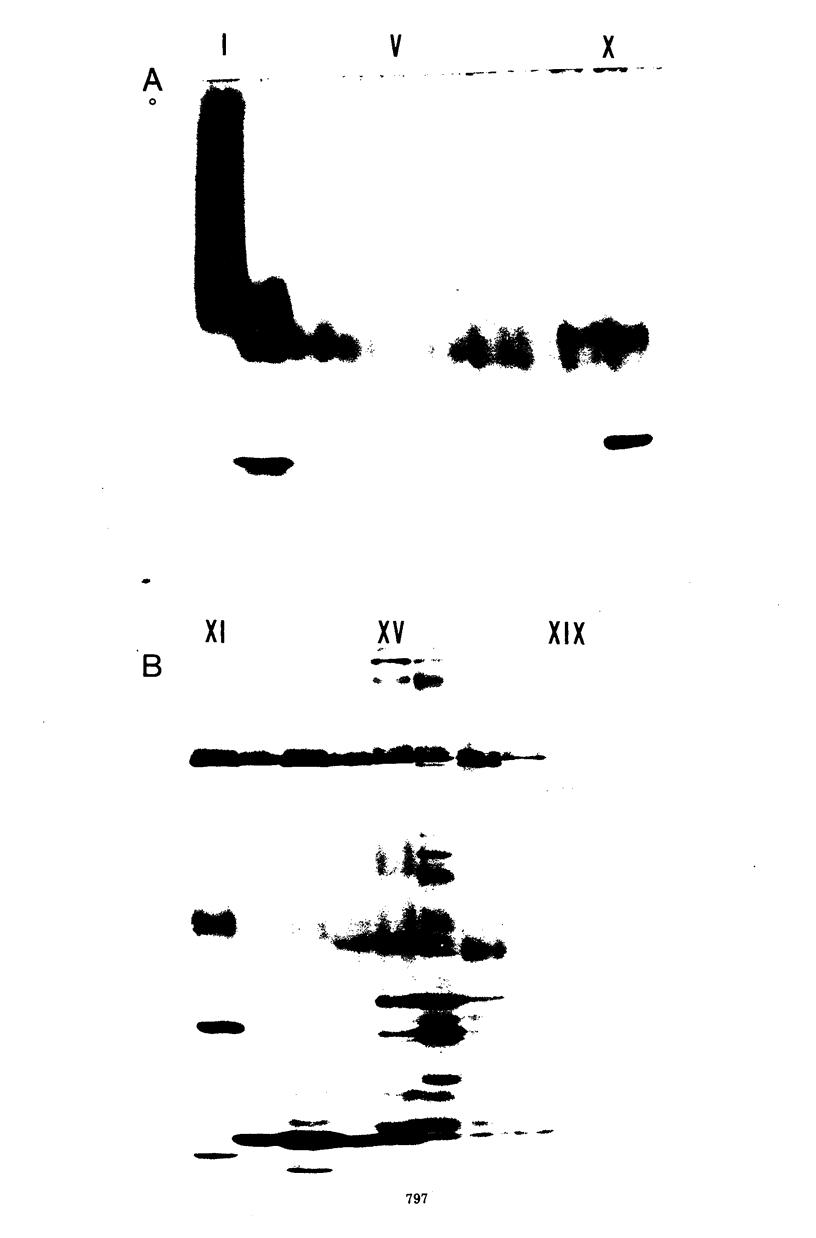
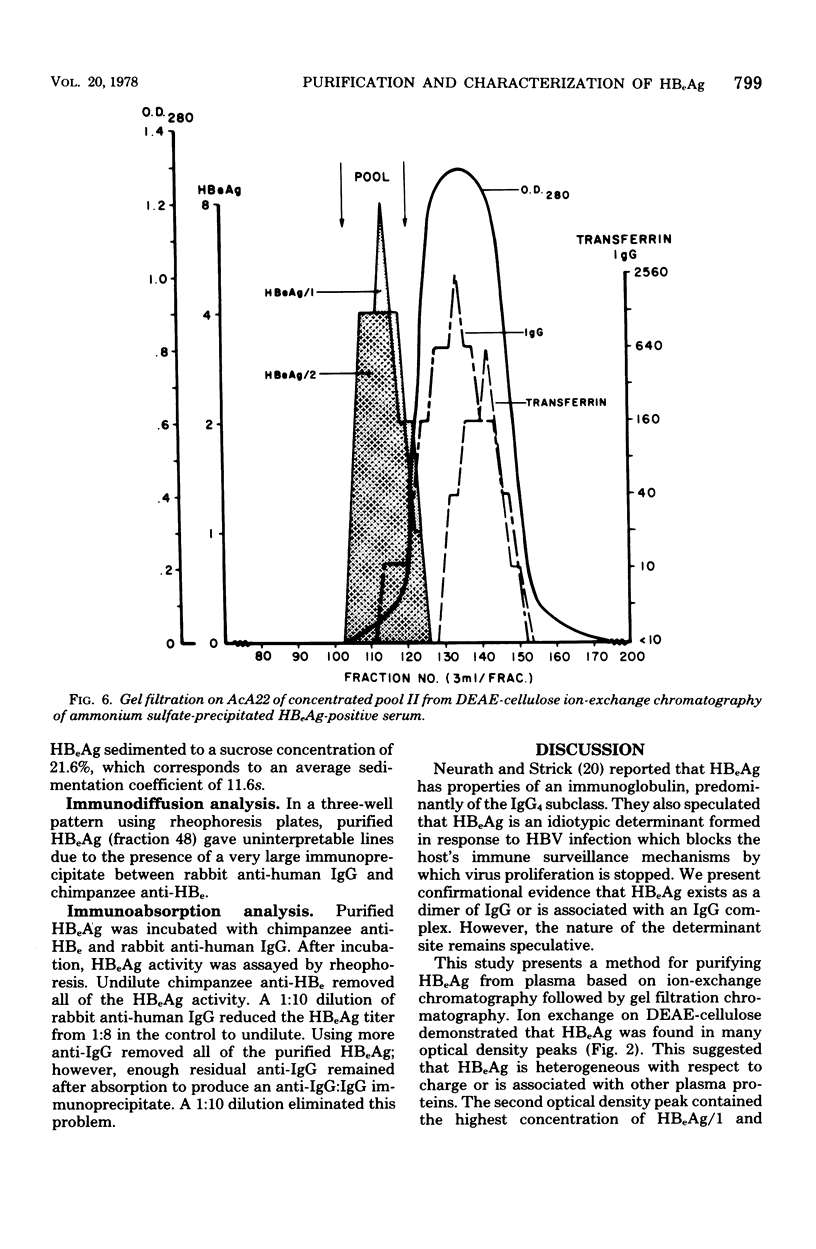
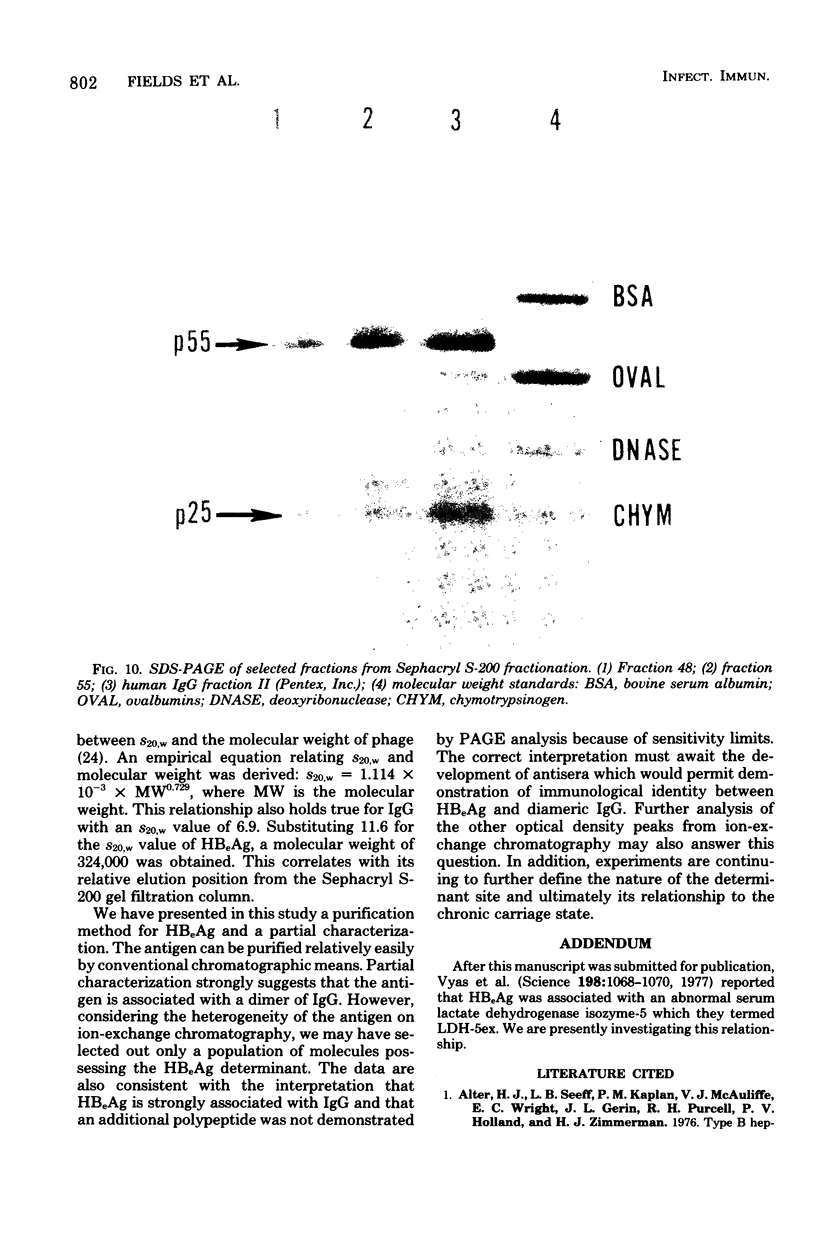
Purification of hepatitis e antigen (HBeAg) from 200 ml of chimpanzee plasma was accomplished by a combination of ion-exchange chromatography on diethylaminoethyl-cellulose followed by gel filtration. High-resolution sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of purified HBeAg demonstrated two major polypeptides with estimated molecular weights of 22,000 and 55,000. HBeAg labeled with 125I showed a high affinity for protein A-conjugated Sepharose CL-4B. The precipitation reaction between HBeAg and anti-HBe was inhibited by preincubating the purified antigen with rabbit anti-human immunoglobulin G (IgG). These data show that HBeAg is associated with a serum fraction with the biophysical and antigenic properties of an immunoblobulin of the IgG class. Sedimentation coefficient analysis of purified HbeAg resulted in an S20w value of 11.6 and a molecular weight value of 324,000. These findings, supported by gel filitration and polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis, revealed that HBeAg has properties analogous to those of a dimer of IgG.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter H. J., Seeff L. B., Kaplan P. M., McAuliffe V. J., Wright E. C., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Holland P. V., Zimmerman H. J. Type B hepatitis: the infectivity of blood positive for e antigen and DNA polymerase after accidental needlestick exposure. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 21;295(17):909–913. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610212951701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berquist K. R., Maynard J. E., Murphy B. L. Letter: Infectivity of serum containing HBsAg and antibody to e antigen. Lancet. 1976 May 8;1(7967):1026–1027. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91908-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chairez R., Hollinger F. B., Melnick J. L., Dreesman G. R. Biophysical properties of purified morphologic forms of hepatitis B antigen. Intervirology. 