Abstract
Congenitally athymic nude (nu/nu) mice, when injected intraperitoneally with Histoplasma capsulatum, developed a rapidly fatal disseminated infection characterized by heavy parasitization of reticuloendothelial tissues. In contrast, their heterozygous (nu/X) littermates, which possessed a functioning thymus, developed only a low-grade infection which was apparently self-limited and rarely fatal. Transplantation of thymic tissue into nu/nu mice diminished greatly the severity of infection and reduced mortality by about 50%. These studies emphasize the importance of cell-mediated immunity in host defense against histoplasmosis and suggest that the nude mouse may be a valuable model for the study of this chronic intracellular infection.
Full text
PDF
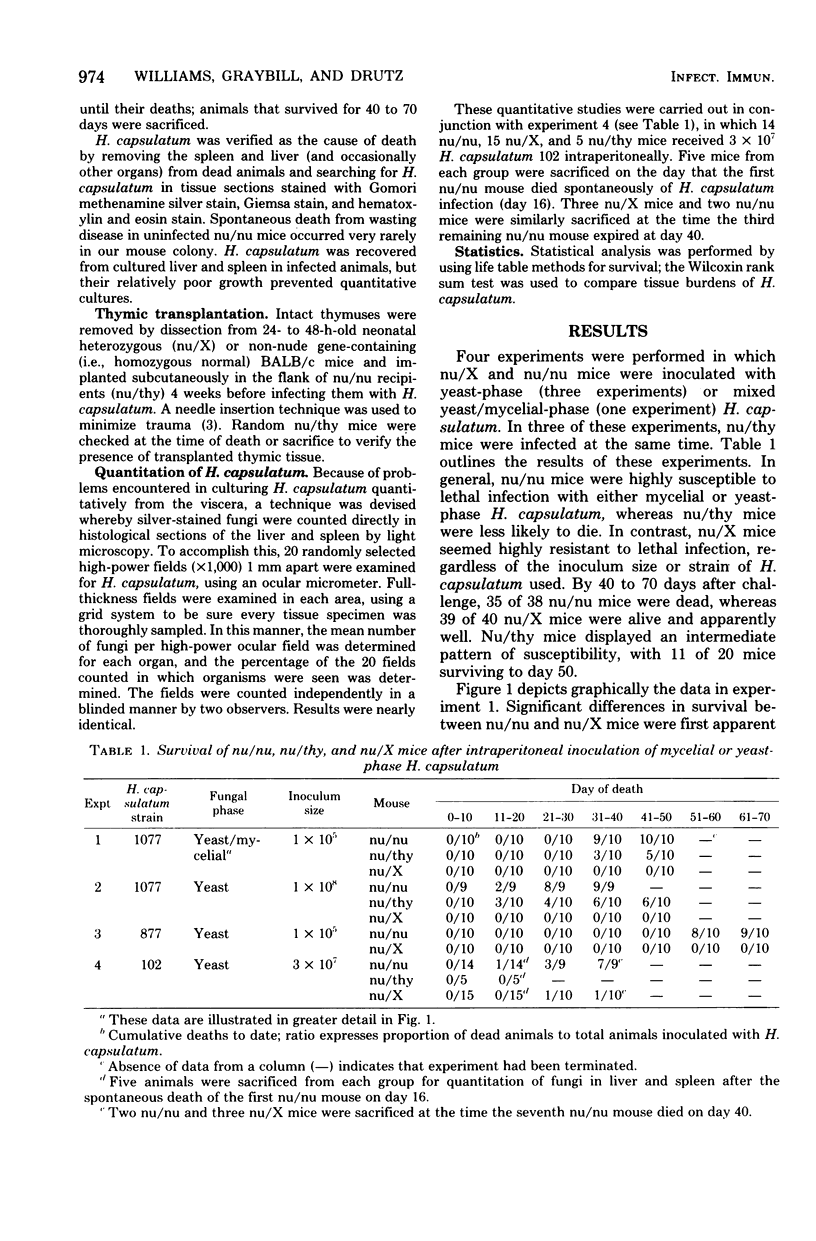
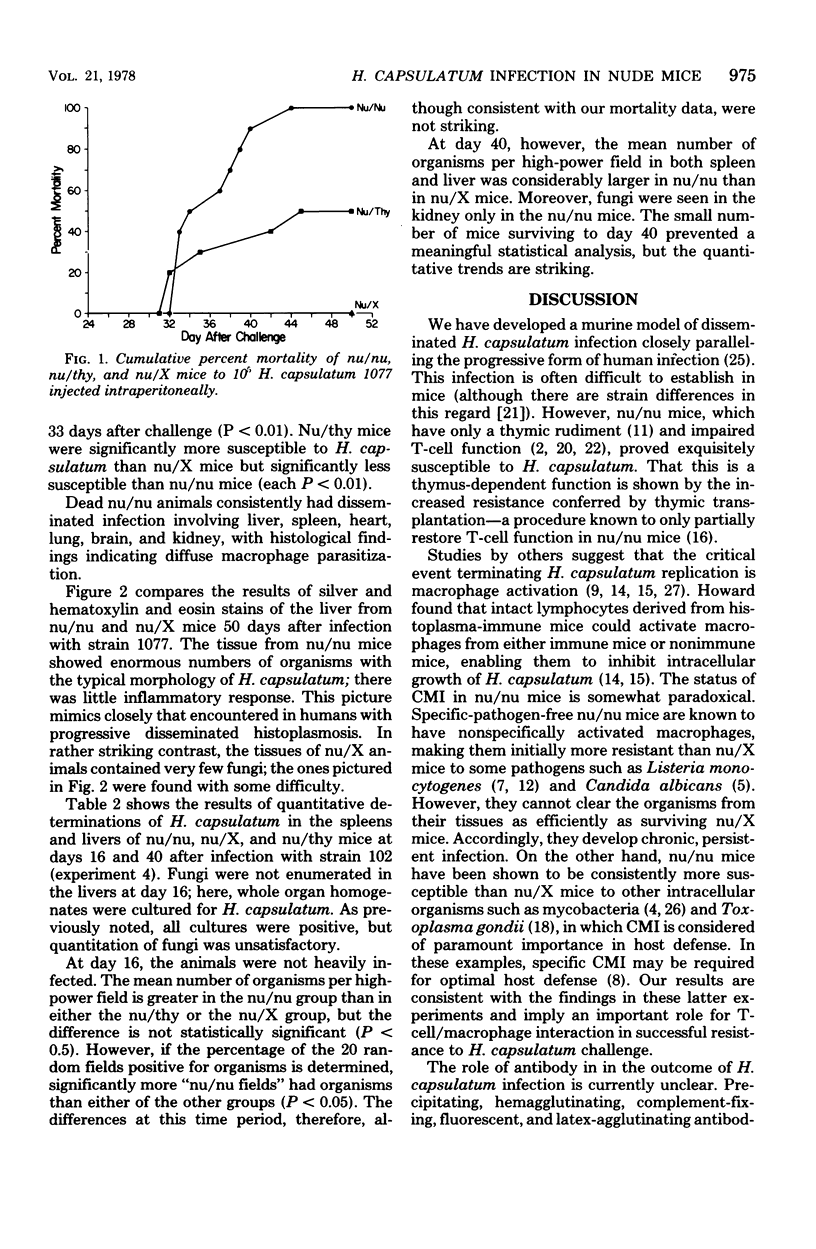


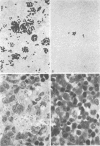
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauman D. S., Smith C. D. Comparison of immunodiffusion and complement fixation tests in the diagnosis of histoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;2(2):77–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns W., Billups L. C., Notkins A. L. Thymus dependence of viral antigens. Nature. 1975 Aug 21;256(5519):654–656. doi: 10.1038/256654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. A. Rapid, safe and simple method for grafting whole thymus in the mouse. J Immunol Methods. 1976;12(3-4):377–385. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colston M. J., Hilson G. R. Growth of Mycobacterium leprae and M. marinum in congenitally athymic (nude) mice. Nature. 1976 Jul 29;262(5567):399–401. doi: 10.1038/262399a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E. Acute systemic candidiasis in normal and congenitally thymic-deficient (nude) mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 Feb;19(2):121–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards Phyllis Q., Palmer Carroll E. Nationwide histoplasmin sensitivity and histoplasmal infection. Public Health Rep. 1963 Mar;78(3):241–260. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerling P., Finger H., Bockemühl J. Listeria monocytogenes infection in nude mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):437–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.437-439.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Caldwell S. A. Specific immunity and nonspecific resistance to infection: listeria, protozoa, and viruses in mice and hamsters,. J Infect Dis. 1975 Mar;131(3):201–209. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.3.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. A., Jr, Des Prez R. M. Pathogenesis and clinical spectrum of histoplasmosis. South Med J. 1973 Jan;66(1):13–25. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197301000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Alford R. H. Variability of sequential studies of lymphocyte blastogenesis in normal adults. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):28–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD D. H. INTRACELLULAR GROWTH OF HISTOPLASMA CAPSULATUM. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:518–523. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.518-523.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymer B., Hof H., Emmerling P., Finger H. Morphology and time course of experimental listeriosis in nude mice. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):832–835. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.832-835.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P., Holland N. H. Histoplasmosis in early infancy. Hematologic, histochemical, and immunologic observations. Am J Dis Child. 1966 Nov;112(5):412–421. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1966.02090140084006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard D. H., Otto V. Experiments on lymphocyte-mediated cellular immunity in murine histoplasmosis. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):226–231. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.226-231.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindred B., Loor F. Activity of host-derived T cells which differentiate in nude mice grafted with co-isogenic or allogeneic thymuses. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1215–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. E., Frenkel J. K. Toxoplasmosis in nude mice. J Parasitol. 1977 Apr;63(2):219–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton R. M., Riggs A. R., Compton S. B., Chick E. W. Histoplasmosis in purebred mice: influence of genetic susceptibility and immune depression on treatment. Mycopathologia. 1976 Dec 10;60(1):39–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00442546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelleitier M., Montplaisir S. The nude mouse: a model of deficient T-cell function. Methods Achiev Exp Pathol. 1975;7:149–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picardi J. L., Kauffman C. A., Schwarz J., Phair J. P. Detection of precipitating antibodies to Histoplasma capsulatum by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jul;114(1):171–176. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P., Gorelick D. F., Brasher C. A., Larsh H. Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis as seen in adults. Am J Med. 1970 May;48(5):629–636. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(70)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Utz J. P. Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis. A prospective study of 26 patients. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Apr;76(4):557–565. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-4-557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Yamazaki S., Someya S. Experimental mycobacterial infection in congenitally athymic "nude" mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 Feb;19(2):77–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelstein J. A., Swift A. J. Host defense against the pneumococcus in T-lymphocyte-deficient, nude mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1222–1223. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1222-1223.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]