Abstract
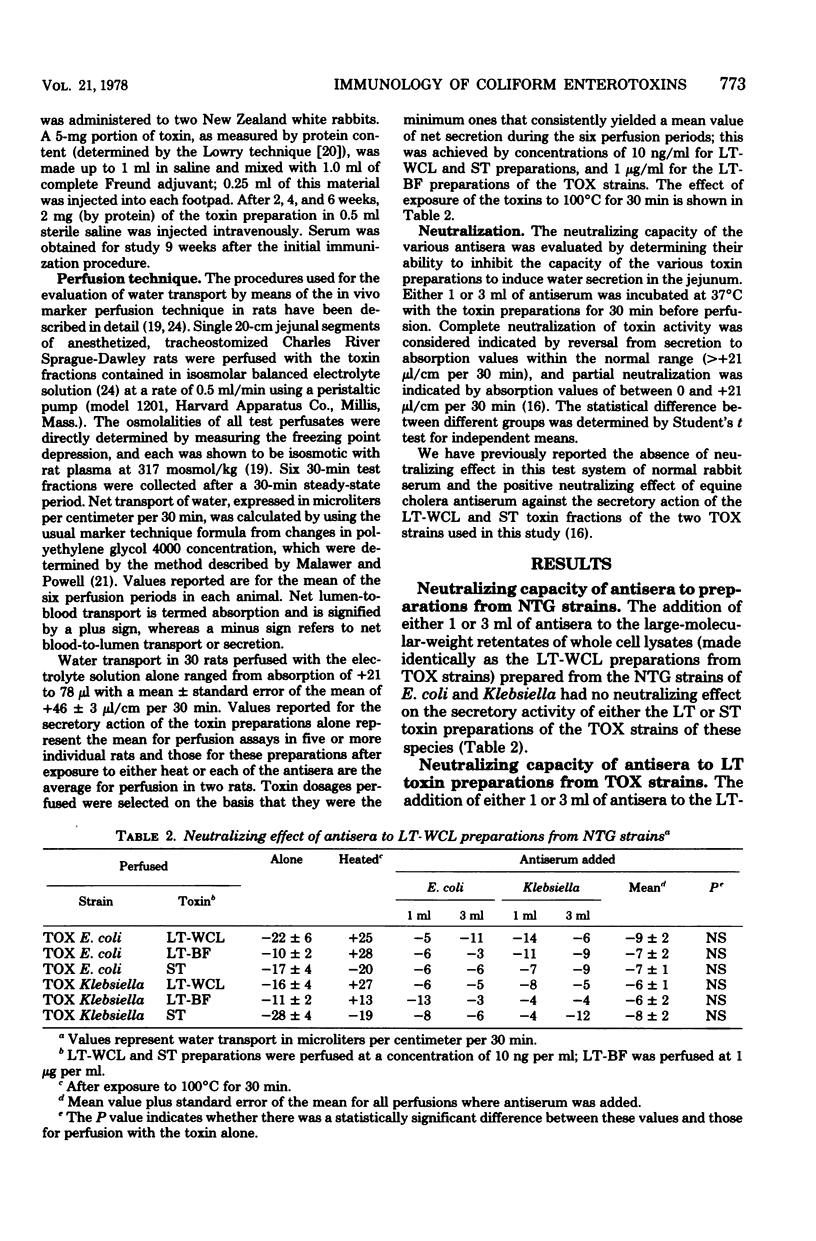
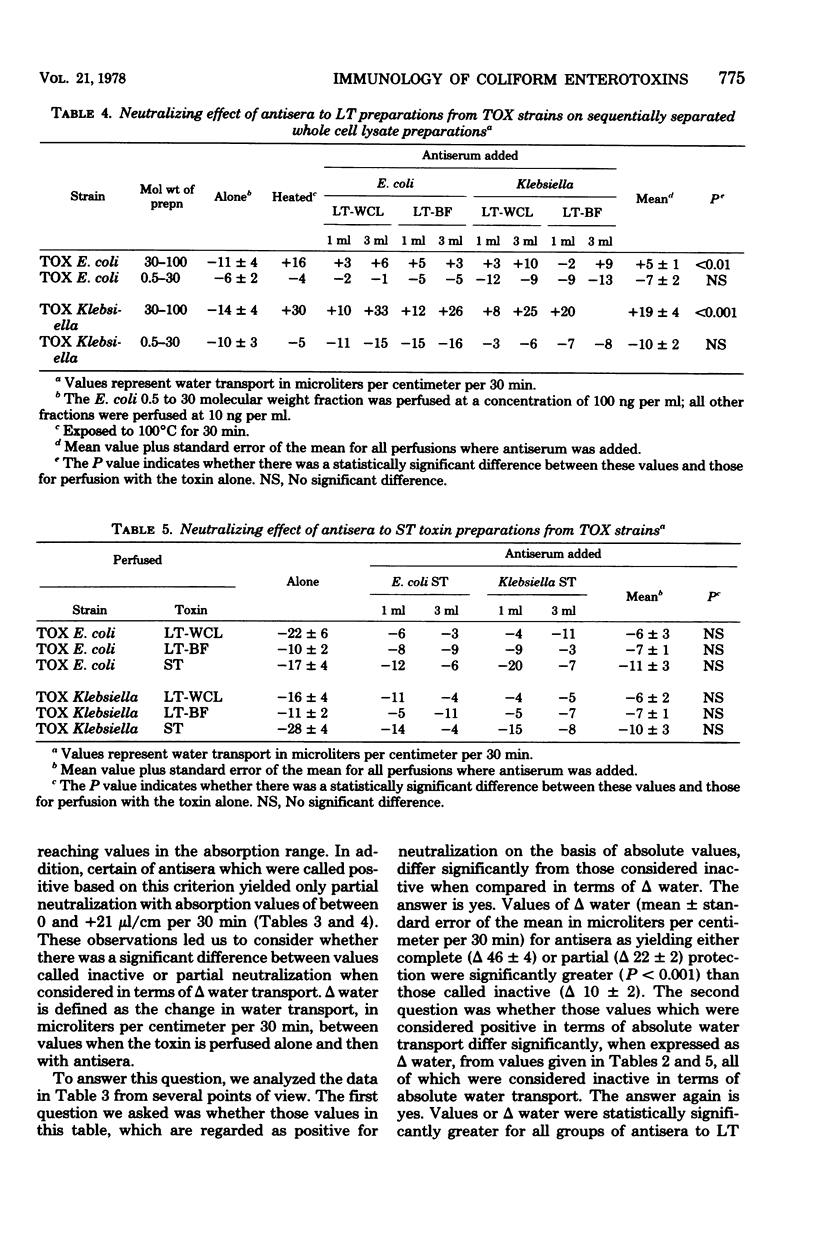
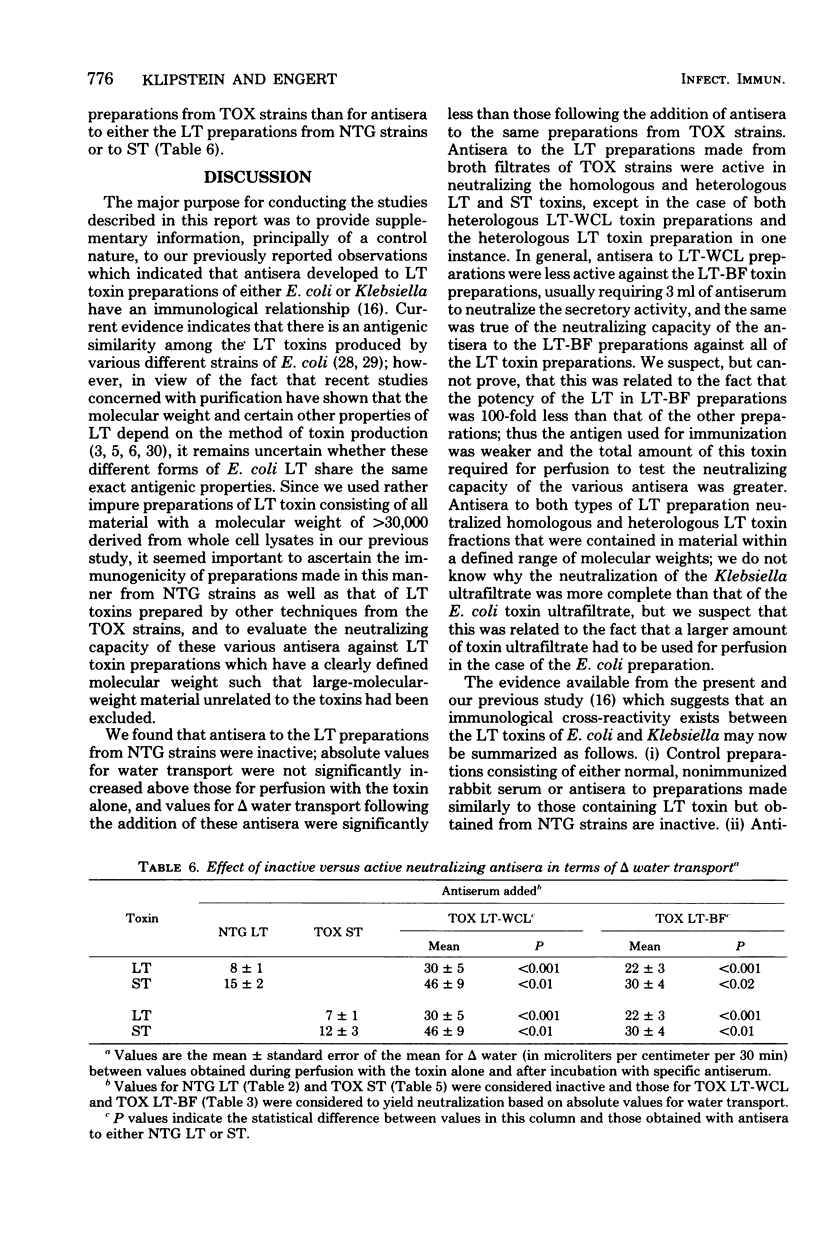
Antisera raised in rabbits to ultrafiltrate toxin preparations containing either the heat-labile (LT) toxin form obtained from whole cell lysates or broth filtrates or the heat-stable (ST) toxin form prepared from broth filtrates from nontoxigenic and toxigenic strains of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella were examined for their ability to neutralize the secretory effect on water transport of these toxins in the rat jejunum as determined by the in vivo marker perfusion technique. Antisera to the heat-labile toxin derived from whole cell lysate preparations from nontoxigenic strains had no neutralizing effect. Antisera to both types of LT preparation from both toxigenic strains neutralized, with several exceptions, all of the homologous and heterologous LT toxins as well as a heat-labile toxin preparation derived from sequential ultrafiltration of cell-free whole cell lysates which had a defined molecular weight of between 30,000 and 100,000. These antisera also neutralized homologous and heterologous ST preparations obtained from broth filtrates, but they had no neutraliziṅg effect on low-molecular-weight, ST toxin material obtained during the sequential ultrafiltration of cell lysates. Antisera to ST prepared from broth filtrates had no neutralizing capacity against either LT or ST toxin preparations. These observations (i) indicate that the immunological relationship of E. coli and Klebsiella LT and ST toxins extends to antisera raised against LT prepared by several different methods, (ii) raise the possibility that, based on the response to antisera to LT, there may be several immunologically heterogeneous forms of low-molecular-weight ST toxin, and (c) confirm the lack of immunogenicity of ST.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Smith D. M. Stimulation of steroidogenesis in tissue culture by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and its neutralization by specific antiserum. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.500-505.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner F., Jaksche H., Stöckl W. Escherichia coli enterotoxin: purification, partial characterization, and immunological observations. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133 (Suppl):142–156. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_1.s142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Pierce N. F. Differences in the response of rabbit small intestine to heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.873-880.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Polymyxin B-Induced Release of Low-Molecular-Weight, Heat-Labile Enterotoxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1010–1017. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1010-1017.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., LaRue M. K., Johnston D. W., Vasil M. L., Cho G. J., Jones J. R. Isolation and properties of heat-labile enterotoxin(s) from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133 (Suppl):120–137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_1.s120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Dickens M. D., Wenzel R. P., Kapikian A. Z. Toxigenic bacterial diarrhea: nursery outbreak involving multiple bacterial strains. J Pediatr. 1976 Dec;89(6):885–891. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80591-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Moore R. A., Kirschenfeld P. M., Sande M. A. Role of toxigenic and invasive bacteria in acute diarrhea of childhood. N Engl J Med. 1975 Sep 18;293(12):567–572. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197509182931201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. A heat-labile enterotoxin from strains of Eschericha coli enteropathogenic for pigs. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):419–426. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L. Relationships among heat-labile enterotoxins of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):277–283. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Söderlind O., Wadström T. Cross-reactivity between heat labile enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli in neutralization tests in rabbit ileum and skin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Dec;81(6):757–762. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. M., Wu B. J. Biochemical properties of Escherichia coli low-molecular-weight, heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):342–347. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.342-347.