1974;3(3):129–140. doi: 10.1159/000149749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Sheikh N., Woolf I. L., Galbraith R. M., Eddleston A. L., Dymock I. W., Williams R. e Antigen-antibody system as indicator of liver damage in patients with hepatitis-B antigen. Br Med J. 1975 Nov 1;4(5991):252–253. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5991.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinman S. V., Berris B., Sinclair J. C., Wrobel D. M., Murphy B. L., Maynard J. E. e antigen and anti-e in HBsAg carriers. Lancet. 1975 Dec 13;2(7946):1173–1174. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92658-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields H. A., Hollinger F. B., Desmyter J., Melnick J. L., Dreesman G. R. Biochemical and biophysical properties of hepatitis B core particles derived from Dane particles and infected hepatocytes. Intervirology. 1977;8(6):336–350. doi: 10.1159/000148909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger F. B., Morrison M., Chairez R., Dreesman G. R. Immunological and biophysical properties of hepatitis B antigen labeled by the chloramine-T and by the lactoperoxidase methods. J Immunol Methods. 1975;8(1-2):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Grey H. M., Williams R. C., Jr Protein A reactivity with mouse immunoglobulins. Structural relationship between some mouse and human immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1116–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Williams R. C., Jr Differences in anti-protein A activity among IgG subgroups. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):828–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnius L. O. Characterization of a new antigen-antibody system associated with hepatitis B. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 May;20(2):209–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnius L. O., Espmark A. A new antigen complex co-occurring with Australia antigen. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(2):335–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnius L. O., Espmark J. A. New specificities in Australia antigen positive sera distinct from the Le Bouvier determinants. J Immunol. 1972 Nov;109(5):1017–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnius L. O., Lindholm A., Lundin P., Iwarson S. A new antigen-antibody system. Clinical significance in long-term carriers of hepatitis B surface antigen. JAMA. 1975 Jan 27;231(4):356–359. doi: 10.1001/jama.231.4.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis J. Practical system for ployacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis. Lab Pract. 1973 Feb;22(2):107–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard J. E., Barrett D. H., Murphy B. L., Bradley D. W., Berquist K. R., Bender T. R. Relation of e antigen to hepatitis B virus infection in an area of hyperendemicity. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133(3):339–342. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen C. R. Tables for estimating sedimentation through linear concentration gradients of sucrose solution. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):114–149. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N. Host specificity of a serum marker for hepatitis B: evidence that "e antigen" has the properties of an immunoglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1702–1706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Trepo C., Chen M., Prince A. M. Identification of additional antigenic sites on Dane particles and the tubular forms of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Gen Virol. 1976 Mar;30(3):277–285. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-3-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. O., Dietrichson O., Juhl E. Incidence and meaning of the "e" determinant among hepatitis-B-antigen positive patients with acute and chronic liver diseases. Report from the Copenhagen Hepatitis Acuta Programme. Lancet. 1974 Oct 19;2(7886):913–915. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh Y. H., Sanders B. E. Improved chromatographic fractionation and characterization of human plasma proteins. Anal Biochem. 