Abstract
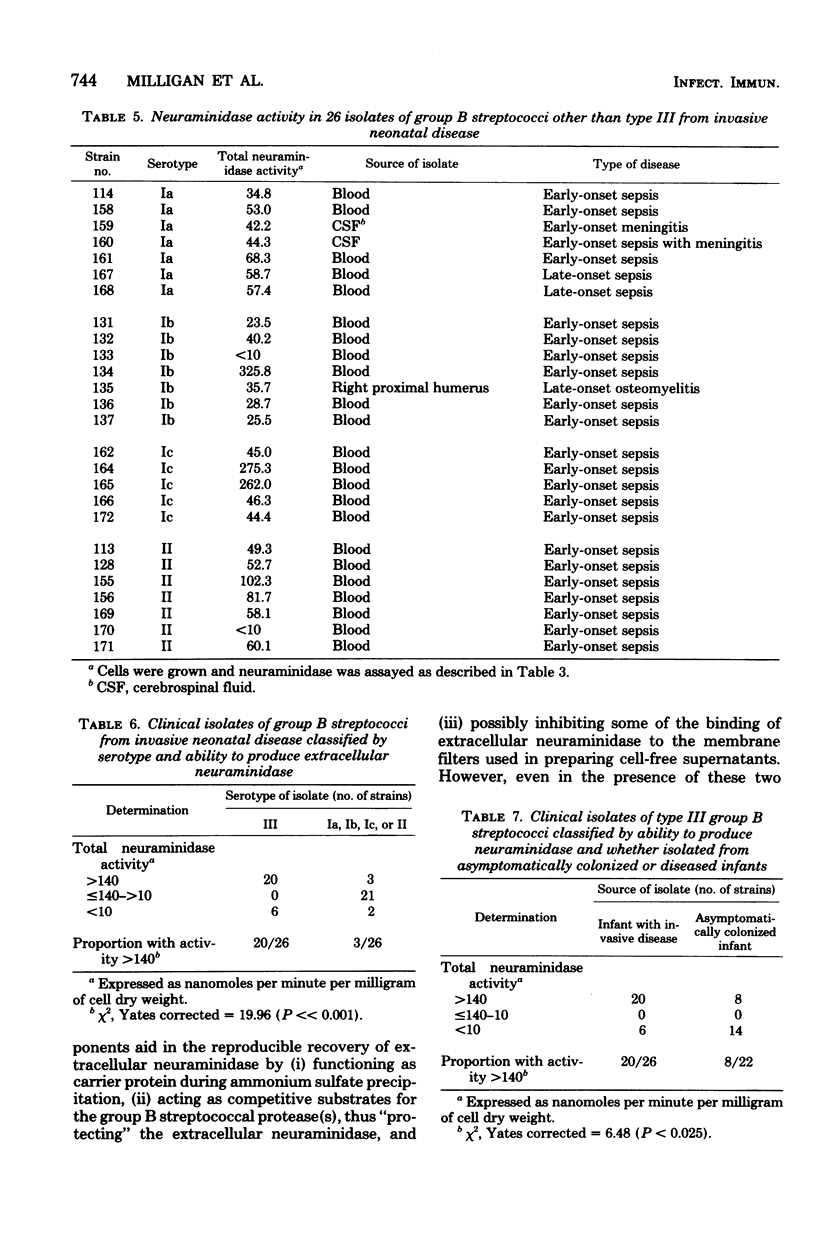
The level of total extracellular neuraminidase produced by 74 clinical isolates of group B streptococci isolated from diseased or asymptomatically colonized infants was assayed. Extracellular neuraminidase was obtained from concentrated filtrates of exponentially growing cultures of group B streptococci grown in a chemically defined medium (FMC) containing supplemental protein. The total activity of extracellular enzyme produced by these clinical isolates ranged from less than 10 to 360 nmol of sialic acid released per min per mg of cell dry weight. Strains were arbitrarily classified as either nonproducers (less than 10 nmol/min per mg of cell dry weight), low producers (greater than 10 to less than or equal 140 nmol/min per mg of cell dry weight), or high producers (greater than 140 to 360 nmol/min per mg of cell dry weight). Type III isolates from diseased infants were significantly more often classified as high producers than strains of group B streptococci of other serotypes from diseased infants (P less than 0.001). Furthermore, the serotype III strains isolated from neonatal infections were more often high producers than those of the same serotype from asymptomatically colonized infants (P less than 0.025). These results suggest that the ability to produce elevated levels of neuraminidase may be related to the frequent association of type III strains with disease among neonates.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aber R. C., Allen N., Howell J. T., Wilkenson H. W., Facklam R. R. Nosocomial transmission of group B streptococci. Pediatrics. 1976 Sep;58(3):346–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aminoff D., Bruegge W. F., Bell W. C., Sarpolis K., Williams R. Role of sialic acid in survival of erythrocytes in the circulation: interaction of neuraminidase-treated and untreated erythrocytes with spleen and liver at the cellular level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1521–1524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony B. F., Okada D. M. The emergence of group B streptococci in infections of the newborn infant. Annu Rev Med. 1977;28:355–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.28.020177.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Barrett F. F., Gordon R. C., Yow M. D. Suppurative meningitis due to streptococci of Lancefield group B: a study of 33 infants. J Pediatr. 1973 Apr;82(4):724–729. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80606-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Barrett F. F. Group B streptococcal infections in infants. The importance of the various serotypes. JAMA. 1974 Nov 25;230(8):1158–1160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Barrett F. F. Transmission of group B streptococci among parturient women and their neonates. J Pediatr. 1973 Dec;83(6):919–925. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80524-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Correlation of maternal antibody deficiency with susceptibility to neonatal group B streptococcal infection. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):753–756. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604012941404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Identification of sialic acid in polysaccharide antigens in group B Streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):284–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.284-288.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Microcapsule of type III strains of group B Streptococcus: production and morphology. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):189–194. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.189-194.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L., Tager IRAB, Paredes A., Alpert S., McCormack W. M., Goroff D. Quantitative determination of antibody to capsular polysaccharide in infection with type III strains of group B Streptococcus. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):810–818. doi: 10.1172/JCI108703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franciosi R. A., Knostman J. D., Zimmerman R. A. Group B streptococcal neonatal and infant infections. J Pediatr. 1973 Apr;82(4):707–718. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80604-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK A. Correlation between composition, structure, shape and function of a salivary mucoprotein. Nature. 1960 Jun 18;186:949–951. doi: 10.1038/186949a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan T. W., Doran T. I., Straus D. C., Mattingly S. J. Growth and amino acid requirements of various strains of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):28–33. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.28-33.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan T. W., Straus D. C., Mattingly S. J. Extracellular neuraminidase production by group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):189–195. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.189-195.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A. G., Gregoriadis G., Scheinberg I. H., Hickman J., Ashwell G. The role of sialic acid in determining the survival of glycoproteins in the circulation. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1461–1467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W. Analysis of group B streptococcal types associated with disease in human infants and adults. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):176–179. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.176-179.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Facklam R. R., Wortham E. C. Distribution by serological type of group B streptococci isolated from a variety of clinical material over a five-year period (with special reference to neonatal sepsis and meningitis). Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):228–235. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.228-235.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. J., Gesner B. M. The effect of neuraminidase on the fate of transfused lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1969 Mar 1;129(3):551–567. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.3.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


