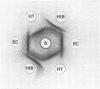
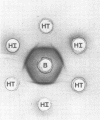
Abstract
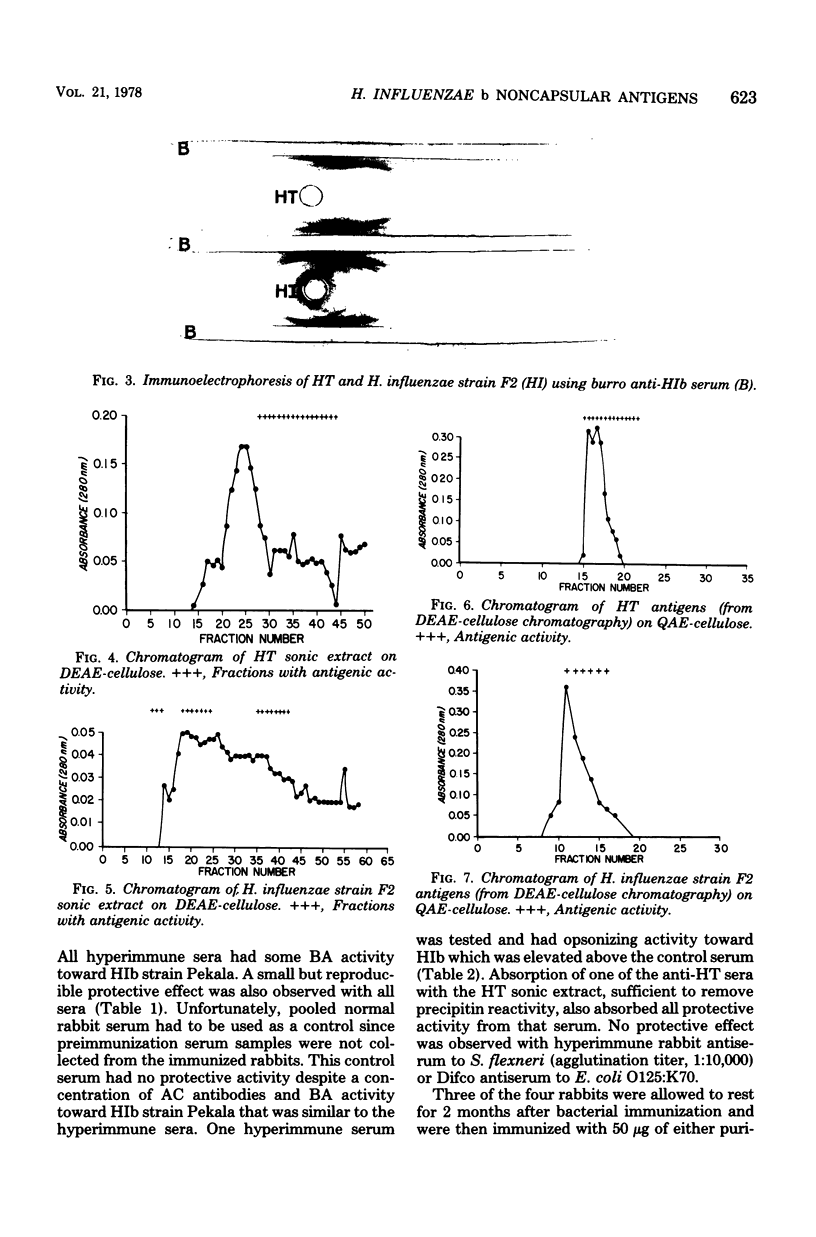
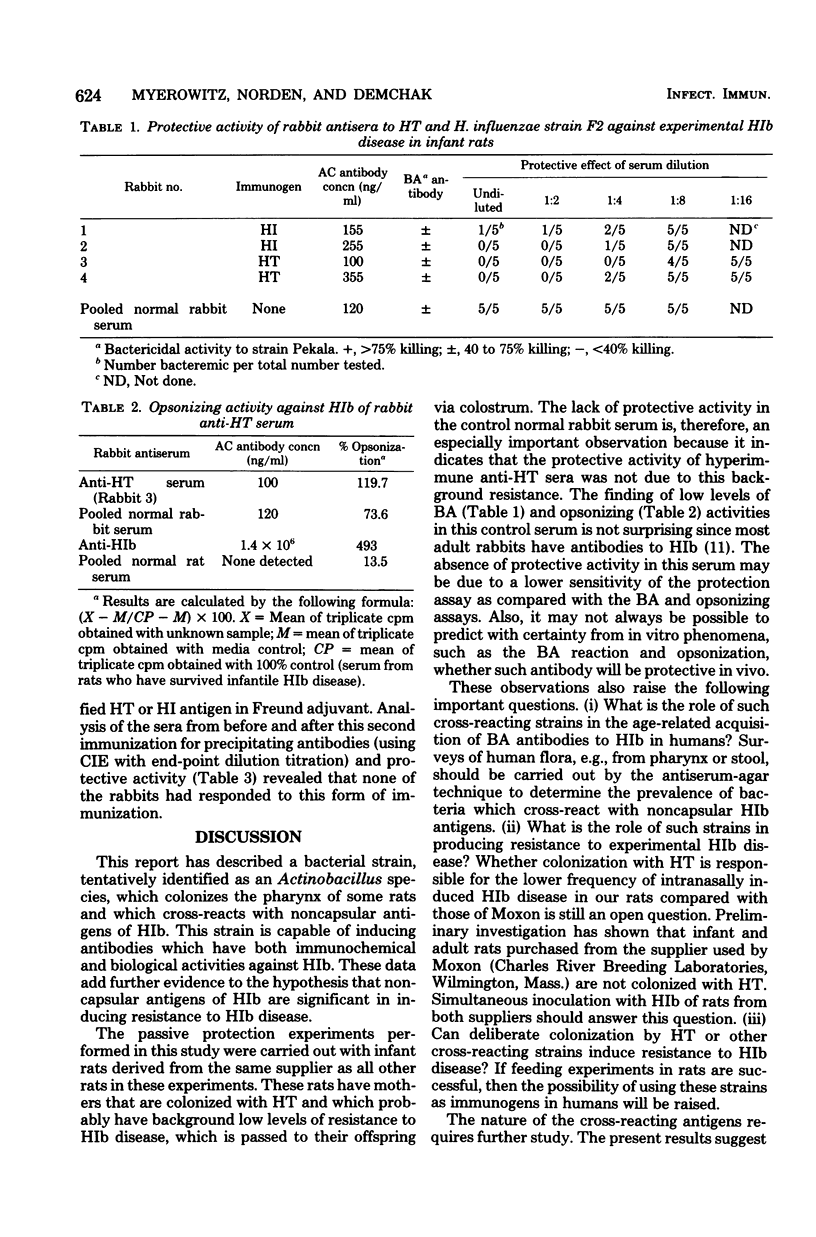
A bacterial strain, tentatively identified as an Actinobacillus species, was found to asymptomatically colonize the pharynx of some rats and to bear cell wall antigens which cross-react with noncapsular antigens of Haemophilus influenzae type b (HIb). The cross-reacting antigens appeared to be a heterogeneous mixture with varying molecular size and charge. The antigenic moieties are probably carbohydrate in nature. Antisera raised with this strain had both immunochemical and biological (bactericidal, opsonizing, and protective against experimental infection) activity against HIb. These findings lend further evidence to the idea that noncapsular antigens are important in the induction of resistance to HIb disease. The findings also raise the possibility of using bacteria which cross-react with noncapsular antigens for immunization against HIb disease in humans through nasopharyngeal or enteric colonization.
Full text
PDF

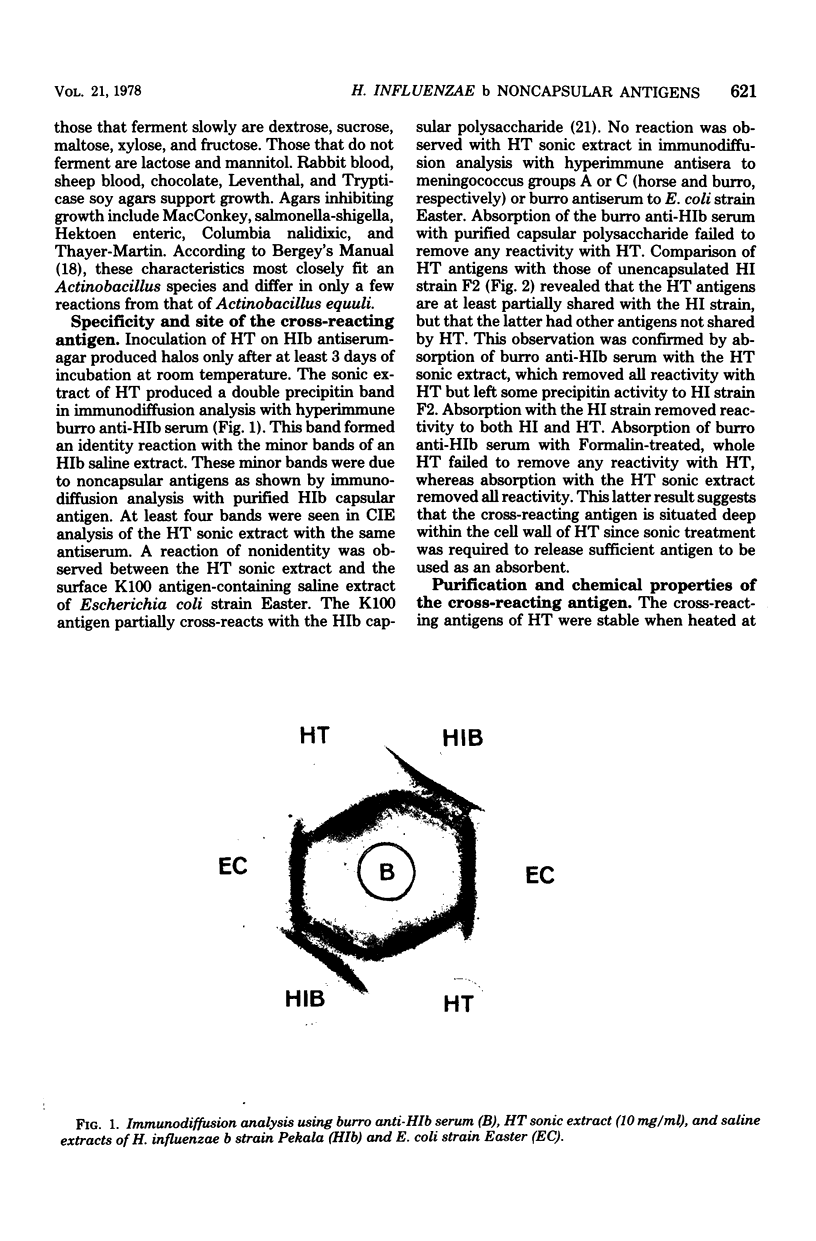
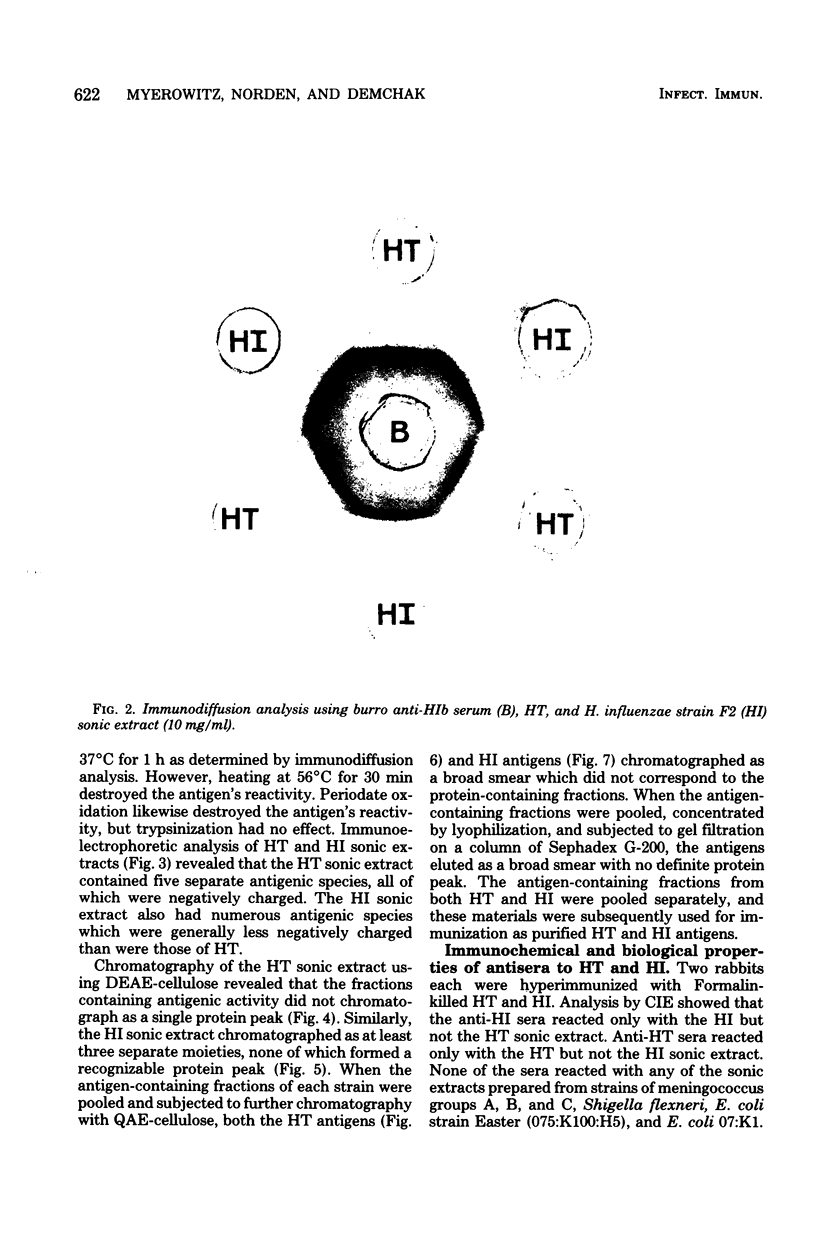


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Johnston R. B., Jr, Smith D. H. Human serum activities against Hemophilus influenzae, type b. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):31–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI106793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Rockwell R. Experimental Haemophilus influenzae type b meningitis: immunological investigation of the infant rat model. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):705–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.705-713.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handzel Z. T., Argaman M., Parke J. C., Jr, Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. Heteroimmunization to the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b induced by enteric cross-reacting bacteria. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1045–1052. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1045-1052.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels R. H., Myerowitz R. L., Klaw R. Potentiation of experimental meningitis due to Haemophilus influenzae by influenza A virus. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):641–645. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels R. H., Poziviak C. S. Countercurrent immunoelectrophoresis for the diagnosis of pneumococcal pneumonia in children. J Pediatr. 1976 Jan;88(1):72–74. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80730-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels R. H., Stonebraker F. E., Robbins J. B. Use of antiserum agar for detection of Haemophilus influenzae type b in the pharynx. Pediatr Res. 1975 May;9(5):513–516. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197505000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Smith A. L., Averill D. R., Smith D. H. Haemophilus influenzae meningitis in infant rats after intranasal inoculation. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):154–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mpairwe Y. Immunity to Haemophilus influenzae type B: the role of the capsular antibody. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Feb;4(1):85–88. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Handzel Z. T., Scheerson R., Robbins J. B. Induction of Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular antibody in neonatal rabbits by gastrointestinal colonization with cross-reacting Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):137–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.137-140.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Klaw R., Johnson B. L. Experimental endogenous endophthalmitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1043–1051. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1043-1051.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Norden C. W. Effect of neonatal gastrointestinal colonization with cross reacting Escherichia coli on anticapsular antibody production and bacteremia in experimental Haemophilus influenzae type b disease of rats. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):83–90. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.83-90.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Norden C. W. Immunology of the infant rat experimental model of Haemophilus influenzae type b meningitis. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):218–225. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.218-225.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W., Melish M., Overall J. C., Jr, Baum J. Immunologic responses to Hemophilus influenzae meningitis. J Pediatr. 1972 Feb;80(2):209–214. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80580-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W., Michaels R. Immunologic response in patients with epiglottitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1973 Dec;128(6):777–780. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.6.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Myerowitz L., Whisnant J. K., Argaman M., Schneerson R., Handzel Z. T., Gotschlich E. C. Enteric bacteria cross-reactive with Neisseria meningitidis groups A and C and Diplococcus pneumoniae types I and 3. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):651–656. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.651-656.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Bradshaw M., Whisnant J. K., Myerowitz R. L., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. An Escherichia coli antigen cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b: occurrence among known serotypes, and immunochemical and biologic properties of E. coli antisera toward H. influenzae type b. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1551–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. Induction of serum Haemophilus influenzae type B capsular antibodies in adult volunteers fed cross-reacting Escherichia coli 075:K100:H5. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 22;292(21):1093–1096. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505222922103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Rodrigues L. P., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. Immunity to disease caused by Hemophilus influenzae type b. II. Specificity and some biologic characteristics of "natural," infection-acquired, and immunization-induced antibodies to the capsular polysaccharide of Hemophilus influenzae type b. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1081–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Smith D. H., Averill D. R., Jr, Marino J., Moxon E. R. Production of Haemophilus influenzae b meningitis in infant rats by intraperitoneal inoculation. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):278–290. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.278-290.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Peter G., Ingram D. L., Harding A. L., Anderson P. Responses of children immunized with the capsular polysaccharide of Hemophilus influenzae, type b. Pediatrics. 1973 Nov;52(5):637–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J., Robbins J. B., Nieschlag E., Ross G. T. A method for producing specific antisera with small doses of immunogen. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Dec;33(6):988–991. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-6-988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]