1966 May;15(2):232–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitout M. J., Conradie J. D., Van Rensburg A. J. Relationship between the sedimentation coefficient and molecular weight of bacteriophages. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jun;4(4):577–583. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-4-577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer I. L., Edwards V. M., Brezina M. Letter: e Antigen in HBs Ag-carrier mothers. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 30;293(18):940–940. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510302931823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist J., Meloun B., Hjelm H. Protein A isolated from Staphylococcus aureus after digestion with lysostaphin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Sep 25;29(3):572–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. L., Murphy B. L., Auslander M. O., Maynard J. E., Schalm S. S., Summerskill W. H., Gitnick G. L. Studies of the "e" antigen in acute and chronic hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1976 Aug;71(2):208–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thamer G., Gmelin K., Kommerell B. Letter: E antigen: prognostic marker in acute viral hepatitis B? Lancet. 1976 Sep 11;2(7985):577–577. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91828-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepo C. G., Magnius L. O., Schaefer R. A., Prince A. M. Detection of e antigen and antibody: correlations with hapatitis B surface and hepatitis B core antigens, liver disease, and outcome in hepatitis B infections. Gastroenterology. 1976 Nov;71(5):804–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Peterson D. L., Townsend R. M., Damle S. R., Magnius L. O. Hepatitis B "e" antigen: an apparent association with lactate dehydrogenase isozyme-5. Science. 1977 Dec 9;198(4321):1068–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.73221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]