Abstract
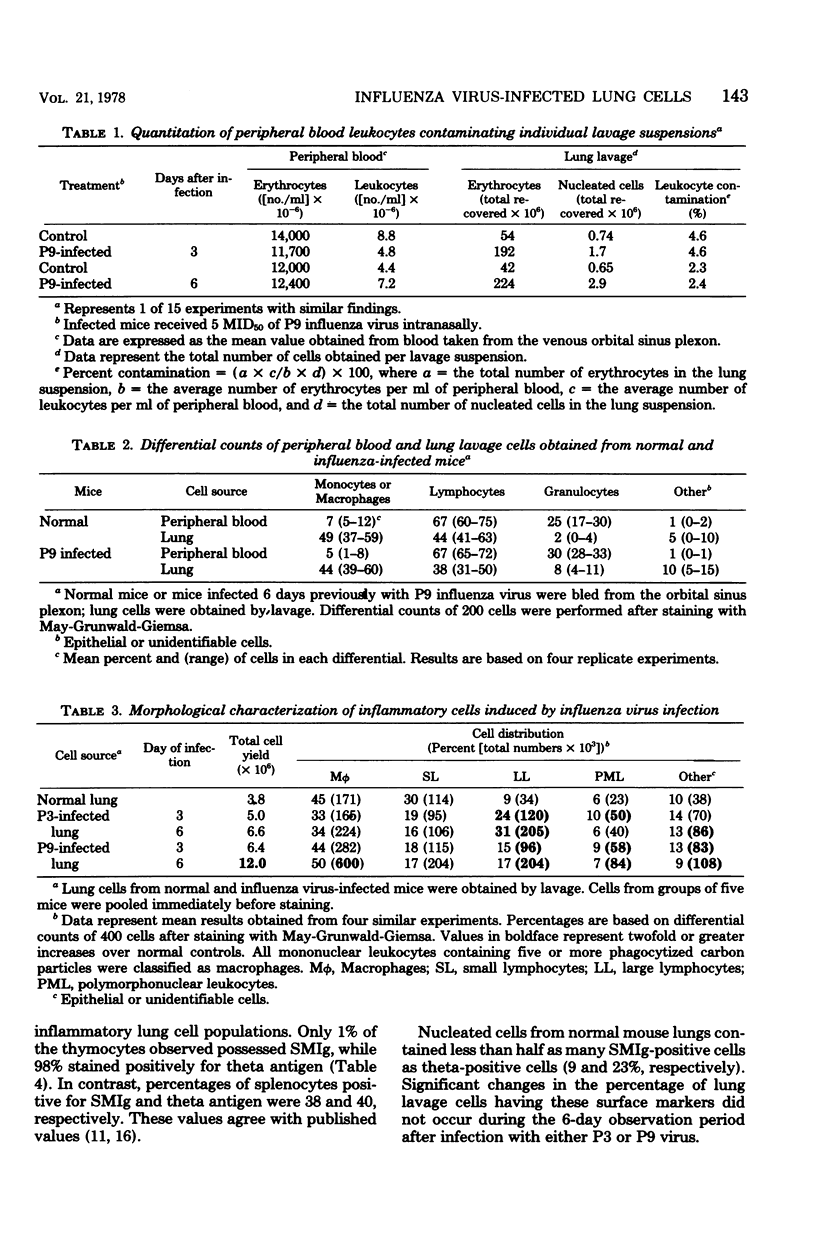
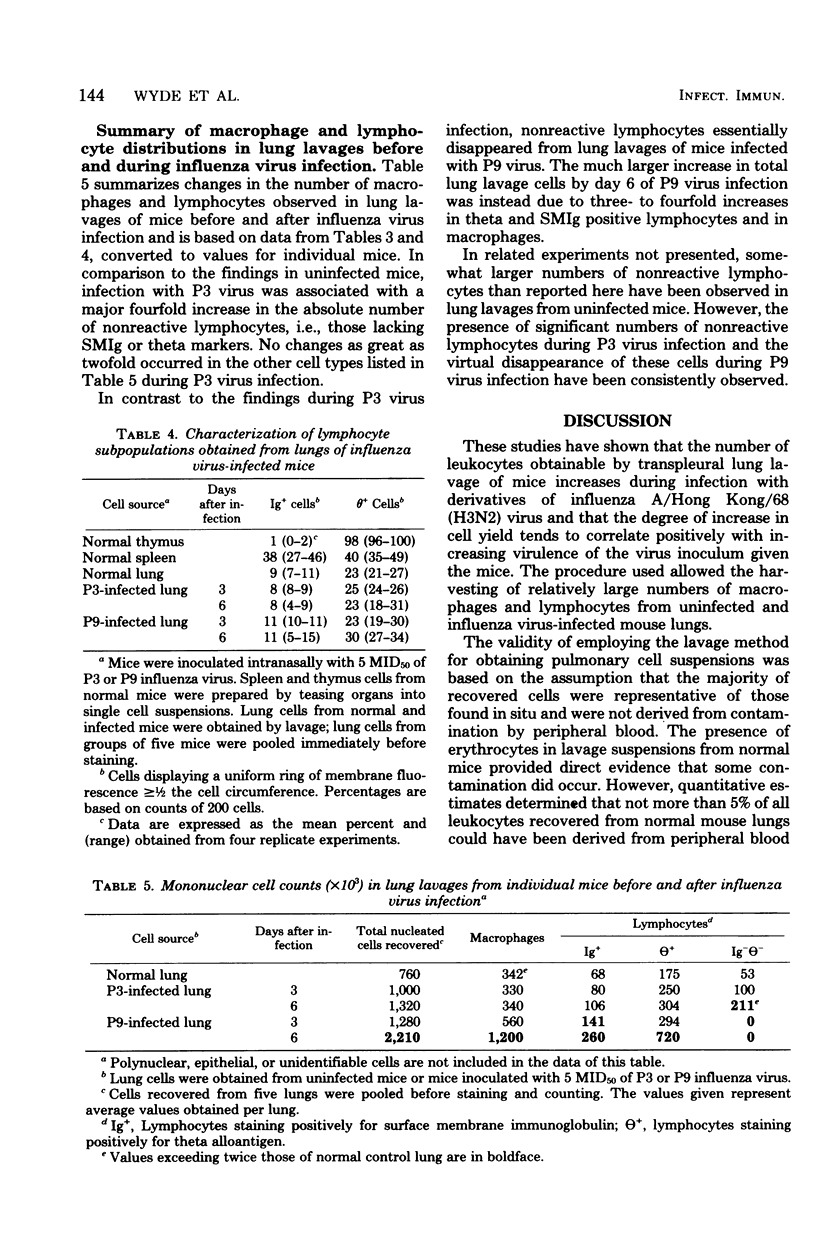
To initiate evaluation of the cell-mediated immunological response to influenza virus in a major site of disease, lung cells were obtained by transpleural lavage from lungs of uninfected mice and from those infected 3 or 6 days previously with 5 50% mouse infectious doses (MID50) of avirulent (P3) or virulent (P9) influenza A Hong Kong (H3N2) virus. The number of cells recovered by lavage was dependent on the dose, time after inoculation, and the type of virus used for inoculation. Although lavage pools were shown to contain peripheral blood leukocytes, this contamination was shown to be consistently less than 5% of the total leukocytes harvested. Among the ca. 0.75 × 106 lavage cells obtained from each uninfected mouse, about 90% were macrophages or lymphocytes in approximately equal proportion. T, B, and null (lyphocytes lacking theta or surface immunoglobulin markers) lymphocytes averaged 23, 9, and 7% of cells in these suspensions, respectively. After infection with either P3 or P9 virus, increased numbers of activated macrophages and lymphoblasts were observed. The major change during P3 infection was an increase in absolute numbers of null lymphocytes. In contrast, during P9 infection, T and B lymphocytes and macrophages progressively increased in absolute numbers while null cells decreased. These data suggest that cell-mediated immunological responses to influenza virus occur in the lung during infection, but that the responses to virulent and avirulent variants may differ both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davidson W. F., Parish C. R. A procedure for removing red cells and dead cells from lymphoid cell suspensions. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Jun;7(2-3):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERS J. F., MUDLER J., MASUREL N., vd KUIP L., TYRRELL D. A. Studies on the pathogenesis of influenza virus pneumonia in mice. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1962 Jan;83:207–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltreider H. B. Expression of immune mechanisms in the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Mar;113(3):347–379. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.3.