Abstract
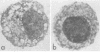
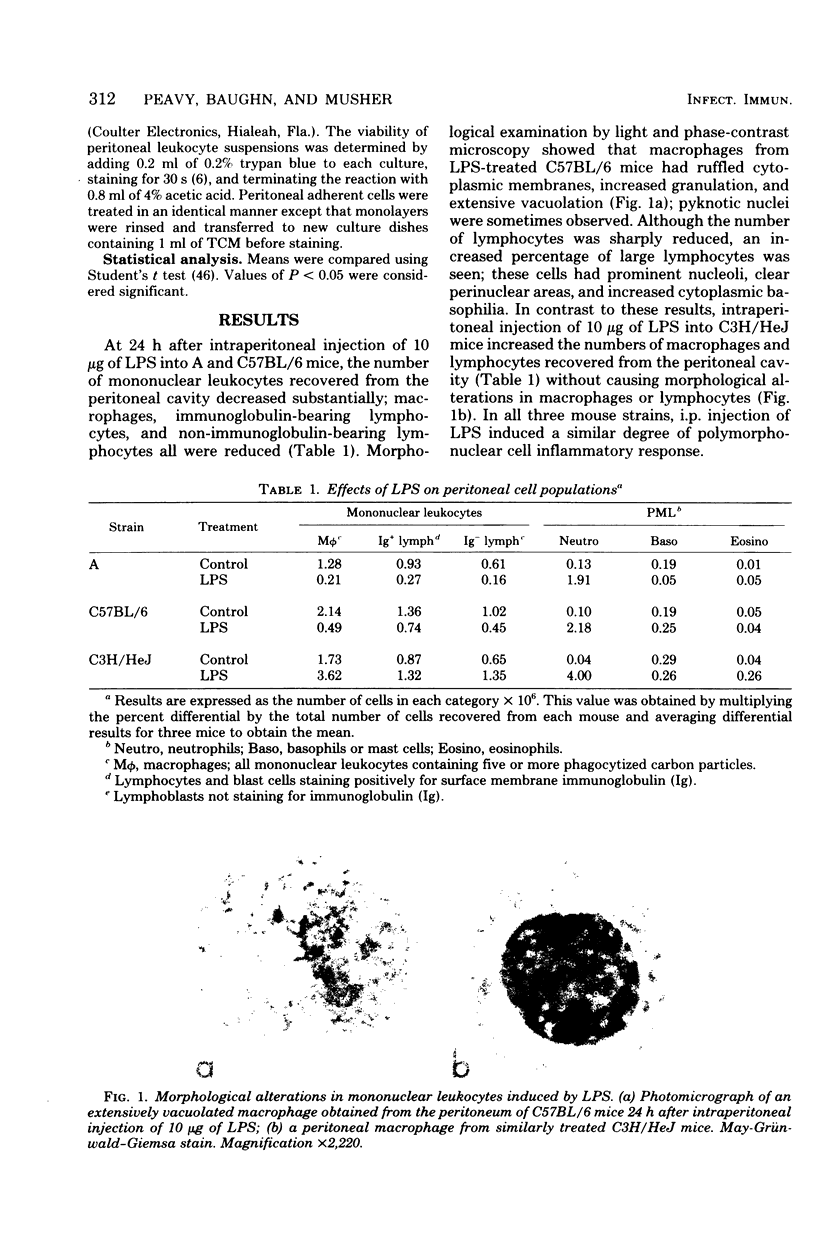
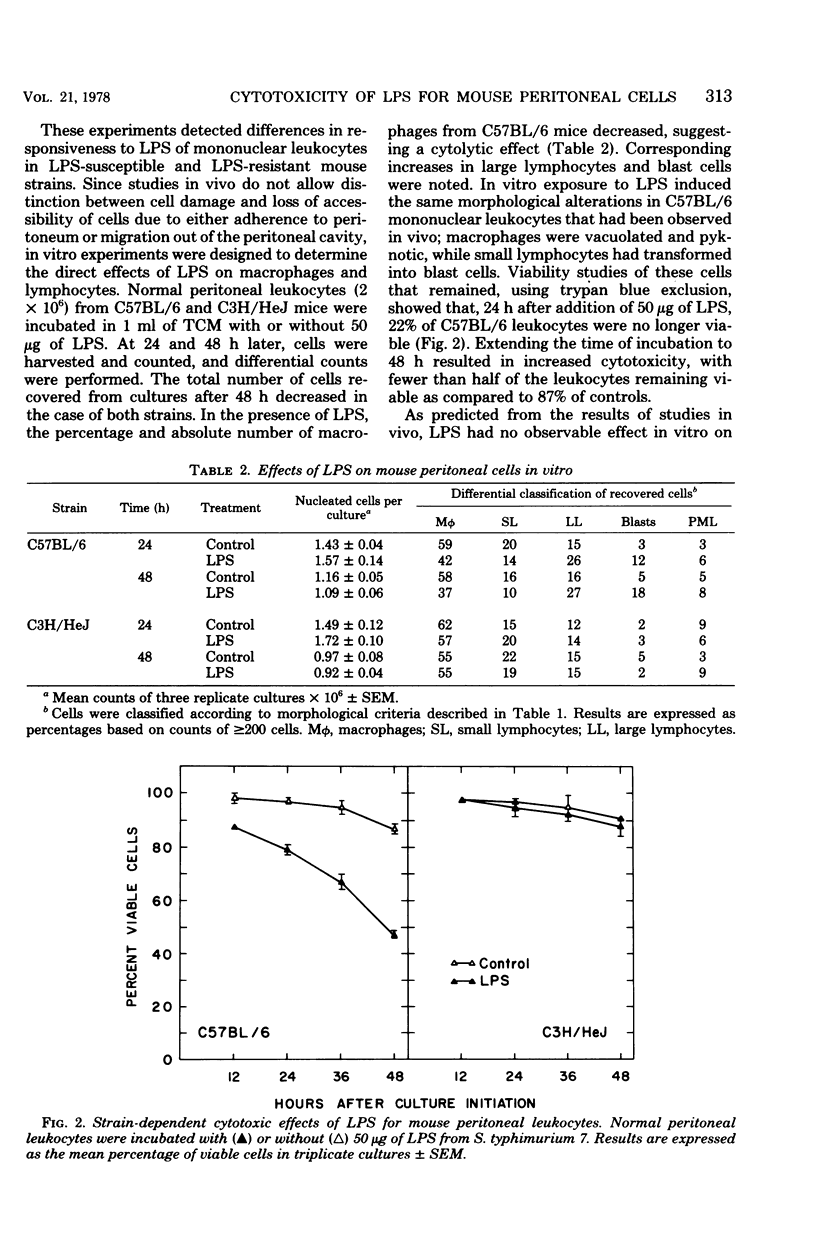
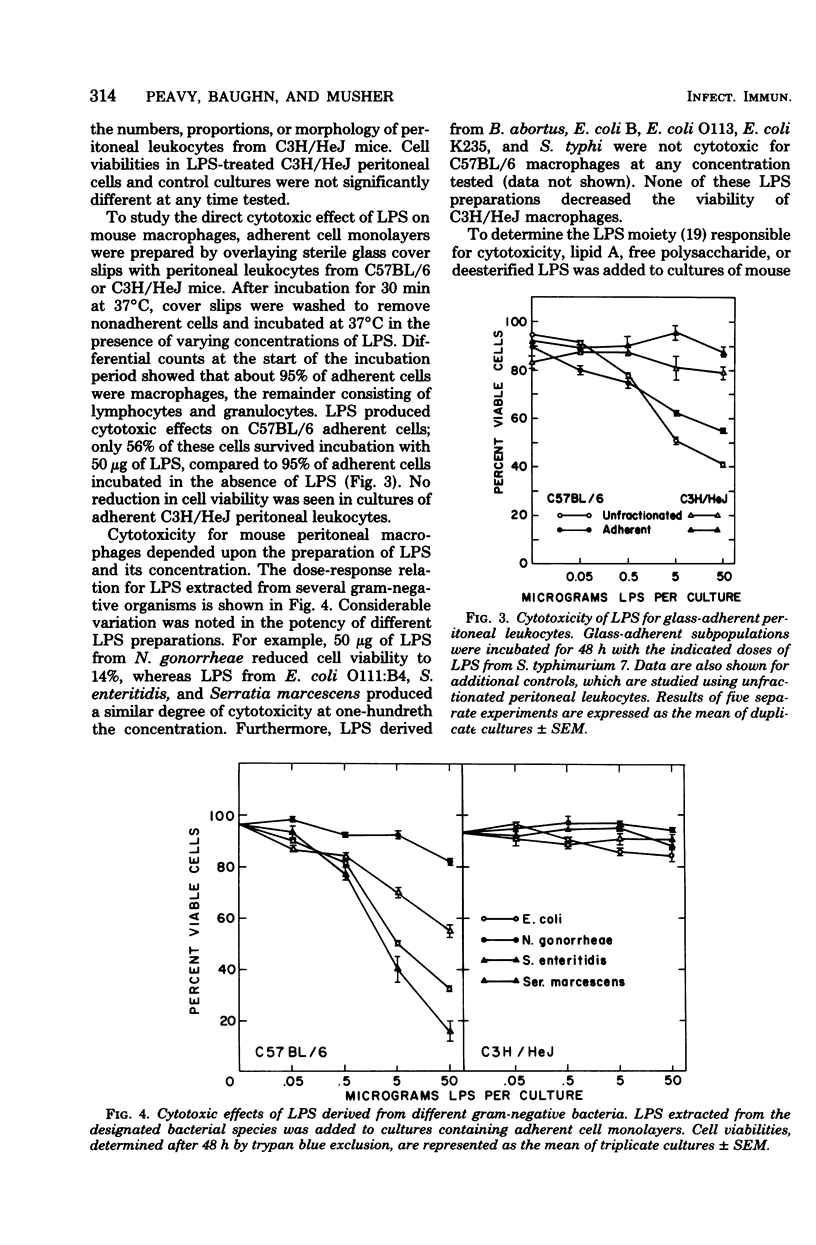
The cytotoxic effects of bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS) on mouse leukocytes have been examined in vivo and in vitro. Intraperitoneal injection of LPS into C57BL/6 mice greatly reduced the recovery of mononuclear cells; LPS was cytotoxic for macrophages, but had a mitogenic effect on lymphocytes. Similar effects of LPS on peritoneal leukocytes were observed in vitro. When monolayers of adherent peritoneal cells were studied in vitro, cytotoxicity was also observed, suggesting that the effect of LPS on macrophages is direct and does not require participation by lymphocytes. Entirely different results were obtained when peritoneal macrophages from LPS-resistant C3H/HeJ mice were studied. LPS failed to activate lymphocytes and was not cytotoxic for macrophages in vitro or in vivo. The effect of LPS on polymorphonuclear leukocytes appeared to be the same in all mouse stains studied. Lipid A was shown to be the most biologically active portion of the LPS molecule. Whereas polysaccharide-deficient endotoxins extracted from rough mutants of Salmonella typhimurium were cytotoxic for macrophages in vitro, polysaccharides that lacked esterified fatty acids did not exhibit this activity. Since LPS may mediate its effects through affinity for mammalian cell membranes, the cellular unresponsiveness of C3H/H3J mice to LPS may reflect an inability of cells from LPS-resistant strains to interact with LPS at the membrane level.
Full text
PDF

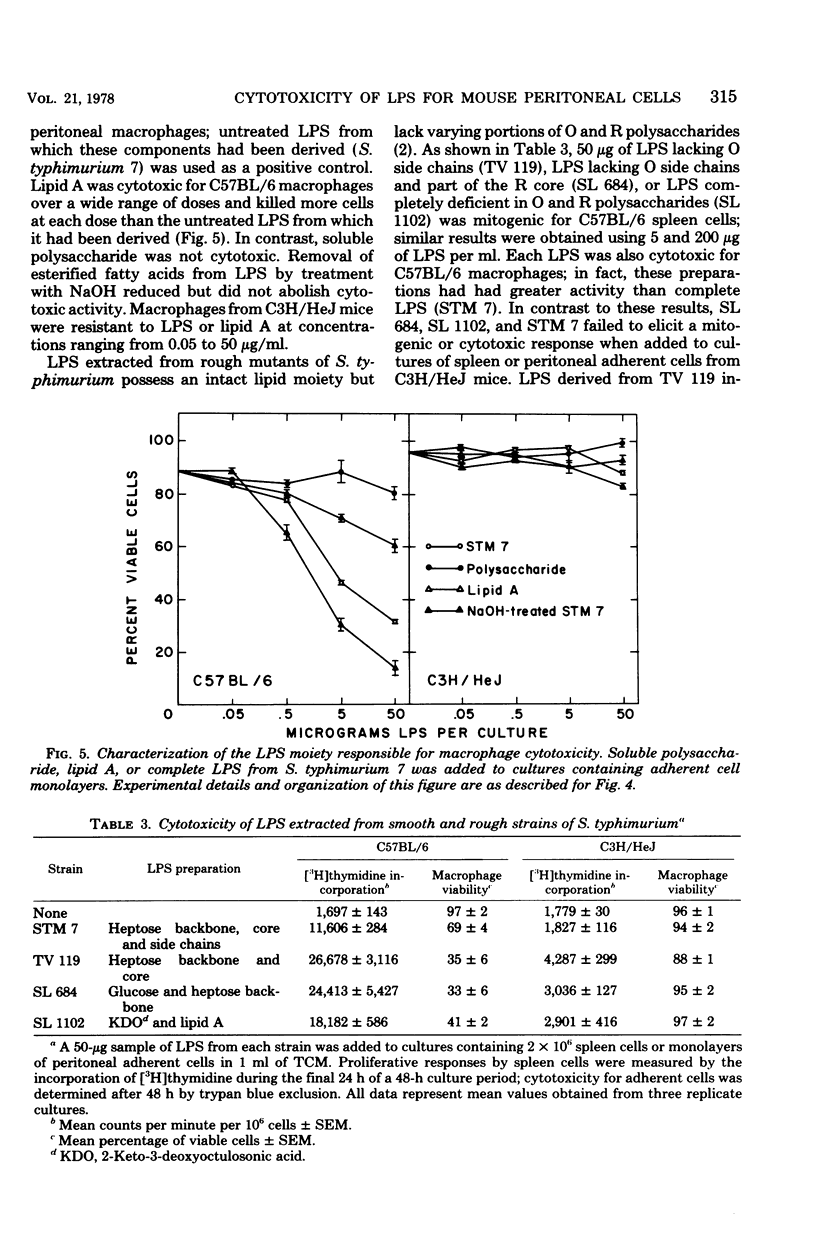




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANACKER R. L., FINKELSTEIN R. A., HASKINS W. T., LANDY M., MILNER K. C., RIBI E., STASHAK P. W. ORIGIN AND PROPERTIES OF NATURALLY OCCURRING HAPTEN FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1705–1720. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1705-1720.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams G. A., Singh P. P. Structural features of lipid A preparations isolated from Escherichia coli and Shigella flexneri. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 5;202(3):553–555. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson B., Blomgren H. Evidence for thymus-independent humoral antibody production in mice against polyvinylpyrrolidone and E. coli lipopolysaccharide. Cell Immunol. 1971 Oct;2(5):411–424. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYSE E. A., OLD L. J., STOCKERT E. Some further data on cytotoxic isoantibodies in the mouse. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Oct 24;99:574–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb45339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller F. K. The role of endotoxin in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh Suppl. 1969;36:125–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. E., Cohn Z. A. The isolation and selected properties of blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):145–160. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., MORSE S. I. Functional and metabolic properties of polymorphonuclear leucocytes. II. The influence of a lipopolysaccharide endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1960 May 1;111:689–704. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.5.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Damais C., Parant F., Juy D., Galelli A. Failure of endotoxin to increase nonspecific resistance to infection of lipopolysaccharide low-responder mice. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):722–727. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.722-727.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Parant F., Boyer F. A proposed mechanism for natural immunity to enterobacterial pathogens. J Immunol. 1968 Feb;100(2):292–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Melmon K. L., Davis W. C., Williams H. E. Mechanism of endotoxin interaction with human leucocytes. Br J Haematol. 1968 Dec;15(6):539–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb01576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cluff L. E. Effects of endotoxins on susceptibility to infections. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):205–215. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glode L. M., Jacques A., Mergenhagen S. E., Rosenstreich D. L. Resistance of macrophages from C3H/HeJ mice to the in vitro cytotoxic effects of endotoxin. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):162–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glode L. M., Scher I., Osborne B., Rosenstreich D. L. Cellular mechanism of endotoxin unresponsiveness in C3H/HeJ mice. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):454–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASKINS W. T., LANDY M., MILNER K. C., RIBI E. Biological properties of parent endotoxins and lipoid fractions, with a kinetic study of acid-hydrolyzed endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1961 Nov 1;114:665–684. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.5.