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Immunological interrelationships between cholera toxin and the heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of coliform bacteria. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):110–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.110-117.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Purification and properties of Klebsiella pneumoniae heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):373–381. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.373-381.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F., Short H. B. Relative enterotoxigenicity of coliform bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136(2):205–215. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.2.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Holdeman L. V., Corcino J. J., Moore W. E. Enterotoxigenic intestinal bacteria in tropical sprue. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Nov;79(5):632–641. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-5-632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLARTE J., FERGUSON W. W., HENDERSON N. D., TORREGROSA L. Klebsiella strains isolated from diarrheal infants. Human volunteer studies. Am J Dis Child. 1961 Jun;101:763–770. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1961.04020070077011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F. Protection against challenge with Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin by immunization of rats with cholera toxin/toxoid. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):338–341. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.338-341.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W., Malawer S. J. Relationship between water and solute transport from isosmotic solutions by rat intestine in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):49–55. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Sack D. A., Kapikian A. Z., McLaughlin J. C., Chakraborty J., Mizanur Rahman A. S., Merson M. H., Wells J. G. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Reovirus-like agent in rural Bangladesh. Lancet. 1976 Mar 27;1(7961):659–663. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92776-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Wachsmuth I. K., Buxton A. E., Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Mason E., Barrett F. F. Infantile diarrhea produced by heat-stable enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 14;295(16):849–853. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610142951601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Froehlich J. L. Antigenic similarity of heat-labile enterotoxins from diverse strains of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):570–572. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.570-572.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Immunization with Escherichia coli enterotoxin protects against homologous enterotoxin challenge. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):641–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.641-644.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkein I., Green R. F., Santos D. S., Maas W. K. Partial purification and characterization of a heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1710–1720. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1710-1720.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The relationship between two apparently different enterotoxins produced by enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli of porcine origin. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):387–401. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. The production of diarrhoea in baby rabbits by the oral administration of cell-free preparations of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae: the effect of antisera. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Aug;5(3):299–303. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-3-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. W., Sack R. B. Immunologic cross-reactions of enterotoxins from Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):164–170. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenser T. V., Metzger J. F. Comparison of the action of Escherichia coli enterotoxin on the thymocyte adenylate cyclase-cyclic adenosine monophosphate system to that of cholera toxin and prostaglandin E1. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):503–509. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.503-509.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