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loosli C. G., Buckley R. D., Hardy J. D., Hertweck M. S., Kow S. Y., Serebrin R., Ryan D. P., Stinson S. F. The pathogenesis of postinfluenzal collapse of the lungs of mice. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1971;84:182–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Baughn R. E., Musher D. M. Mitogenic activity of bacterial lipopolysaccharides in vivo: morphological and functinal characterization of responding cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):71–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.71-78.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Two distinct populations of peripheral lymphocytes in mice distinguishable by immunofluorescence. Immunology. 1970 Oct;19(4):637–650. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott G. H., Walker J. S. Immunoglobulin-bearing cells in lungs of mice infected with influenza virus. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1525–1527. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1525-1527.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr, Peavy D. L., Gormus B. J., McGraw J. In vitro and in vivo effects of endotoxin on mouse peritoneal cells. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):106–112. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.106-112.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. L., Mayner R. E., Barry D. W., Ennis F. A. Influenza virus infection in nude mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):91–94. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldkamp J., De Reuver M. J., Willers J. M. Distribution of different cell types in the lymphoid organs of the mouse, as determined with sera against thymus and Peyer's patches. Immunology. 1974 Feb;26(2):359–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Fu S. M., Hoffman T., Kunkel H. G. IgG on lymphocyte surfaces; technical problems and the significance of a third cell population. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1210–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyde P. R., Couch R. B., Mackler B. F., Cate T. R., Levy B. M. Effects of low- and high-passage influenza virus infection in normal and nude mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):221–229. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.221-229.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