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEILMAN D. H., BERNTON H. W. The effect of endotoxin on tissue cultures of spleen of normal and tuberculin-sensitive animals. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Dec;84:862–871. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.84.6.862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEILMAN D. H. THE SELECTIVE TOXICITY OF ENDOTOXIN FOR PHAGOCYTIC CELLS OF THE RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1965;26:63–79. doi: 10.1159/000229555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. M., Kind P. D. Enhancing effect of bacterial endotoxins on bone marrow cells in the immune response to SRBC. J Immunol. 1972 May;108(5):1453–1455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDY M., PILLEMER L. Increased resistance to infection and accompanying alteration in properidin levels following administration of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1956 Sep 1;104(3):383–409. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.3.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies A. S., Melmon K. L. Mechanism of endotoxin-induced kinin production in human plasma. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Jan;20(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90468-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Adler W. H., Shands J. W., Smith R. T. Selective effects of mitogens on subpopulations of mouse lymphoid cells. Cell Immunol. 1974 Mar 30;11(1-3):86–98. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Baughn R. E., Musher D. M. Mitogenic activity of bacterial lipopolysaccharides in vivo: morphological and functinal characterization of responding cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):71–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.71-78.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Shands J. W., Jr, Adler W. H., Smith R. T. Mitogenicity of bacterial endotoxins: characterization of the mitogenic principle. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):352–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. W. Immune responses in vitro. I. Cellular requirements for the immune response by nonprimed and primed spleen cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1969 Aug 1;130(2):345–364. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. W., Johnson B. M., Gershon H. E., Asofsky R. Immune responses in vitro. 3. Development of primary gamma-M, gamma-G, and gamma-A plaque-forming cell responses in mouse spleen cell cultures stimulated with heterologous erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1971 Aug 1;134(2):395–416. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIBI E., HASKINS W. T., MILNER K. C., ANACKER R. L., RITTER D. B., GOODE G., TRAPANI R. J., LANDY M. Physicochemical changes in endotoxin associated with loss of biological potency. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:803–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.803-814.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Gottert H., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Nature and linkages of the fatty acids present in the lipid-A component of Salmonella lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):166–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Glode L. M. Difference in B cell mitogen responsiveness between closely related strains of mice. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):777–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr, Graham J. A., Nath K. The morphologic structure of isolated bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr, Peavy D. L., Gormus B. J., McGraw J. In vitro and in vivo effects of endotoxin on mouse peritoneal cells. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):106–112. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.106-112.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr, Peavy D. L., Smith R. T. Differential morphology of mouse spleen cells stimulated in vitro by endotoxin, phytohemagglutinin, pokeweed mitogen and staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Am J Pathol. 1973 Jan;70(1):1–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore B. J., Chiller J. M., Morrison D. C., Weigle W. O. Immunologic properties of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS): correlation between the mitogenic, adjuvant, and immunogenic activities. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):770–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore B. J., Chiller J. M., Weigle W. O., Riblet R., Watson J. Immunologic properties of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). III. Genetic linkage between the in vitro mitogenic and in vivo adjuvant properties of LPS. J Exp Med. 1976 Jan 1;143(1):143–150. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell E. S., Atkins E. Interactions of gram-negative bacterial endotoxin with rabbit blood in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1967 May;212(5):1103–1112. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.5.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Phillips J. K., Mergenhagen S. E. Biological activity of complement in vivo. Role of C5 in the accumulation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in inflammatory exudates. J Exp Med. 1971 Nov 1;134(5):1131–1143. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.5.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M. Genetic control of host responses to endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1972 Jan;5(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.1.107-113.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M. Genetic control of leucocyte responses to endotoxin. Nature. 1968 Sep 21;219(5160):1253–1254. doi: 10.1038/2191253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M., Goodman G. W. Endotoxin protein: a B-cell mitogen and polyclonal activator of C3H/HeJ lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):821–827. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Perkins W. D., Karnovsky M. J. Ligand-induced movement of lymphocyte membrane macromolecules. I. Analysis by immunofluorescence and ultrastructural radioautography. J Exp Med. 1972 Oct 1;136(4):885–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.4.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMANN G., THOMAS L. Studies on lysosomes. I. The effects of endotoxin, endotoxin tolerance, and cortisone on the release of acid hydrolases from a granular fraction of rabbit liver. J Exp Med. 1962 Oct 1;116:433–450. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIENER E., SHILO M., BECK A. EFFECT OF BACTERIAL LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDES ON MOUSE PERITONEAL LEUKOCYTES. Lab Invest. 1965 May;14:475–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Riblet R. Genetic control of responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharides in mice. I. Evidence for a single gene that influences mitogenic and immunogenic respones to lipopolysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1147–1161. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Riblet R. Genetic control of responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharides in mice. II. A gene that influences a membrane component involved in the activation of bone marrow-derived lymphocytes by lipipolysaccharides. J Immunol. 1975 May;114(5):1462–1468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener E., Levanon D. The in vitro interaction between bacterial lipopolysaccharide and differentiating monocytes. Lab Invest. 1968 Dec;19(6):584–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler F., Forsyth R. P., Nies A. S., Neutze J. M., Melmon K. L. Endotoxin-induced regional circulatory changes in the unanesthetized monkey. Circ Res. 1969 Jun;24(6):777–786. doi: 10.1161/01.res.24.6.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]