Abstract
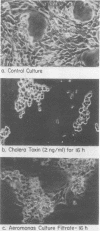
Most strains of Aeromonas hydrophila tested demonstrated cytotoxic activity on several tissue-cultured cell lines. The cytotoxin is heat-labile, non-dialyzable, and immunologically distinct from that of Shigella dysenteriae and Clostridium perfringens. None of the aeromonas isolates was found to be enterotoxigenic by either tissue culture or rabbit ileal loop assays.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annapurna E., Sanyal S. C. Enterotoxicity of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Aug;10(3):317–323. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger Y., Lallier R., Cousineau G. Isolation of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas from fish. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1161–1164. doi: 10.1139/m77-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T. Alteration of tyrosine aminotransferase activity in hepatoma cells in tissue culture by amphotericin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):240–246. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Skartvedt S. M. In vitro production and inactivation of Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Gastroenterology. 1974 Nov;67(5):983–990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Smith D. M. Stimulation of steroidogenesis in tissue culture by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and its neutralization by specific antiserum. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.500-505.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T. The growth of functional rat glial cells in a serumless medium. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Nov;82(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Moore R. A., Kirschenfeld P. M., Sande M. A. Role of toxigenic and invasive bacteria in acute diarrhea of childhood. N Engl J Med. 1975 Sep 18;293(12):567–572. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197509182931201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketover B. P., Young L. S., Armstrong D. Septicemia due to Aeromonas hydrophila: clinical and immunologic aspects. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):284–290. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Donta S. T. Classification of enterotoxins on the basis of activity in cell culture. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jan;131(1):58–63. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Immunological interrelationships between cholera toxin and the heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of coliform bacteria. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):110–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.110-117.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Schenk E. A. Enterotoxigenic intestinal bacteria in tropical sprue. II. Effect of the bacteria and their enterotoxins on intestinal structure. Gastroenterology. 1975 Apr;68(4 Pt 1):642–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Popoff M., Wadstrom T. Aeromonas hydrophila in acute diarrheal disease: detection of enterotoxin and biotyping of strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):96–100. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.96-100.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T. A., Mitchell C. A., Hughes W. T. Aeromonas hydrophila septicemia. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Jun;123(6):579–582. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110120103012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qadri S. M., Gordon L. P., Wende R. D., Williams R. P. Meningitis due to Aeromonas hydrophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Feb;3(2):102–104. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.2.102-104.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay A. M., Rosenbaum B. J., Yarbrough C. L., Hotz J. A. Aeromonas hydrophila sepsis in a patient undergoing hemodialysis therapy. JAMA. 1978 Jan 9;239(2):128–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S. C., Singh S. J., Sen P. C. Enteropathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):195–198. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford P. G., Ratzan S. A., Shearer W. T. Ecthyma gangrenosum produced by Aeromonas hydrophilia. J Pediatr. 1973 Jul;83(1):100–101. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80326-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper M. L., McCarthy L. R., Mayo J. B., Armstrong D. Recurrent Aeromonas sepsis in a patient with leukemia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975 Oct;64(4):525–530. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/64.4.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Aust-Kettis A., Habte D., Holmgren J., Meeuwisse G., Möllby R., Söderlind O. Enterotoxin-producing bacteria and parasites in stools of Ethiopian children with diarrhoeal disease. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Nov;51(11):865–870. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.11.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Ljungh A., Wretlind B. Enterotoxin, haemolysin and cytotoxic protein in Aeromonas hydrophila from human infections. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Apr;84(2):112–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]