Abstract
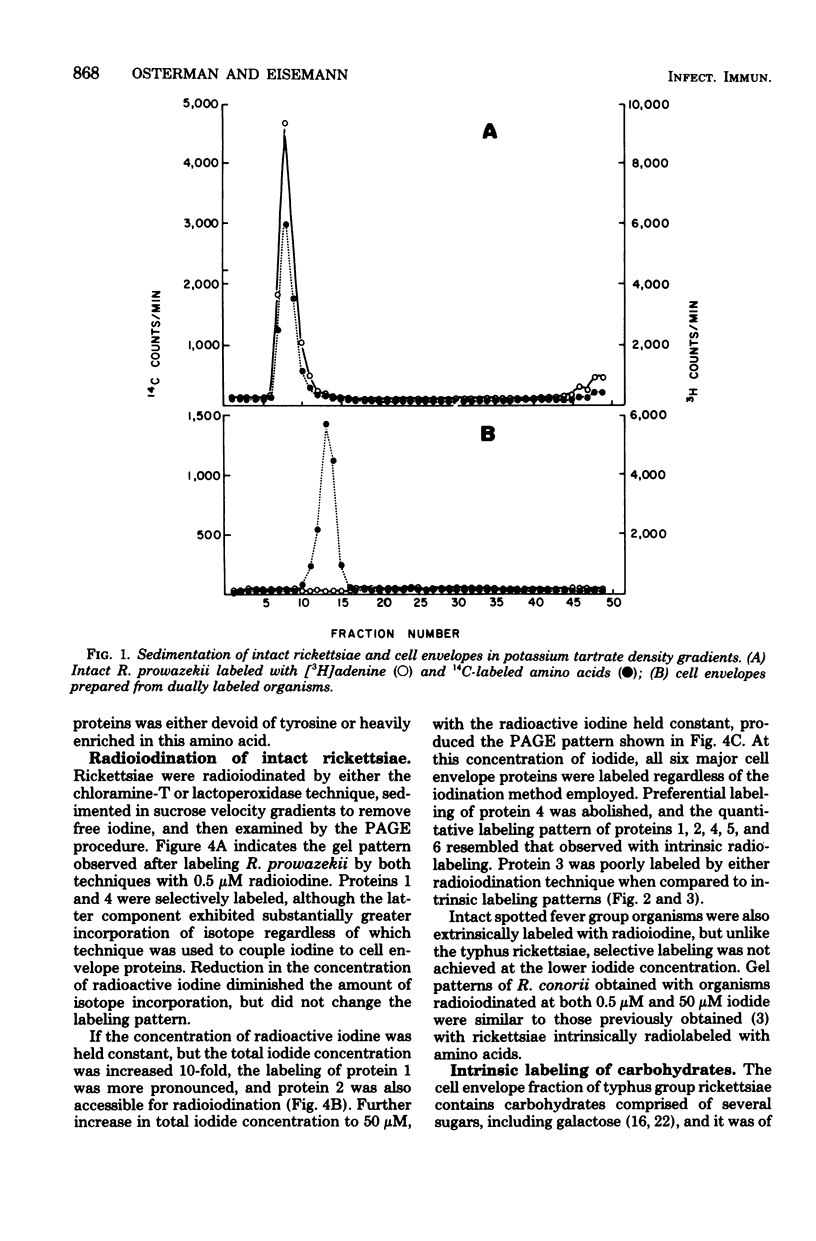
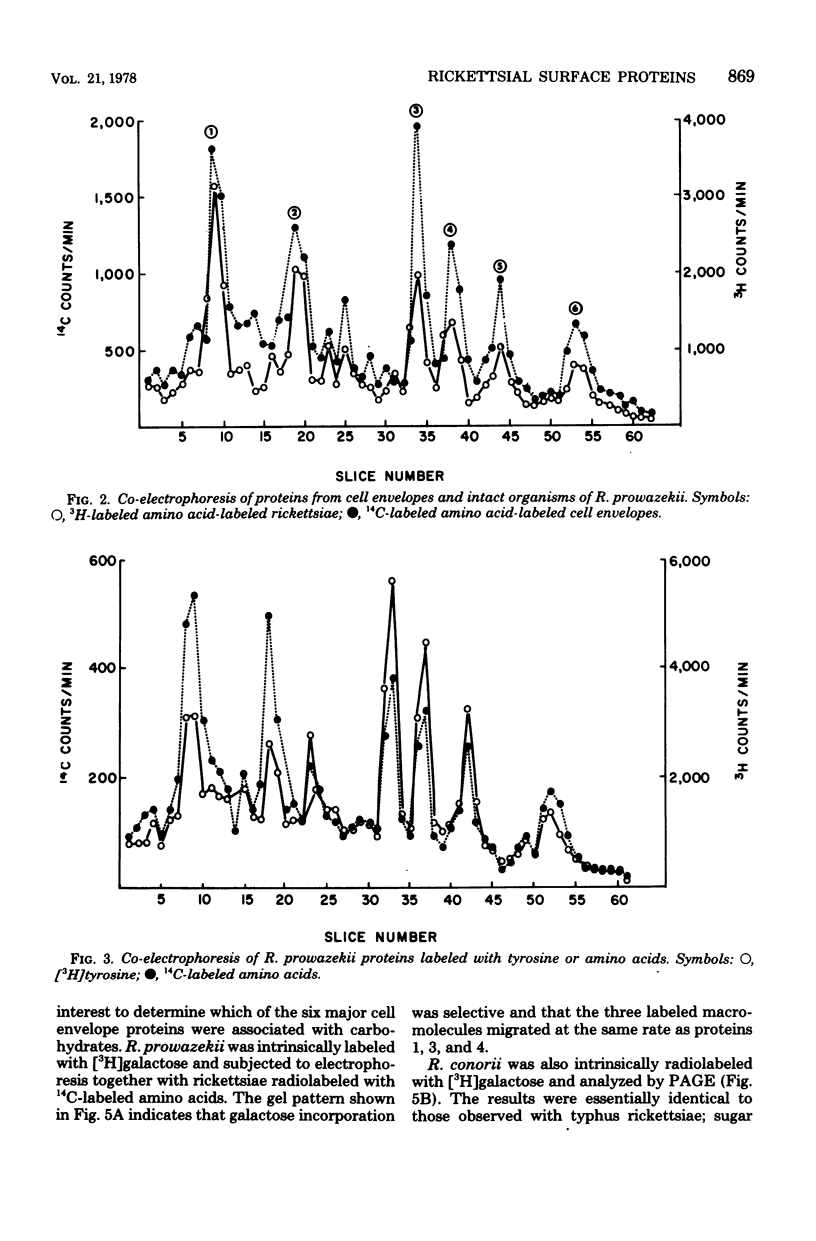
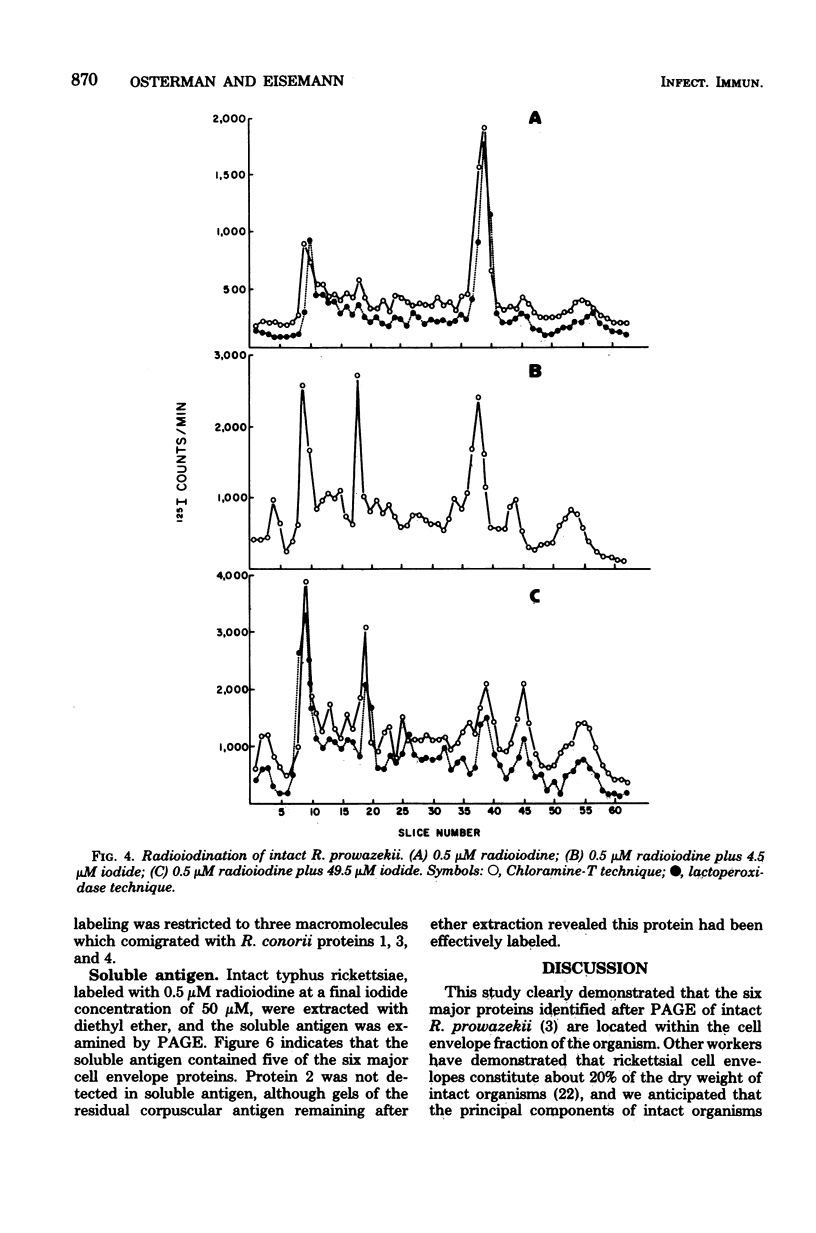
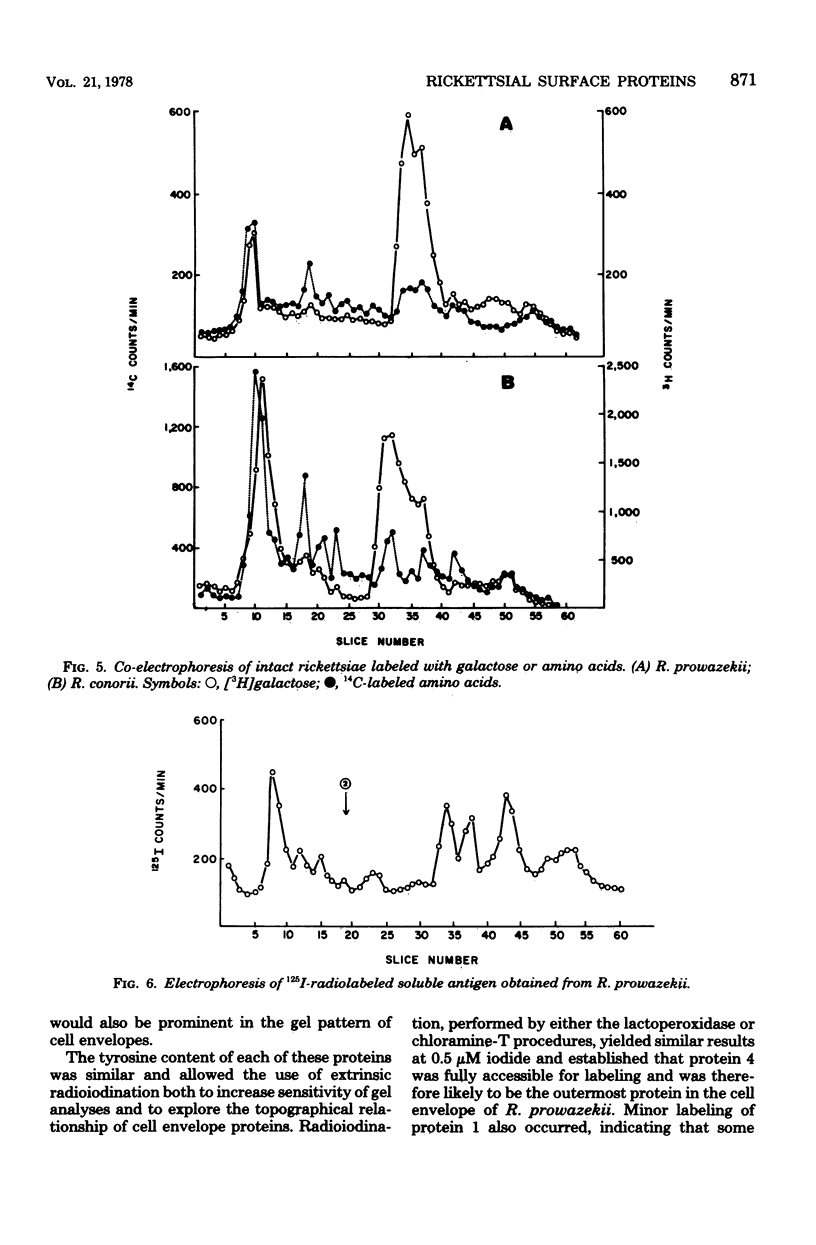
Six proteins, previously established as major constituents of intact organisms, were identified in cell envelopes obtained from intrinsically radiolabeled Rickettsia prowazekii. Extrinsic radioiodination of intact organisms conducted at 0.5 micronM iodide indicated that protein 4 was the most peripheral, although protein 1 also had reactive groups exposed on the surface of the organisms. A 10-fold increase in iodide concentration resulted in labeling of protein 2, and at 50 micronM iodide, all six major proteins were radiolabeled. Similar selective labeling was not achieved with R. conorii. Analysis of both typhus and spotted fever group organisms radiolabeled with galactose suggested that carbohydrate was associated with proteins 1, 3, and 4. Typhus soluble antigen included all major proteins except protein 2, which remained attached to particulate rickettsiae after ether extraction. Protein 4 appeared to be prominent in the surface topography of R. prowazekii, was a component of soluble antigen and may have an important role in rickettsiae-host interactions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dasch G. A., Samms J. R., Weiss E. Biochemical characteristics of typhus group rickettsiae with special attention to the Rickettsia prowazekii strains isolated from flying squirrels. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):676–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.676-685.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasch G. A., Weiss E. Characterization of the Madrid E strain of Rickettsia prowazekii purified by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):280–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.280-286.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisemann C. S., Osterman J. V. Proteins of typhus and spotted fever group rickettsiae. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):155–162. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.155-162.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg G. H., Jr, Osterman J. V. Experimental scrub typhus immunogens: gamma-irradiated and formalinized rickettsiae. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):124–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.124-131.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRYGIN C. [Electrophoretic, immunoelectrophoretic and chromatographic analysis of the soluble antigen of Rickettsia prowazekli]. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 1963;15:29–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelaro R. C., Rueckert R. R. On the use of chloramine-T to iodinate specifically the surface proteins of intact enveloped viruses. J Gen Virol. 1975 Oct;29(1):127–131. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore N. F., Kelley J. M., Wagner R. R. Envelope proteins of vesicular stomatitis virions: accessibility to iodination. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):292–296. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90264-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen C. E., Jr, Walters V. D. Comparative electrophoresis of spotted fever group rickettsial proteins. Life Sci. 1978 Feb;22(7):583–587. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90337-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Morrison M. The arrangement of proteins in the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 27;40(2):284–289. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAECHTER M., TOUSIMIS A. J., COHN Z. A., ROSEN H., CAMPBELL J., HAHN F. E. Morphological, chemical, and serological studies of the cell walls of Rickettsia mooseri. J Bacteriol. 1957 Dec;74(6):822–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.6.822-829.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Wickus G. G., Burge B. W. Enzymatic iodination of Sindbis virus proteins. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):730–735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.730-735.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P., Haslam E. A. The polypeptides of influenza virus. V. Localization of polypeptides in the virion by iodination techniques. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):764–773. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzianabos T., Palmer E. L., Obijeski J. F., Martin M. L. Origin and structure of the group-specific, complement-fixing antigen of Rickettsia rickettsii. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Sep;28(3):481–488. doi: 10.1128/am.28.3.481-488.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. H., Jr, Wisseman C. L., Jr Studies of Rickettsia mooseri cell walls. II. Immunologic properties. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1224–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. H., Jr, Wisseman C. L., Jr The cell wall of Rickettsia mooseri. I. Morphology and chemical composition. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1113–1118. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1113-1118.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


